Scheduler 用于在 React 应用中进行任务调度。它可以帮助开发人员在处理复杂的任务和操作时更好地管理和优化性能。
关于 Scheduler 在React 如何渲染的可以参考 React 第三十四章 React 渲染流程
下面我们根据流程图先简单的了解 Scheduler 的调度过程
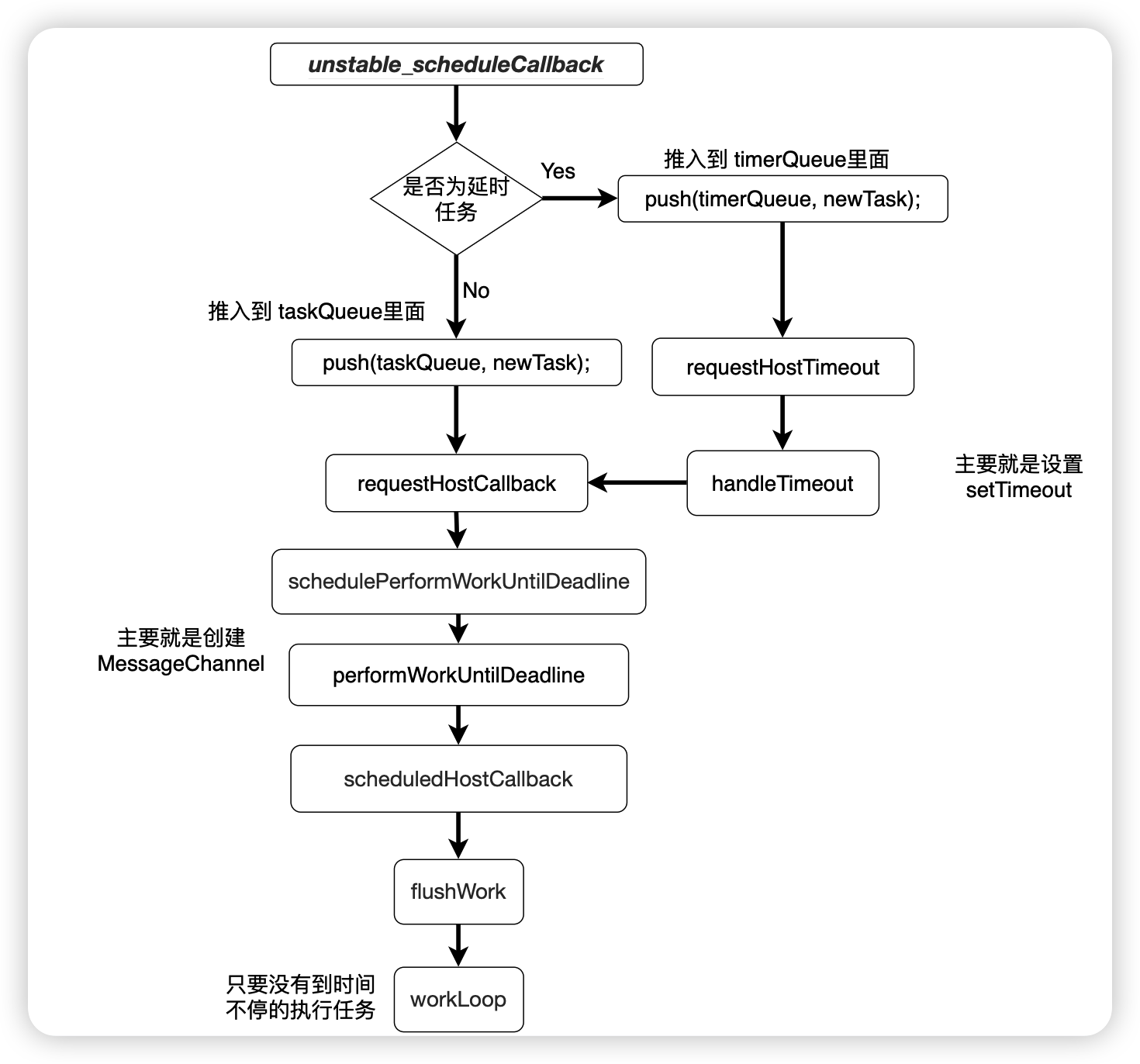
Scheduler 维护两个队列,分别存放普通任务和延时任务
- taskQueue::普通任务
- timerQueue:延时任务
当 Scheduler 接收的是普通任务时,会加入普通任务队列,然后执行 requestHostCallback。
schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline 根据环境创建宏任务(主要创建的就是 MessageChannel),然后执行 performWorkUntilDeadline。该方法实际上主要就是在调用 scheduledHostCallback(flushWork),调用之后,返回一个布尔值,根据这个布尔值来判断是否还有剩余的任务,如果还有,就是用 messageChannel 进行一个宏任务的包装,放入到任务队列里面。flushWork 主要是调用 wookLoop。workLoop 在当前贞中只要还有时间,就会不停的执行任务
当 Scheduler 接收的是延时任务时,会加入延时队列,然后执行 requestHostTimout(主要是设置setTimeout),然后执行 handleTimeout,将 到时间的延时任务加入到 普通任务队列,然后执行 requestHostTimout。接下来的操作就和普通任务队列接下来的操作一致。
下面我们来看源码的具体实现。Scheduler 的核心源码位于 packages/scheduler/src/forks/Scheduler.js。 unstable_scheduleCallback就是我们要看到的 Scheduler
schedule调度普通任务
scheduleCallback 该函数的主要目的就是用调度任务,该方法的分析如下:
let getCurrentTime = () => performance.now();
// 有两个队列分别存储普通任务和延时任务
// 里面采用了一种叫做小顶堆的算法,保证每次从队列里面取出来的都是优先级最高(时间即将过期)
var taskQueue = []; // 存放普通任务
var timerQueue = []; // 存放延时任务
var maxSigned31BitInt = 1073741823;
// Timeout 对应的值
var IMMEDIATE_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT = -1;
var USER_BLOCKING_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT = 250;
var NORMAL_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT = 5000;
var LOW_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT = 10000;
var IDLE_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT = maxSigned31BitInt;
/**
*
* @param {*} priorityLevel 优先级等级
* @param {*} callback 具体要做的任务
* @param {*} options { delay: number } 这是一个对象,该对象有 delay 属性,表示要延迟的时间
* @returns
*/
function unstable_scheduleCallback(priorityLevel, callback, options) {
// 获取当前的时间
var currentTime = getCurrentTime();
var startTime;
// 整个这个 if.. else 就是在设置起始时间,如果有延时,起始时间需要添加上这个延时
if (typeof options === "object" && options !== null) {
var delay = options.delay;
// 如果设置了延时时间,那么 startTime 就为当前时间 + 延时时间
if (typeof delay === "number" && delay > 0) {
startTime = currentTime + delay;
} else {
startTime = currentTime;
}
} else {
startTime = currentTime;
}
var timeout;
// 根据传入的优先级等级来设置不同的 timeout
switch (priorityLevel) {
case ImmediatePriority:
timeout = IMMEDIATE_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT;
break;
case UserBlockingPriority:
timeout = USER_BLOCKING_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT;
break;
case IdlePriority:
timeout = IDLE_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT;
break;
case LowPriority:
timeout = LOW_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT;
break;
case NormalPriority:
default:
timeout = NORMAL_PRIORITY_TIMEOUT;
break;
}
// 接下来就计算出过期时间
// 计算出来的时间有些比当前时间要早,绝大部分比当前的时间要晚一些
var expirationTime = startTime + timeout;
// 创建一个新的任务
var newTask = {
id: taskIdCounter++, // 任务 id
callback, // 该任务具体要做的事情
priorityLevel, // 任务的优先级别
startTime, // 任务开始时间
expirationTime, // 任务的过期时间
sortIndex: -1, // 用于后面在小顶堆(这是一种算法,可以始终从任务队列中拿出最优先的任务)进行排序的索引
};
if (enableProfiling) {
newTask.isQueued = false;
}
if (startTime > currentTime) {
// This is a delayed task.
// 说明这是一个延时任务
newTask.sortIndex = startTime;
// 将该任务推入到 timerQueue 的任务队列中
push(timerQueue, newTask);
if (peek(taskQueue) === null && newTask === peek(timerQueue)) {
// 进入此 if,说明 taskQueue 里面的任务已经执行完毕了
// 并且从 timerQueue 里面取出一个最新的任务又是当前任务
// All tasks are delayed, and this is the task with the earliest delay.
// 下面的 if.. else 就是一个开关
if (isHostTimeoutScheduled) {
// Cancel an existing timeout.
cancelHostTimeout();
} else {
isHostTimeoutScheduled = true;
}
// Schedule a timeout.
// 如果是延时任务,调用 requestHostTimeout 进行任务的调度
requestHostTimeout(handleTimeout, startTime - currentTime);
}
} else {
// 说明不是延时任务
newTask.sortIndex = expirationTime; // 设置了 sortIndex 后,可以在任务队列里面进行一个排序
// 推入到 taskQueue 任务队列
push(taskQueue, newTask);
if (enableProfiling) {
markTaskStart(newTask, currentTime);
newTask.isQueued = true;
}
// Schedule a host callback, if needed. If we're already performing work,
// wait until the next time we yield.
// 最终调用 requestHostCallback 进行任务的调度
if (!isHostCallbackScheduled && !isPerformingWork) {
isHostCallbackScheduled = true;
requestHostCallback(flushWork);
}
}
// 向外部返回任务
return newTask;
}
该方法主要注意以下几个关键点:
- 关于任务队列有两个,一个 taskQueue,另一个是 timerQueue,taskQueue 存放普通任务,timerQueue 存放延时任务,任务队列内部用到了小顶堆的算法,保证始终放进去(push)的任务能够进行正常的排序,回头通过 peek 取出任务时,始终取出的是时间优先级最高的那个任务
- 根据传入的不同的 priorityLevel,会进行不同的 timeout 的设置,任务的 timeout 时间也就不一样了,有的比当前时间还要小,这个代表立即需要执行的,绝大部分的时间比当前时间大。
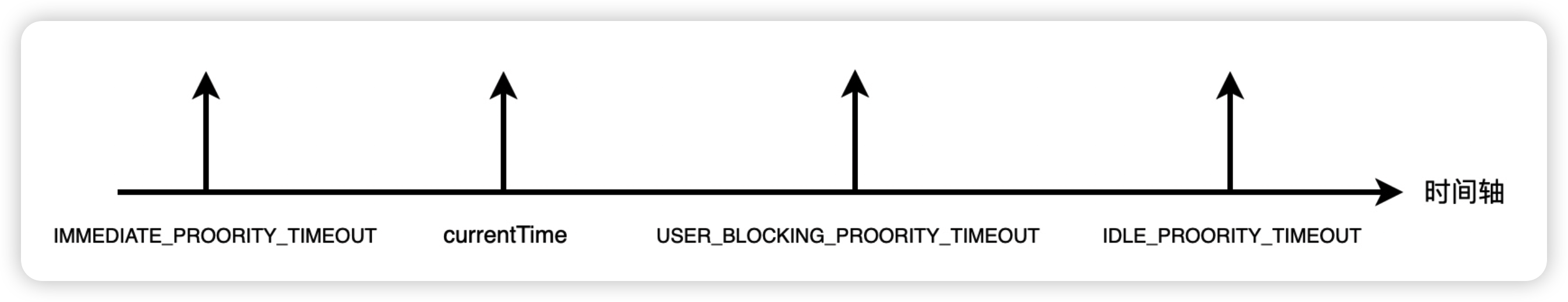
- 不同的任务,最终调用的函数不一样
- 普通任务:requestHostCallback(flushWork)
- 延时任务:requestHostTimeout(handleTimeout, startTime - currentTime);
requestHostCallback 和 schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline
/**
*
* @param {*} callback 是在调用的时候传入的 flushWork
* requestHostCallback 这个函数没有做什么事情,主要就是调用 schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline
*/
function requestHostCallback(callback) {
scheduledHostCallback = callback;
// scheduledHostCallback ---> flushWork
if (!isMessageLoopRunning) {
isMessageLoopRunning = true;
schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline(); // 实例化 MessageChannel 进行后面的调度
}
}
let schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline; // undefined
if (typeof localSetImmediate === 'function') {
// Node.js and old IE.
// https://github.com/facebook/react/issues/20756
schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline = () => {
localSetImmediate(performWorkUntilDeadline);
};
} else if (typeof MessageChannel !== 'undefined') {
// 大多数情况下,使用的是 MessageChannel
const channel = new MessageChannel();
const port = channel.port2;
channel.port1.onmessage = performWorkUntilDeadline;
schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline = () => {
port.postMessage(null);
};
} else {
// setTimeout 进行兜底
schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline = () => {
localSetTimeout(performWorkUntilDeadline, 0);
};
}
- requestHostCallback 主要就是调用了 schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline
- schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline 一开始是 undefiend,根据不同的环境选择不同的生成宏任务的方式
performWorkUntilDeadline
let startTime = -1;
const performWorkUntilDeadline = () => {
// scheduledHostCallback ---> flushWork
if (scheduledHostCallback !== null) {
// 获取当前的时间
const currentTime = getCurrentTime();
// Keep track of the start time so we can measure how long the main thread
// has been blocked.
// 这里的 startTime 并非 unstable_scheduleCallback 方法里面的 startTime
// 而是一个全局变量,默认值为 -1
// 用来测量任务的执行时间,从而能够知道主线程被阻塞了多久
startTime = currentTime;
const hasTimeRemaining = true; // 默认还有剩余时间
// If a scheduler task throws, exit the current browser task so the
// error can be observed.
//
// Intentionally not using a try-catch, since that makes some debugging
// techniques harder. Instead, if `scheduledHostCallback` errors, then
// `hasMoreWork` will remain true, and we'll continue the work loop.
let hasMoreWork = true; // 默认还有需要做的任务
try {
// scheduledHostCallback ---> flushWork(true, 开始时间): boolean
// 如果是 true,代表工作没做完
// false 代表没有任务了
hasMoreWork = scheduledHostCallback(hasTimeRemaining, currentTime);
} finally {
if (hasMoreWork) {
// If there's more work, schedule the next message event at the end
// of the preceding one.
// 那么就使用 messageChannel 进行一个 message 事件的调度,就将任务放入到任务队列里面
schedulePerformWorkUntilDeadline();
} else {
// 说明任务做完了
isMessageLoopRunning = false;
scheduledHostCallback = null; // scheduledHostCallback 之前为 flushWork,设置为 null
}
}
} else {
isMessageLoopRunning = false;
}
// Yielding to the browser will give it a chance to paint, so we can
// reset this.
needsPaint = false;
};
- 该方法实际上主要就是在调用 scheduledHostCallback(flushWork),调用之后,返回一个布尔值,根据这个布尔值来判断是否还有剩余的任务,如果还有,就是用 messageChannel 进行一个宏任务的包装,放入到任务队列里面
flushWork 和 workLoop
/**
*
* @param {*} hasTimeRemaining 是否有剩余的时间,一开始是 true
* @param {*} initialTime 做这一个任务时开始执行的时间
* @returns
*/
function flushWork(hasTimeRemaining, initialTime) {
// ...
try {
if (enableProfiling) {
try {
// 核心实际上是这一句,调用 workLoop
return workLoop(hasTimeRemaining, initialTime);
} catch (error) {
// ...
}
} else {
// 核心实际上是这一句,调用 workLoop
return workLoop(hasTimeRemaining, initialTime);
}
} finally {
// ...
}
}
/**
*
* @param {*} hasTimeRemaining 是否有剩余的时间,一开始是 true
* @param {*} initialTime 做这一个任务时开始执行的时间
* @returns
*/
function workLoop(hasTimeRemaining, initialTime) {
let currentTime = initialTime;
// 该方法实际上是用来遍历 timerQueue,判断是否有已经到期了的任务
// 如果有,将这个任务放入到 taskQueue
advanceTimers(currentTime);
// 从 taskQueue 里面取一个任务出来
currentTask = peek(taskQueue);
while (
currentTask !== null &&
!(enableSchedulerDebugging && isSchedulerPaused)
) {
if (
currentTask.expirationTime > currentTime &&
(!hasTimeRemaining || shouldYieldToHost())
) {
// This currentTask hasn't expired, and we've reached the deadline.
// currentTask.expirationTime > currentTime 表示任务还没有过期
// hasTimeRemaining 代表是否有剩余时间
// shouldYieldToHost 任务是否应该暂停,归还主线程
// 那么我们就跳出 while
break;
}
// 没有进入到上面的 if,说明这个任务到过期时间,并且有剩余时间来执行,没有到达需要浏览器渲染的时候
// 那我们就执行该任务即可
const callback = currentTask.callback; // 拿到这个任务
if (typeof callback === "function") {
// 说明当前的任务是一个函数,我们执行该任务
currentTask.callback = null;
currentPriorityLevel = currentTask.priorityLevel;
const didUserCallbackTimeout = currentTask.expirationTime <= currentTime;
if (enableProfiling) {
markTaskRun(currentTask, currentTime);
}
// 任务的执行实际上就是在这一句
const continuationCallback = callback(didUserCallbackTimeout);
currentTime = getCurrentTime();
if (typeof continuationCallback === "function") {
// If a continuation is returned, immediately yield to the main thread
// regardless of how much time is left in the current time slice.
// $FlowFixMe[incompatible-use] found when upgrading Flow
currentTask.callback = continuationCallback;
if (enableProfiling) {
// $FlowFixMe[incompatible-call] found when upgrading Flow
markTaskYield(currentTask, currentTime);
}
advanceTimers(currentTime);
return true;
} else {
if (enableProfiling) {
// $FlowFixMe[incompatible-call] found when upgrading Flow
markTaskCompleted(currentTask, currentTime);
// $FlowFixMe[incompatible-use] found when upgrading Flow
currentTask.isQueued = false;
}
if (currentTask === peek(taskQueue)) {
pop(taskQueue);
}
advanceTimers(currentTime);
}
} else {
// 直接弹出
pop(taskQueue);
}
// 再从 taskQueue 里面拿一个任务出来
currentTask = peek(taskQueue);
}
// Return whether there's additional work
if (currentTask !== null) {
// 如果不为空,代表还有更多的任务,那么回头外部的 hasMoreWork 拿到的就也是 true
return true;
} else {
// taskQueue 这个队列是空了,那么我们就从 timerQueue 里面去看延时任务
const firstTimer = peek(timerQueue);
if (firstTimer !== null) {
requestHostTimeout(handleTimeout, firstTimer.startTime - currentTime);
}
// 没有进入上面的 if,说明 timerQueue 里面的任务也完了,返回 false,回头外部的 hasMoreWork 拿到的就也是 false
return false;
}
}
- flushWork 主要就是在调用 workLoop
- workLoop 首先有一个 while 循环,该 while 循环保证了能够从任务队列中不停的取任务出来
while (
currentTask !== null &&
!(enableSchedulerDebugging && isSchedulerPaused)
){
// ...
}
- 当然,不是说一直从任务队列里面取任务出来执行就完事儿,每次取出一个任务后,我们还需要一系列的判断
if (
currentTask.expirationTime > currentTime &&
(!hasTimeRemaining || shouldYieldToHost())
) {
break;
}
- currentTask.expirationTime > currentTime 表示任务还没有过期
- hasTimeRemaining 代表是否有剩余时间
- shouldYieldToHost 任务是否应该暂停,归还主线程
- 如果进入 if,说明因为某些原因不能再执行任务,需要立即归还主线程,那么我们就跳出 while
shouldYieldToHost
function shouldYieldToHost() {
// getCurrentTime 获取当前时间
// startTime 是我们任务开始时的时间,一开始是 -1,之后任务开始时,将任务开始时的时间复值给了它
const timeElapsed = getCurrentTime() - startTime;
// frameInterval 默认设置的是 5ms
if (timeElapsed < frameInterval) {
// 主线程只被阻塞了一点点时间,远远没达到需要归还的时候
return false;
}
// 如果没有进入上面的 if,说明主线程已经被阻塞了一段时间了
// 需要归还主线程
if (enableIsInputPending) {
if (needsPaint) {
// There's a pending paint (signaled by `requestPaint`). Yield now.
return true;
}
if (timeElapsed < continuousInputInterval) {
// We haven't blocked the thread for that long. Only yield if there's a
// pending discrete input (e.g. click). It's OK if there's pending
// continuous input (e.g. mouseover).
if (isInputPending !== null) {
return isInputPending();
}
} else if (timeElapsed < maxInterval) {
// Yield if there's either a pending discrete or continuous input.
if (isInputPending !== null) {
return isInputPending(continuousOptions);
}
} else {
// We've blocked the thread for a long time. Even if there's no pending
// input, there may be some other scheduled work that we don't know about,
// like a network event. Yield now.
return true;
}
}
// `isInputPending` isn't available. Yield now.
return true;
}
- 首先计算 timeElapsed,然后判断是否超时,没有的话就返回 false,表示不需要归还,否则就返回 true,表示需要归还。
- frameInterval 默认设置的是 5ms
advanceTimers
function advanceTimers(currentTime) {
// Check for tasks that are no longer delayed and add them to the queue.
// 从 timerQueue 里面获取一个任务
let timer = peek(timerQueue);
// 遍历整个 timerQueue
while (timer !== null) {
if (timer.callback === null) {
// 这个任务没有对应的要执行的 callback,直接从这个队列弹出
pop(timerQueue);
} else if (timer.startTime <= currentTime) {
// 进入这个分支,说明当前的任务已经不再是延时任务
// 我们需要将其转移到 taskQueue
pop(timerQueue);
timer.sortIndex = timer.expirationTime;
push(taskQueue, timer); // 推入到 taskQueue
// ...
} else {
return;
}
// 从 timerQueue 里面再取一个新的进行判断
timer = peek(timerQueue);
}
}
- 该方法就是遍历整个 timerQueue,查看是否有已经过期的方法,如果有,不是说直接执行,而是将这个过期的方法添加到 taskQueue 里面。
Scheduler调度延时任务
function unstable_scheduleCallback(priorityLevel,callback,options){
//...
if (startTime > currentTime) {
// 调度一个延时任务
requestHostTimeout(handleTimeout, startTime - currentTime);
} else {
// 调度一个普通任务
requestHostCallback(flushWork);
}
}
- 可以看到,调度一个延时任务的时候,主要是执行 requestHostTimeout
requestHostTimeout
// 实际上在浏览器环境就是 setTimeout
const localSetTimeout = typeof setTimeout === 'function' ? setTimeout : null;
/**
*
* @param {*} callback 就是传入的 handleTimeout
* @param {*} ms 延时的时间
*/
function requestHostTimeout(callback, ms) {
taskTimeoutID = localSetTimeout(() => {
callback(getCurrentTime());
}, ms);
/**
* 因此,上面的代码,就可以看作是
* id = setTimeout(function(){
* handleTimeout(getCurrentTime())
* }, ms)
*/
}
可以看到,requestHostTimeout 实际上就是调用 setTimoutout,然后在 setTimeout 中,调用传入的 handleTimeout
handleTimeout
/**
*
* @param {*} currentTime 当前时间
*/
function handleTimeout(currentTime) {
isHostTimeoutScheduled = false;
// 遍历timerQueue,将时间已经到了的延时任务放入到 taskQueue
advanceTimers(currentTime);
if (!isHostCallbackScheduled) {
if (peek(taskQueue) !== null) {
// 从普通任务队列中拿一个任务出来
isHostCallbackScheduled = true;
// 采用调度普通任务的方式进行调度
requestHostCallback(flushWork);
} else {
// taskQueue任务队列里面是空的
// 再从 timerQueue 队列取一个任务出来
// peek 是小顶堆中提供的方法
const firstTimer = peek(timerQueue);
if (firstTimer !== null) {
// 取出来了,接下来取出的延时任务仍然使用 requestHostTimeout 进行调度
requestHostTimeout(handleTimeout, firstTimer.startTime - currentTime);
}
}
}
}
- handleTimeout 里面主要就是调用 advanceTimers 方法,该方法的作用是将时间已经到了的延时任务放入到 taskQueue,那么现在 taskQueue 里面就有要执行的任务,然后使用 requestHostCallback 进行调度。如果 taskQueue 里面没有任务了,再次从 timerQueue 里面去获取延时任务,然后通过 requestHostTimeout 进行调度。






















 595
595

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








