文章目录
1. PyTorch基础
1.1. 导入PyTorch包
import torch
1.2. 张量的初始化
(1) 创建并初始化张量
# 创建一个任意张量
tensor = torch.tensor([5.5, 3, 0])
'''
tensor([5.5000, 3.0000, 0.0000])
'''
# 创建一个数列张量,从1开始,到10结束,间隔为2
tensor_arange = torch.arange(1, 10, 2)
'''
tensor([1, 3, 5, 7, 9])
'''
# 创建一个空张量,大小为 5*3
tensor_empty = torch.empty((5, 3))
'''
tensor([[7.1819e+22, 4.0666e+21, 1.0999e+27],
[2.6277e+17, 7.2368e+25, 2.7516e+17],
[4.4721e+21, 1.8497e+31, 2.6845e+17],
[4.4724e+21, 1.8497e+31, 5.4214e-11],
[9.1720e-04, 1.9086e-41, 0.0000e+00]])
'''
# 创建一个0张量,大小为 5*3
tensor_zeros = torch.zeros((5, 3))
'''
tensor([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]])
'''
# 创建一个1张量,大小为 5*3
tensor_ones = torch.ones((5, 3))
'''
tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]])
'''
# 创建一个任意值张量,大小为 5*3,填充值为99
tensor_full = torch.full([5, 3], 99.)
'''
tensor([[99., 99., 99.],
[99., 99., 99.],
[99., 99., 99.],
[99., 99., 99.],
[99., 99., 99.]])
'''
# 创建一个在[0,1)内均匀分布的随机张量,大小为 5*3
tensor_rand = torch.rand((5, 3))
'''
tensor([[0.4991, 0.5687, 0.9626],
[0.3185, 0.2407, 0.6076],
[0.2600, 0.0289, 0.1632],
[0.4269, 0.9201, 0.4774],
[0.7576, 0.9349, 0.5644]])
'''
# 创建一个服从标准正态分布的随机张量,大小为 5*3
tensor_randn = torch.randn((5, 3))
'''
tensor([[-0.6753, -1.6975, -1.1010],
[-1.9736, 0.6005, 0.5844],
[ 0.3015, -0.5700, 1.1196],
[ 0.3156, -0.4194, -0.8618],
[-1.1506, 0.5248, 0.0401]])
'''
# 创建一个服从均值为mean、标准差为std正态分布的随机张量,大小为 1*10
# 更多关于随机正态分布张量的内容:https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.normal.html#torch-normal
tensor_normal = torch.normal(mean=torch.arange(0., 1.), std=torch.arange(0, 10, 1))
'''
tensor([ 0.0000, -0.9662, -0.2848, 5.5105, 0.9495, 3.0639, -3.4798,
6.9719, -11.6149, -6.0056])
'''
(2) 从已有张量创建大小一致的张量
# 根据已有的张量创建大小一致的0张量
tensor_zeros = torch.zeros_like(tensor_empty)
'''
tensor([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]])
'''
# 根据已有的张量创建大小一致的1张量
tensor_ones = torch.ones_like(tensor_empty)
'''
tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]])
'''
# 根据已有的张量创建大小一致在[0,1)内的均匀分布的随机张量
tensor_rand = torch.rand_like(tensor_empty)
'''
tensor([[0.0437, 0.9776, 0.1685],
[0.5190, 0.6811, 0.3768],
[0.4864, 0.7169, 0.4813],
[0.4596, 0.4703, 0.2497],
[0.9778, 0.9880, 0.9152]])
'''
(3) 指定张量的数据类型 dtype
# 创建long数据类型的张量
tensor_long = torch.ones((5, 3), dtype=torch.long)
'''
tensor([[1, 1, 1, 1, 1]])
'''
# 查看张量的数据类型
print(tensor_long.dtype)
'''
torch.int64
'''
# 改变张量的数据类型
print(tensor_long.float())
'''
torch.float32
'''
# 张量的数据类型总结:
# 8位无符号整型:torch.uint8
# 8位整型:torch.int8
# 16位整型:torch.int16 | torch.short
# 32位整型:torch.int32 | torch.int
# 64位整型:torch.int64 | torch.long
# 16位浮点型:torch.float16 | torch.half
# 32位浮点型:torch.float32 | torch.float
# 64位浮点型:torch.float64 | torch.double
1.3. 张量的基本操作
(1) 查看张量的大小
tensor_empty = torch.empty((5, 3))
print(tensor_empty.size())
'''
torch.Size([5, 3])
'''
print(tensor_empty.shape)
'''
torch.Size([5, 3])
'''
(2) 张量堆叠
# 创建一个空张量,大小为 5*3
tensor_empty = torch.tensor([[1,2,3]])
'''
tensor([[1, 2, 3]])
'''
# 张量按维度0堆叠,即添加行
tensor_cat0 = torch.cat((tensor_empty,tensor_empty,tensor_empty), 0)
'''
tensor([[1, 2, 3],
[1, 2, 3],
[1, 2, 3]])
'''
# 张量按维度0堆叠,即添加列
tensor_cat1 = torch.cat((tensor_empty,tensor_empty,tensor_empty), 1)
'''
tensor([[1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3]])
'''
(3) 张量增减维度
tensor_zeros = torch.zeros(3, 2, 4, 1, 2, 1)
print(tensor_zeros.shape)
'''
torch.Size([3, 2, 4, 1, 2, 1])
'''
# 在张量的第dim维增添一个维数为1的维度
tensor_unsqueeze = torch.unsqueeze(tensor_zeros, dim=0)
print(tensor_unsqueeze.shape)
'''
torch.Size([1, 3, 2, 4, 1, 2, 1])
'''
# 删去张量中维数为1的维度,如果未指定dim则删去全部维数为1的维度
tensor_squeeze = torch.squeeze(tensor_zeros, dim=3)
print(tensor_squeeze.shape)
'''
torch.Size([3, 2, 4, 2, 1])
'''
(4) 张量分割
# 创建一个数列张量
tensor_arange = torch.arange(10)
'''
tensor([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
'''
# 把张量均匀分割。4表示分割成4份;dim=0表示按行分割,dim=1表示按列分割
tensor_chunk = torch.chunk(tensor_arange, 4, dim=0)
'''
(tensor([0, 1, 2]), tensor([3, 4, 5]), tensor([6, 7, 8]), tensor([9]))
'''
# 把张量按指定方案分割。[1,2,3,4]表示分割成4份,每份分别有1、2、3、4个元素;dim=0表示按行分割,dim=1表示按列分割
tensor_split = torch.split(tensor_arange, [1,2,3,4], dim=0)
'''
(tensor([0]), tensor([1, 2]), tensor([3, 4, 5]), tensor([6, 7, 8, 9]))
'''
(5) 选择张量中的元素
# 创建一个随机张量
tensor_randn = torch.randn((5, 3))
'''
tensor([[ 0.3567, 1.3366, 0.1045],
[ 0.7795, -0.2843, -0.2252],
[-0.4905, -0.2118, -1.5967],
[ 0.8375, 0.3417, -0.7932],
[-0.5923, -2.4375, -0.9357]])
'''
# 取张量的(0,0)元素
print(tensor_randn[0, 0])
'''
tensor(0.3567)
'''
# 取张量的第一列元素
print(tensor_randn[:, 0])
'''
tensor([ 0.3567, 0.7795, -0.4905, 0.8375, -0.5923])
'''
# 选择张量中行index为0、2、4的元素
print(torch.index_select(tensor_randn, dim=0, index=torch.tensor([0, 2, 4])))
'''
tensor([[ 0.3567, 1.3366, 0.1045],
[-0.4905, -0.2118, -1.5967],
[-0.5923, -2.4375, -0.9357]])
'''
# 选择张量中>=0的元素,mask为条件表达式
print(torch.masked_select(tensor_randn, mask=tensor_randn.ge(0)))
'''
tensor([0.3567, 1.3366, 0.1045, 0.7795, 0.8375, 0.3417])
'''
(6) 改变张量形状
# 创建一个随机张量
tensor_randn = torch.randn((5, 3))
'''
tensor([[ 0.3478, -2.1573, 0.7693],
[-0.3915, -1.2390, -0.7590],
[-0.3685, 0.1261, 0.1424],
[ 0.5710, 0.0483, -1.2647],
[-0.8762, 0.9870, -0.0174]])
'''
# 将tensor_randn从(5,3)转变为(3,5)
tensor_reshape = torch.reshape(tensor_randn, (3,5))
'''
tensor([[ 0.3478, -2.1573, 0.7693, -0.3915, -1.2390],
[-0.7590, -0.3685, 0.1261, 0.1424, 0.5710],
[ 0.0483, -1.2647, -0.8762, 0.9870, -0.0174]])
'''
# 将tensor_randn从(5,3)转变为(3,5)
tensor_view = tensor_randn.view((-1,5)) #当某一维是-1时,会根据另一维自动计算它的大小
'''
tensor([[ 0.3478, -2.1573, 0.7693, -0.3915, -1.2390],
[-0.7590, -0.3685, 0.1261, 0.1424, 0.5710],
[ 0.0483, -1.2647, -0.8762, 0.9870, -0.0174]])
'''
(7) 张量运算
# 创建一个数列张量
tensor_arange1 = torch.arange(10, 20, 2)
tensor_arange2 = torch.arange(0, -10, -2)
'''
tensor([10., 12., 14., 16., 18.])
tensor([-1., -3., -5., -7., -9.])
'''
# 张量元素相加 + 两种方法
tensor_add = torch.add(tensor_arange1,tensor_arange2, out=None)
# torch.add(tensor_arange1,tensor_arange2, out=tensor_arange1) # 此时操作结果直接存储在tensor_arange1中
# tensor_arange2.add_(tensor_arange1) # 此时操作结果直接存储在tensor_arange2中
'''
tensor([9., 9., 9., 9., 9.])
'''
# 张量元素相乘 ×
tensor_mul = torch.mul(tensor_arange1, tensor_arange2, out=None)
'''
tensor([ -10., -36., -70., -112., -162.])
'''
# 张量元素相除 ÷ 这里要注意除法的结果一般为浮点数,所以张量类型也应当为浮点数类型
tensor_div = torch.div(tensor_arange1, tensor_arange2, out=None)
'''
tensor([-10.0000, -4.0000, -2.8000, -2.2857, -2.0000])
'''
# 张量元素求幂 ^
tensor_pow = torch.pow(tensor_arange1, tensor_arange2, out=None)
'''
tensor([1.0000e-01, 5.7870e-04, 1.8593e-06, 3.7253e-09, 5.0414e-12])
'''
# 张量元素开平方根 √
tensor_sqrt = torch.sqrt(tensor_arange1, out=None)
'''
tensor([3.1623, 3.4641, 3.7417, 4.0000, 4.2426])
'''
# 张量元素四舍五入
tensor_round = torch.round(tensor_arange1, out=None)
'''
tensor([10., 12., 14., 16., 18.])
'''
# 张量元素取绝对值
tensor_abs = torch.abs(tensor_arange2, out=None)
'''
tensor([1., 3., 5., 7., 9.])
'''
# 张量元素向上取整,等于向下取整+1
tensor_ceil = torch.ceil(tensor_arange2, out=None)
'''
tensor([-1., -3., -5., -7., -9.])
'''
# 张量元素限定值域,把输入数据规范在min-max区间,超过范围的用min、max代替
tensor_clamp = torch.clamp(tensor_arange1, min=12, max=16, out=None)
'''
tensor([12., 12., 14., 16., 16.])
'''
# 张量取最大值的下标,dim=1时取出每一列中的最大值的下标,dim=0时取出每一行中的最大值的下标
tensor_argmax = torch.argmax(tensor_arange1, dim=0, keepdim=False)
'''
tensor(4)
'''
# 张量元素输入sigmoid函数进行处理
tensor_sigmoid = torch.sigmoid(tensor_arange1, out=None)
'''
tensor([1.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000, 1.0000])
'''
# 张量元素输入tanh函数进行处理
tensor_tanh = torch.tanh(tensor_arange1, out=None)
'''
tensor([1., 1., 1., 1., 1.])
'''
1.4. Tensor与Numpy、List的互相转换
(1) Tensor 转 Numpy 再转 List
# 创建一个1张量
tensor_ones = torch.ones((2,4))
'''
tensor([[1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1.]])
'''
# 将tensor张量转换为array数组
# 转换后,numpy的变量和原来的tensor会共用底层内存地址,所以如果原来的tensor改变了,numpy变量也会随之改变
tensor_numpy = tensor_ones.numpy()
'''
[[1. 1. 1. 1.]
[1. 1. 1. 1.]]
'''
tensor_list = tensor_numpy.tolist()
'''
[[1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1.]]
'''
(2) List 转 Numpy 再转 Tensor
# 创建一个1列表
list_ones = [1 for i in range(0, 5)]
'''
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
'''
# 将list转换为array
array_ones = numpy.array(list_ones)
'''
[1 1 1 1 1]
'''
# 将array数组转换为tensor张量
# 转换后,tensor和原来的numpy的变量会共用底层内存地址,所以如果原来的tensor改变了,numpy变量也会随之改变
tensor_form_numpy = torch.from_numpy(array_ones)
'''
tensor([1., 1., 1., 1., 1.], dtype=torch.int)
'''
# 改变tensor的数据类型
tensor_form_numpy = tensor_form_numpy.float()
'''
tensor([1., 1., 1., 1., 1.], dtype=torch.float32)
'''
1.5. GPU加速
在Pytorch使用GPU进行加速之前,需要先安装机器显卡对应的 CUDA ,然后即可利用GPU进行运算
(1) 将数据从CPU迁入GPU
# 一般而言,我们将网络模型、损失函数、张量三种数据迁入GPU中进行加速
# 将网络模型和损失函数迁入GPU
net = Net()
loss_func = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
if(torch.cuda.is_available()):
net = net.cuda()
loss_func = loss_func.cuda()
# 将张量迁入GPU,实际上只需要将输入网络的张量数据迁入GPU即可,因为根据这些数据产生的中间数据以及预测结果均在GPU中,所以只要把握住源头数据,后面的数据就不需要再显式地迁入GPU
# 有些旧版的Pytorch需要将张量封装成Variable类型才可以迁入GPU,不过这已经是过去式了
if (torch.cuda.is_available()):
tensor_x, tensor_y = tensor_x.cuda(), tensor_y.cuda()
# tensor_x, tensor_y = Variable(tensor_x).cuda(), Variable(tensor_y).cuda() # 旧版Pytorch
(2) 将数据从GPU迁出到CPU
# 将网络模型预测的结果迁出GPU,一般是最终损失值、精确度,也可以是其他迁入了GPU的数据
if(torch.cuda.is_available()):
loss = loss.cpu()
accurate = accurate.cpu()
2. 自动微分
2.1. 开启自动微分
# 创建一个张量并在初始化时设置requires_grad=True开启自动微分功能
tensor_ones = torch.ones(2, 2, requires_grad=True)
'''
tensor([[1., 1.],
[1., 1.]], requires_grad=True)
'''
# 创建一个张量,初始化时不开启自动微分
tensor_randn = torch.randn(2, 2)
tensor_randn = (tensor_randn * 3) / (tensor_randn - 1)
print(tensor_randn.requires_grad)
# 设置该张量为自动微分
tensor_randn.requires_grad_(True)
print(tensor_randn.requires_grad)
'''
False
True
'''
2.2. 梯度计算
(1) 查看梯度方程 grad_fn
# 创建一个1张量,并查看其梯度方程grad_fn
tensor_ones = torch.ones(2, 2, requires_grad=True)
print(tensor_ones)
print(tensor_ones.grad_fn) # 可以看到,单独的张量是没有梯度方程的
'''
tensor([[1., 1.],
[1., 1.]], requires_grad=True)
None
'''
# 构建一个张量方程,并查看其梯度方程grad_fn
tensor_add = tensor_ones + 2
print(tensor_add)
print(tensor_add.grad_fn) # 该张量方程是由加法构建的张量方程,因此梯度方程是AddBackward类型的
'''
tensor([[3., 3.],
[3., 3.]], grad_fn=<AddBackward0>)
<AddBackward0 object at 0x00000245B1025CA0>
'''
# 构建一个张量方程,并查看其梯度方程grad_fn
tensor_mul = tensor_ones * tensor_ones * 2
print(tensor_mul)
print(tensor_mul.grad_fn) # 该张量方程是由乘法构建的张量方程,因此梯度方程是MulBackward类型的
'''
tensor([[2., 2.],
[2., 2.]], grad_fn=<MulBackward0>)
<MulBackward0 object at 0x000001A309525CA0>
'''
(2) 反向传播计算标量梯度
# 创建一个1张量
tensor_x = torch.ones(2, 2, requires_grad=True)
tensor_y = tensor_x + 2
tensor_z = tensor_y * tensor_y * 3
out = tensor_z.mean()
print(out)
'''
tensor(27., grad_fn=<MeanBackward0>)
'''
# 反向传播计算梯度
# out是标量,因此不需要为backward()函数指定参数,相当于out.backward(torch.tensor(1))
out.backward()
print(tensor_x.grad) # 输出梯度
'''
tensor([[4.5000, 4.5000],
[4.5000, 4.5000]])
'''
(3) 反向传播计算矢量梯度
# 创建一个随机张量
tensor_x = torch.randn((1,3), requires_grad=True)
print(tensor_x)
'''
tensor([[0.2427, 0.8484, 0.7631]], requires_grad=True)
'''
# 求 y^(2^(n))>=1000 的最小值
tensor_y = tensor_x * 2
while tensor_y.data.norm() < 1000:
tensor_y = tensor_y * 2
print(tensor_y)
'''
tensor([[248.5333, 868.7134, 781.4405]], grad_fn=<MulBackward0>)
'''
gradients = torch.tensor([[0.1, 1.0, 0.0001]], dtype=torch.float) # 梯度参数
tensor_y.backward(gradients) # 对矢量进行梯度计算需要指定梯度,tensor_x[0,0]与tensor_y[0,0]对应梯度0.1...
print(tensor_x.grad)
'''
tensor([[102.40, 1024.0, 0.10240]])
'''
(4) 不进行梯度计算
# 创建一个随机张量
tensor_x = torch.randn((1,3), requires_grad=True)
print(tensor_x.requires_grad)
'''
True
'''
# 进行梯度计算
tensor_y = tensor_x ** 2
print(tensor_y.requires_grad)
'''
True
'''
# 将变量包裹在no_grad()中,可以不进行梯度计算
with torch.no_grad():
tensor_y = tensor_x ** 2
print(tensor_y.requires_grad)
'''
False
'''
(5) 切断梯度计算
# 创建一个随机张量
tensor_x = torch.randn(3, requires_grad=True)
tensor_y = tensor_x ** 2
print(tensor_x.requires_grad)
print(tensor_y.requires_grad)
'''
True
True
'''
# 切断tensor_y的梯度计算
tensor_y = tensor_y.detach()
print(tensor_y.requires_grad)
'''
False
'''
3. 神经网络要素
3.1. 构建网络
(1) 使用torch.nn模块构建神经网络
关于torch.nn模块包含的全部方法在官方文档 torch.nn 中有详细介绍。翻译版可以在 PyTorch中的torch.nn模块使用详解 中查看
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class Net(nn.Module):
#定义Net的初始化函数,这个函数定义了该神经网络的基本结构
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__() #复制并使用Net的父类的初始化方法,即先运行nn.Module的初始化函数
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 6, 5) # 定义二维卷积层:输入为3通道图像,输出6个特征图, 卷积核为5x5正方形
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5)# 定义二维卷积层:输入为6张特征图,输出16个特征图, 卷积核为5x5正方形
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16*5*5, 120) # 定义线性全连接层:y = Wx + b,并将16*5*5个特征连接到120个节点上
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)#定义线性全连接层:y = Wx + b,并将120个节点连接到84个节点上
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)#定义线性全连接层:y = Wx + b,并将84个节点连接到10个节点上
#定义该神经网络的向前计算函数,该函数定义成功后,会自动生成反向传播函数(autograd)
def forward(self, x):
x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv1(x)), (2, 2)) #输入x经过卷积conv1之后,经过激活函数ReLU(原来这个词是激活函数的意思),使用2x2的窗口进行最大池化Max pooling,然后更新到x。
x = F.max_pool2d(F.relu(self.conv2(x)), 2) #输入x经过卷积conv2之后,经过激活函数ReLU,使用2x2的窗口进行最大池化Max pooling,然后更新到x。
x = x.view(-1, 16*5*5) #view函数将张量x变形成一维的向量形式,总特征数并不改变,为接下来的全连接作准备,可验算这里的-1值为32。。
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x)) #输入x经过全连接1,再经过ReLU激活函数处理,然后更新x
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x)) #输入x经过全连接2,再经过ReLU激活函数处理,然后更新x
x = self.fc3(x) #输入x经过全连接3处理,然后更新x
return x
(2) 查看神经网络的参数
# 实例化一个神经网络
net = Net()
layers = list(net.parameters())
# 查看神经网络的基本结构信息
print(net)
'''
Net(
(conv1): Conv2d(3, 6, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(conv2): Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(fc1): Linear(in_features=400, out_features=120, bias=True)
(fc2): Linear(in_features=120, out_features=84, bias=True)
(fc3): Linear(in_features=84, out_features=10, bias=True)
)
'''
# 查看神经网络的总层数
print(len(layers))
'''
10
'''
# 查看最后一层的参数
print(layers[-1])
'''
Parameter containing:
tensor([-0.0674, 0.0600, 0.0800, -0.0760, 0.0293, 0.0745, 0.0182, 0.0616,
-0.0197, 0.0729], requires_grad=True)
'''
# 查看第一层的大小
print(layers[0].size())
'''
torch.Size([6, 3, 5, 5])
'''
# 查看每一层的参数和节点数量
total_parameter=0
layer_num = 1
for layer in layers:
parameter = 1
for _ in layer.size():
parameter *= _
print("第" + str(layer_num) + "层的结构:"+ str(list(layer.size())) + ",参数和:"+ str(parameter))
total_parameter = total_parameter + parameter
layer_num += 1
print("总参数和:"+ str(total_parameter))
'''
第1层的结构:[6, 3, 5, 5],参数和:450
第2层的结构:[6],参数和:6
第3层的结构:[16, 6, 5, 5],参数和:2400
第4层的结构:[16],参数和:16
第5层的结构:[120, 400],参数和:48000
第6层的结构:[120],参数和:120
第7层的结构:[84, 120],参数和:10080
第8层的结构:[84],参数和:84
第9层的结构:[10, 84],参数和:840
第10层的结构:[10],参数和:10
总参数和:62006
Process finished with exit code 0
'''
(3) 查看前向计算过程
# 实例化一个神经网络
net = Net()
input = torch.randn(2, 3, 32, 32) # 产生2个3通道,32*32的随机输入,这是nn.Conv2d的接收格式
out = net(input)
print(out)
'''
tensor([[-0.1063, 0.0641, -0.0391, -0.0517, 0.1174, -0.0600, 0.0044, -0.0311,
-0.1074, 0.0226],
[-0.0779, 0.0697, -0.0486, -0.0842, 0.1377, -0.0276, -0.0247, -0.0504,
-0.1054, 0.0065]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward>)
'''
(4) 查看反向传播过程
net = Net() # 实例化一个神经网络
net.zero_grad() # 梯度初始化
input = torch.randn(1, 3, 32, 32)
out = net(input)
out.backward(torch.randn(1, 10)) # 随机选取参数进行反向传播
print(out)
'''
tensor([[-0.0829, 0.0556, -0.0088, -0.0263, -0.0518, 0.0802, -0.0923, 0.0091,
0.0122, 0.0927]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward>)
'''
3.2. 损失函数
(1) 定义损失函数并计算损失
net = Net()
criterion = nn.MSELoss() # 定义均方误差损失函数
target = torch.randn(10).view(1, -1) # 定义10个随机真值(因为网络最后一层有10个输出),并转换为行向量
print(target)
'''
tensor([[-1.1115, -0.3807, 0.5877, -1.0567, -0.0541, -0.3390, -1.9487, -0.2775,
-0.0366, 0.7521]])
'''
output = net(torch.randn(1, 3, 32, 32)) # 用随机输入计算输出
loss = criterion(output, target) # 计算损失
print(output)
print(loss)
'''
tensor([[ 0.0881, -0.0362, -0.1039, -0.0116, 0.0952, 0.0953, -0.0499, 0.0214,
-0.0549, -0.0493]], grad_fn=<AddmmBackward>)
tensor(0.7676, grad_fn=<MseLossBackward>)
'''
PyTorch的损失函数有十九种,可以在官方文档 PyTorch Loss-Functions 中查看,中文译版可以在博客 Pytorch学习之十九种损失函数 中查看,常用的损失函数如下:
| 描述 | 损失函数 |
|---|---|
| L1损失 | L1Loss |
| 平滑L1损失 | SmoothL1Loss |
| 均方误差损失 | MSELoss |
| 交叉熵损失 | CrossEntropyLoss |
| KL散度损失 | KLDivLoss |
| 余弦损失 | CosineEmbeddingLoss |
| 二分类逻辑损失 | SoftMarginLoss |
| 负对数似然损失 | NLLLoss |
| 二维负对数似然损失 | NLLLoss2d |
| 泊松负对数似然损失 | PoissonNLLLoss |
(2) 计算损失的反向传播
net = Net()
net.zero_grad() # 梯度初始化
criterion = nn.MSELoss() # 定义均方误差损失函数
target = torch.randn(10).view(1, -1) # 定义10个随机真值(因为网络最后一层有10个输出),并转换为行向量
output = net(torch.randn(1, 3, 32, 32)) # 用随机输入计算输出
loss = criterion(output, target) # 计算损失
loss.backward() # 损失反向传播
print('conv1.bias.grad before backward: ' + str(net.conv1.bias.grad))
print('conv2.bias.grad before backward: ' + str(net.conv2.bias.grad))
print('fc3.bias.grad before backward: ' + str(net.fc3.bias.grad))
'''
conv1.bias.grad before backward: tensor([ 0.0213, -0.0110, 0.0120, -0.0252, -0.0081, 0.0115])
conv2.bias.grad before backward: tensor([ 0.0169, 0.0230, 0.0039, -0.0125, 0.0182, 0.0000, -0.0253, 0.0000, -0.0133, -0.0038, 0.0196, -0.0379, -0.0142, -0.0147, -0.0534, 0.0265])
fc3.bias.grad before backward: tensor([ 0.2603, -0.1132, 0.0708, 0.1399, -0.2388, 0.1579, -0.0635, 0.0143, -0.5937, 0.1236])
'''
3.3. 优化器
优化器用于管理并更新模型中可学习参数(权值、偏置bias)的值。
(1) 定义优化器算法,并使用优化器更新权重
net = Net()
net.zero_grad() # 梯度初始化
criterion = nn.MSELoss() # 定义均方误差损失函数
optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.01) # 定义随机梯度下降优化算法,并设置学习率为0.01
optimizer.zero_grad() # 优化器梯度初始化
target = torch.randn(10).view(1, -1) # 定义10个随机真值(因为网络最后一层有10个输出),并转换为行向量
output = net(torch.randn(1, 3, 32, 32)) # 用随机输入计算输出
loss = criterion(output, target) # 计算损失
loss.backward() # 损失反向传播
optimizer.step() # 对网络模型参数进行优化
print('conv1.bias.grad before backward: ' + str(net.conv1.bias.grad))
print('conv2.bias.grad before backward: ' + str(net.conv2.bias.grad))
print('fc3.bias.grad before backward: ' + str(net.fc3.bias.grad))
print(loss)
'''
conv1.bias.grad before backward: tensor([ 0.0046, 0.0145, -0.0112, -0.0003, 0.0035, 0.0078])
conv2.bias.grad before backward: tensor([-0.0040, -0.0106, 0.0092, 0.0102, 0.0140, -0.0078, -0.0187, -0.0118,
-0.0066, -0.0005, -0.0054, 0.0032, 0.0016, 0.0033, -0.0020, -0.0043])
fc3.bias.grad before backward: tensor([ 0.0078, -0.0456, 0.0653, -0.0499, 0.2710, -0.1554, 0.0496, -0.2634,
-0.0601, 0.0723])
tensor(0.4679, grad_fn=<MseLossBackward>)
'''
PyTorch的各类优化器可以在官方文档 PyTorch TORCH.OPTIM 中查看,中文译版可以在博客 Pytorch的优化器总结 中查看,常用的优化器如下:
| 描述 | 优化器 |
|---|---|
| 随机梯度下降算法 | SGD |
| 标准动量优化算法 | Momentum |
| 均方根比例算法 | RMSProp |
| 自适应矩估计算法 | Adam |
3.4. 模型存取
(1) 保存训练好的模型
# 实例化一个神经网络
net = Net()
# 方法一,保存整个网络
torch.save(net, './my_net.pth')
# 方法二,保存网络的状态信息
torch.save(net.state_dict(), './my_net.pth')
(2) 读取保存的模型
# 提取整个网络
pretrained_net = torch.load('./my_net.pth')
# 提取网络状态
net_new = Net()
net_new.load_state_dict(torch.load('./my_net.pth'))
4. 神经网络实例
4.1. 分类神经网络
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 构造数据
n_data = torch.ones(100, 2)
x0 = torch.normal(3*n_data, 1)
x1 = torch.normal(-3*n_data, 1)
# 标记为y0=0,y1=1两类标签
y0 = torch.zeros(100)
y1 = torch.ones(100)
# 通过.cat连接数据
x = torch.cat((x0, x1), 0).type(torch.float)
y = torch.cat((y0, y1), 0).type(torch.long)
# 构造一个简单的神经网络
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_feature, n_hidden, n_output):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.inLayer = torch.nn.Linear(n_feature, n_hidden) # 输入层
self.hiddenLayer = torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_hidden) # 隐藏层
self.outLayer = torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_output) # 输出层
# 前向计算函数,定义完成后会隐式地自动生成反向传播函数
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.hiddenLayer(self.inLayer(x)))
x = self.outLayer(x)
return x
net = Net(2, 10, 2) # 初始化一个网络,2个输入层节点,10个隐藏层节点,2个输出层节点
loss_func = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 定义交叉熵损失函数
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.2) # 配置网络优化器
# 将网络模型、损失函数和输入张量迁入GPU
if(torch.cuda.is_available()):
net = net.cuda()
loss_func = loss_func.cuda()
x, y = x.cuda(), y.cuda()
# 训练模型
out = net(x)
for t in range(300):
out = net(x) # 将数据输入网络,得到输出
loss = loss_func(out, y) # 得到损失
optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度初始化
loss.backward() # 反向传播
optimizer.step() # 对网络进行优化
# 使用模型进行预测
prediction = torch.max(F.softmax(out, dim=0), 1)[1]
pred_y = prediction.data.cpu().numpy().squeeze()
# 可视化
plt.scatter(x.data.cpu().numpy()[:, 0], x.data.cpu().numpy()[:, 1], c=pred_y, s=100, lw=0, cmap='RdYlBu')
plt.show()

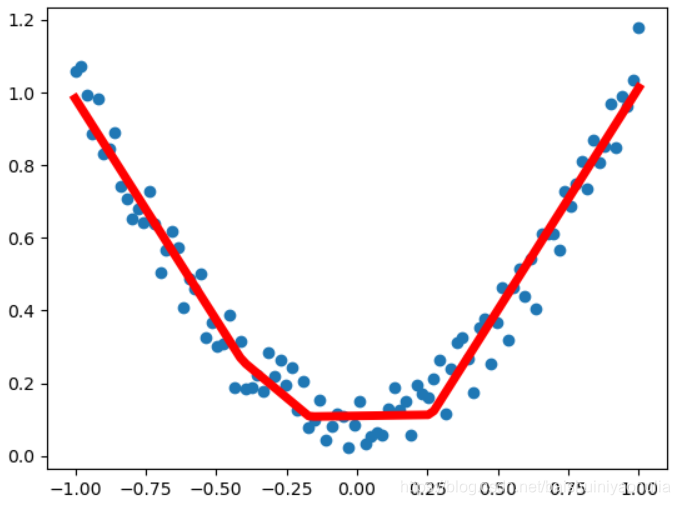
4.2. 回归神经网络
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 构造数据
x = torch.unsqueeze(torch.linspace(-1, 1, 100), dim=1)
y = x.pow(2) + 0.2 * torch.rand(x.size())
# 构造一个简单的神经网络
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_feature, n_hidden, n_output):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.inLayer = torch.nn.Linear(n_feature, n_hidden) # 输入层
self.hiddenLayer = torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_hidden) # 隐藏层
self.outLayer = torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_output) # 输出层
# 前向计算函数,定义完成后会隐式地自动生成反向传播函数
def forward(self, x):
x = F.relu(self.hiddenLayer(self.inLayer(x)))
x = self.outLayer(x)
return x
net = Net(1, 10, 1) # 初始化一个网络,1个输入层节点,10个隐藏层节点,1个输出层节点
loss_func = torch.nn.MSELoss() # 定义均方误差损失函数
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.2) # 配置网络优化器
# 将网络模型、损失函数和输入张量迁入GPU
if(torch.cuda.is_available()):
net = net.cuda()
loss_func = loss_func.cuda()
x, y = x.cuda(), y.cuda()
# 训练模型
out = net(x)
for t in range(300):
out = net(x) # 将数据输入网络,得到输出
loss = loss_func(out, y) # 得到损失
optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度初始化
loss.backward() # 反向传播
optimizer.step() # 对网络进行优化
# 可视化
plt.scatter(x.data.cpu().numpy(), y.data.cpu().numpy())
plt.plot(x.data.cpu().numpy(), out.data.cpu().numpy(), 'r-', lw=5)
plt.show()
4.3. 多分类神经网络
import numpy as np
import sys
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.utils.data as Data
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
sys.path.append('./')
# 构造一个简单的神经网络
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_feature, n_hidden, n_output):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.inLayer = torch.nn.Linear(n_feature, n_hidden) # 输入层
self.hiddenLayer = torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_hidden) # 隐藏层
self.outLayer = torch.nn.Linear(n_hidden, n_output) # 输出层
# 前向计算函数,定义完成后会隐式地自动生成反向传播函数
def forward(self, x):
x = self.inLayer(x)
x = F.relu(self.hiddenLayer(x))
x = self.outLayer(x)
return x
# 读取本地数据文件
def loadData(path):
# delimiter用于设置分隔符,如果是CSV文件那么 delimiter=','
dataset_df = np.loadtxt(path, dtype=int, delimiter=' ')
return dataset_df
def show_curve(ys, title):
'''
画图
:param ys: 损失或F1值数据
:param title: 标题
:return:
'''
x = np.array(range(len(ys)))
y = np.array(ys)
plt.plot(x, y, c='b')
plt.axis()
plt.title('{} curve'.format(title))
plt.xlabel('epoch')
plt.ylabel('{}'.format(title))
plt.show()
plt.savefig(fname= title + ".png", dpi=600)
plt.savefig(fname=title + ".png")
plt.clf()
def fit(model, loss_func, data_loader, test_data_loader, num_epochs, optimizer):
"""
进行训练和测试,训练结束后显示损失和准确曲线,并保存模型
参数:
model: CNN 网络
num_epochs: 训练epochs数量
optimizer: 损失函数优化器
"""
losses = []
f1s = []
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
print('Epoch {}/{}:'.format(epoch + 1, num_epochs))
# 训练
loss = train(model, data_loader, loss_func, optimizer)
losses.append(loss)
# 验证
# 加载模型
# model = torch.load('./my_net.pth')
F1 = evaluate(model, test_data_loader)
f1s.append(F1)
print("------ Epoch END ------")
# 损失函数曲线和准确率曲线
show_curve(losses, "train loss")
show_curve(f1s, "validation F1")
def train(model, train_loader, loss_func, optimizer):
"""
训练模块
model: CNN 网络
train_loader: 训练数据的Dataloader
loss_func: 损失函数
device: 训练所用的设备
"""
total_loss = 0
model.train() # 切换至训练模式
# 批次训练
for i, (data_tensor, labels) in enumerate(train_loader):
# 前向传播
outputs = model(data_tensor)
loss = loss_func(outputs, labels)
# 反向传播和优化
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward(retain_graph=True)
optimizer.step()
total_loss += loss.item()
# 输出总loss
print("Train Loss: {:.4f}".format(total_loss))
return total_loss
def evaluate(model, test_data_loader):
"""
测试模块,这里使用test代替validation
model: CNN 网络
val_loader: 验证集的Dataloader
device: 训练所用的设备
return:准确率
"""
# # 切换至评估模式
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
TP = 0 # 预测正确的正样本(1->1)
FP = 0 # 预测错误的正样本(0->1)
FN = 0 # 预测错误的负样本(1->0)
for i, (data_tensor, labels) in enumerate(test_data_loader):
outputs = model(data_tensor)
# 选取最大输出值的类别进行分类
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, dim=1)
# 根据几个类别的输出值赋予相对应的概率,然后根据概率值进行分类
# _ = F.softmax(outputs.data, dim=1)
# predicted = Categorical(_).sample()
# 输出神经网络的预测值与实际label,比较预测结果
# print(str(i+1) + " Predicted: " + str(predicted))
# print(str(i+1) + " Label: " + str(labels))
for j in range(len(predicted)):
if (labels[j] == 1) and (predicted[j] == labels[j]):
TP += 1
if (labels[j] == 1) and (predicted[j] != labels[j]):
FN += 1
if (labels[j] == 0) and (predicted[j] != labels[j]):
FP += 1
if (TP + FP) == 0: # 精确率
precision = 0
else:
precision = TP / (TP + FP)
if (TP + FN) == 0: # 召回率
recall = 0
else:
recall = TP / (TP + FN)
if (precision + recall) == 0: # F1
F1 = 0
else:
F1 = (2 * precision * recall) / (precision + recall)
print('Precision on Test Set: {:.4f} %'.format(100 * precision))
print('Recall on Test Set: {:.4f} %'.format(100 * recall))
print('F1 on Test Set: {:.4f} %'.format(100 * F1))
return F1
if __name__ == "__main__":
# ------ 构造训练数据 ------ #
n_data = torch.ones(1000, 2) # 1000行2列的矩阵,即1000个二维坐标点
x0 = torch.normal(3 * n_data, 1) # 给原二维坐标点加正太扰动,x0在第一象限
x1 = torch.normal(-3 * n_data, 1) # 给原二维坐标点加正太扰动,x1在第三象限
x = x0 + x1 # 拼接数据
# 构造label,标记为y0=0,y1=1两类标签
y0 = torch.zeros(1000) # 1000个0
y1 = torch.ones(1000) # 1000个1
y = y0 + y1 # 拼接数据
# ------ 将数据载入DataLoader ------ #
x_tensor = torch.Tensor(x).type(torch.float)
y_tensor = torch.Tensor(y).type(torch.long) # label不能是浮点数
torch_dataset = Data.TensorDataset(x_tensor, y_tensor)
data_loader = Data.DataLoader( # 训练数据
dataset=torch_dataset,
batch_size=32, # 从torch_dataset中每次抽出batch size个样本
shuffle=True # 随机排序
)
# 构建测试数据加载器(data+label)
torch_test_dataset = Data.TensorDataset(x_tensor, y_tensor)
test_data_loader = Data.DataLoader( # 测试数据
dataset=torch_dataset,
batch_size=len(torch_test_dataset), # 从torch_dataset中每次抽出全部样本
shuffle=False # 不随机排序
)
# ------ 网络参数定义 ------ #
# 输入数据的维度即输入层的维度,这里是2,因为坐标点是二维的
input_layer_size = len(x[0])
# 初始化一个网络,input_layer_size个输入层节点,256个隐藏层节点,
# 2个输出层节点(因为是2分类任务,n个分类输出层节点个数就是n)
CNN_model = Net(input_layer_size, 256, 2)
loss_func = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 损失函数,这里是交叉熵损失,可以换用其他的损失函数
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(CNN_model.parameters(), lr=0.01, momentum=0.9) # 配置网络优化器
# 训练设备,有GPU就用GPU,没就用CPU
if (torch.cuda.is_available()):
print("Using CUDA")
mgcnn = CNN_model.cuda()
loss_func = loss_func.cuda()
x_tensor = x_tensor.cuda()
y_tensor = y_tensor.cuda()
# 开始训练
epochs = 100 # 训练轮数
fit(CNN_model, loss_func, data_loader, test_data_loader, epochs, optimizer)
torch.save(CNN_model, './my_net.pth') # 保存模型




























 4802
4802

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










