组合模式
一、场景问题
商品类别树
+服装
+男装
-衬衣
-夹克
+女装
-裙子
-套装
- 特点
有一个根节点
树枝节点
叶子节点
不带模式的解决方案:组合对象
package operation;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
class Leaf{
private String name="";
public Leaf(String name) {
this.name=name;
}
public void printStuct(int d) {
for(int i=0;i<d;i++)
System.out.print(" ");
System.out.println('-'+name);
}
}
class Composite{
private Collection<Composite>childComposite=new ArrayList<Composite>();
private Collection<Leaf>childLeaf=new ArrayList<Leaf>();
private String name="";
public Composite(String name) {
this.name=name;
}
public void addComposite(Composite c) {
this.childComposite.add(c);
}
public void addLeaf(Leaf leaf) {
this.childLeaf.add(leaf);
}
public void printStruct(int d) {
for(int i=0;i<d;i++)
System.out.print(" ");
System.out.println('+'+name);
for(Composite c:childComposite) {
c.printStruct(d+2);
}
for(Leaf leaf:childLeaf) {
leaf.printStuct(d+2);
}
}
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Composite root=new Composite("服装");
Composite c1=new Composite("男装");
Composite c2=new Composite("女装");
Leaf leaf1=new Leaf("衬衣");
Leaf leaf2=new Leaf("夹克");
Leaf leaf3=new Leaf("裙子");
Leaf leaf4=new Leaf("套装");
root.addComposite(c1);
root.addComposite(c2);
c1.addLeaf(leaf1);
c1.addLeaf(leaf2);
c2.addLeaf(leaf3);
c2.addLeaf(leaf4);
root.printStruct(0);
}
}
运行结果

要处理的对象可以表示成一个树形结构,而要对树上的分支节点和叶子进行操作时,它能够提供一致的方式,而不用区分它是分支节点还是叶子。–抽象出共同基类Component,继承它产生叶子节点和容器节点。
package operation;
import java.util.ArrayList;
abstract class Component{
protected String name;
public Component(String name) {
this.name=name;
}
public abstract void Add(Component component);
public abstract void Remove(Component component);
public abstract void printStruct(int component);
}
class Leaf extends Component{
public Leaf(String name) {
super(name);
}
public void Add(Component component) {
System.out.println("不能添加分支");
}
public void Remove(Component component) {
System.out.println("不能删除分支");
}
public void printStruct(int d) {
for(int i=0;i<d;i++)
System.out.print(" ");
System.out.println('-'+name);
}
}
class Composite extends Component{
private ArrayList<Component>components=new ArrayList<Component>();
public Composite(String name) {
super(name);
}
public void Add(Component component) {
components.add(component);
}
public void Remove(Component component) {
components.remove(component);
}
public void printStruct(int d) {
for(int i=0;i<d;i++)
System.out.print(" ");
System.out.println('+'+name);
for(Component component:components) {
component.printStruct(d+2);
}
}
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Composite root=new Composite("服装");
Composite c1=new Composite("男装");
Composite c2=new Composite("女装");
Leaf leaf1=new Leaf("衬衣");
Leaf leaf2=new Leaf("夹克");
Leaf leaf3=new Leaf("裙子");
Leaf leaf4=new Leaf("套装");
root.Add(c1);
root.Add(c2);
c1.Add(leaf1);
c1.Add(leaf2);
c2.Add(leaf3);
c2.Add(leaf4);
root.printStruct(0);
}
}
二、组合模式
组合模式:将对象组合成树形结构以表示‘部分-整体’的层次结构。组合模式使得用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性。
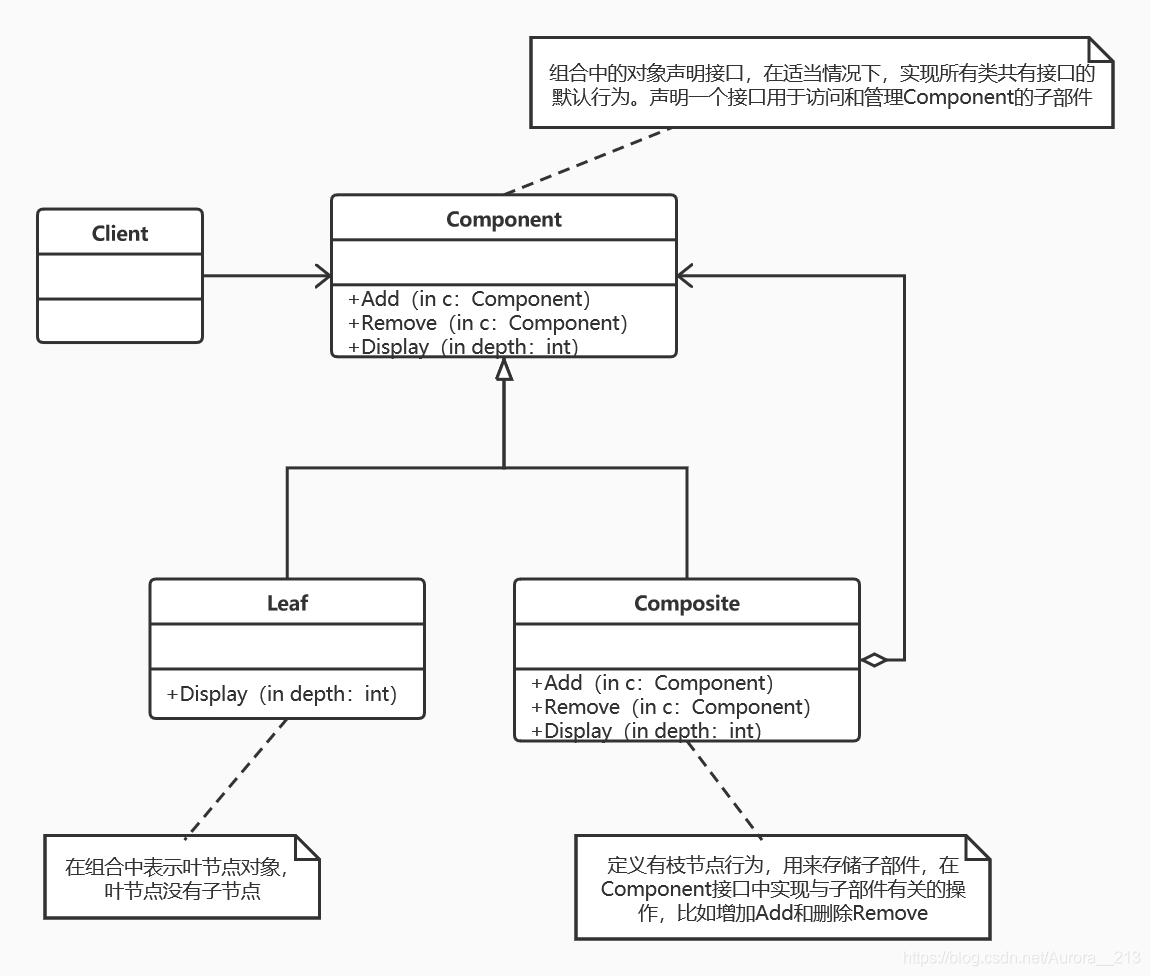
package operation;
import java.util.ArrayList;
abstract class Component{
protected String name;
public Component(String name) {
this.name=name;
}
public void Display() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public abstract void Add(Component c);
public abstract void Remove(Component c);
public abstract void Display(int depth);
}
class Leaf extends Component{
public Leaf(String name) {
super(name);
}
public void Add(Component component) {
System.out.println("Cannot add to a leaf");
}
public void Remove(Component component) {
System.out.println("Cannot remove from a leaf");
}
public void Display(int depth) {
for(int i=0;i<depth;i++)
System.out.print(" ");
System.out.println('-'+name);
}
}
class Composite extends Component{
private ArrayList<Component>components=new ArrayList<Component>();
public Composite(String name) {
super(name);
}
public void Add(Component component) {
components.add(component);
}
public void Remove(Component component) {
components.remove(component);
}
@Override
public void Display(int depth) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
for(int i=0;i<depth;i++)
System.out.print(" ");
System.out.println('+'+name);
for(Component component:components) {
component.Display(depth+2);
}
}
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
//生成树根root,根上长出两叶LeafA和LeafB
Composite root=new Composite("root");
root.Add(new Leaf("Leaf A"));
root.Add(new Leaf("Leaf B"));
//根上长出分枝Composite X,分枝上也有两叶LeafXA和LeafXB
Composite comp=new Composite("Composite X");
comp.Add(new Leaf("Leaf XA"));
comp.Add(new Leaf("Leaf XB"));
root.Add(comp);
//在CompositeX上再长出分枝CompositeXY,分枝上也有两叶LeafXYA和LeafXYB
Composite comp2=new Composite("Composite XY");
comp2.Add(new Leaf("Leaf XYA"));
comp2.Add(new Leaf("Leaf XYB"));
comp.Add(comp2);
root.Add(new Leaf("Leaf C"));
Leaf leaf=new Leaf("Leaf D");
root.Add(leaf);
root.Remove(leaf);
root.Display(1);
}
}
三、透明模式与安全模式
- 为什么Leaf类中也有Add和Remove。
这种方式叫做透明方式,也就是说在Component中声明所有用来管理子对象的方法,其中包括Add,Remove等。这样实现Component接口的所有子类都具备了Add和Remove。这样做的好处是叶节点和枝节点对于外界没有区别,它们具备完全一致的行为接口。但问题也很明显,因为Leaf类本身不具备Add(),Remove()方法的功,所以实现它是没有意义的。
- Leaf类当中不用Add和Remove方法
安全方法,那么子类的Leaf也不需要去实现它,而是在Composite声明所有用来管理子类对象的方法。不过由于不够透明,所以树叶和树枝类将不具有相同接口,客户端的调用需要做相应的判断,带来了不便。
四、何时使用组合模式
需求中是体现部分与整体层次结构时,以及你希望用户可以忽略组合对象与单个对象的不同,统一地使用组合结构中的所有对象时,就应该考虑组合模式了。
五、优缺点
优点: 1、高层模块调用简单。 2、节点自由增加。
缺点:在使用组合模式时,其叶子和树枝的声明都是实现类,而不是接口,违反了依赖倒置原则。





















 1690
1690











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








