逻辑回归(logistic regression)可以用来进行分类预测,一般进行两个类别的预测,因为逻辑回归预测输出仅为0和1.
逻辑回归也可以预测多个分类。可以使用如下技巧:
1)假设类别K个
2)将数据集中类别i(i<=k)对应的标签lable标记为1,其余类别标记为0,使用逻辑回归训练出一组对应参数theta值
3)使用2,重复k次,训练处k组theta。预测时,分别使用k组theta预测数据x,可出k个预测结果,选出最大预测值对应的那组theta
4)选出3中得到的theta对应的类别i,so,i就是预测出的类别。
下面使用逻辑回归学习算法预测10个数字,数字使用图片表示,每张图片由20*20个像素组成,代表一个数字。一共有5000个数字,所以在文件ex3data1.mat中有5000*400这样一个矩阵,5000代表5000个数据,400代表每个数据的20*20个像素。ex3data1.mat中还有一个长度为5000的向量,是对应5000个数据的标签,也就是该行数据代表的数字。
好,先选出100个数据,使用2-D图表示看一下:
def displayData(X, theta=None):
width = 20
rows, cols = 10, 10
out = zeros(( width * rows, width * cols ))
rand_indices = random.permutation(5000)[0:rows * cols]
counter = 0
for y in range(0, rows):
for x in range(0, cols):
start_x = x * width
start_y = y * width
out[start_x:start_x + width, start_y:start_y + width] = X[rand_indices[counter]].reshape(width, width).T
counter += 1
img = scipy.misc.toimage(out)
figure = pyplot.figure()
axes = figure.add_subplot(111)
axes.imshow(img)
if theta is not None:
result_matrix = []
X_biased = c_[ones(shape(X)[0]), X]
for idx in rand_indices:
result = (argmax(theta.T.dot(X_biased[idx])) + 1) % 10
result_matrix.append(result)
result_matrix = array(result_matrix).reshape(rows, cols).transpose()
print result_matrix
pyplot.show() mat = scipy.io.loadmat("ex3data1.mat")
X, y = mat['X'], mat['y']
displayData(X)
显示效果:
下面一步一步实现logistic regression:
1)写sigmoid函数(详细解释看http://blog.csdn.net/bdss58/article/details/41983463):
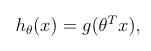
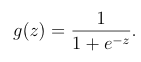
def sigmoid(z):
return 1.0 / (1.0 + exp(-z))2)计算代价函数:

def computeCost(theta, X, y, lamda):
m = shape(X)[0]
hypo = sigmoid(X.dot(theta))
term1 = log(hypo).dot(-y)
term2 = log(1.0 - hypo).dot(1 - y)
left_hand = (term1 - term2) / m
right_hand = theta.T.dot(theta) * lamda / (2 * m)
return left_hand + right_hand
3) 计算梯度:

def gradientCost(theta, X, y, lamda):
m = shape(X)[0]
grad = X.T.dot(sigmoid(X.dot(theta)) - y) / m
grad[1:] = grad[1:] + ( (theta[1:] * lamda ) / m )
return grad
4)训练出K组theta,这里有10个数字,所以k=10:
def oneVsAll(X, y, num_classes, lamda):
m, n = shape(X)
X = c_[ones((m, 1)), X]
all_theta = zeros((n + 1, num_classes))
for k in range(0, num_classes):
theta = zeros(( n + 1, 1 )).reshape(-1)
temp_y = ((y == (k + 1)) + 0).reshape(-1)
result = scipy.optimize.fmin_cg(computeCost, fprime=gradientCost, x0=theta, \
args=(X, temp_y, lamda), maxiter=50, disp=False, full_output=True)
all_theta[:, k] = result[0]
print "%d Cost: %.5f" % (k + 1, result[1])
return all_theta5)预测
def predictOneVsAll(theta, X, y):
m, n = shape(X)
X = c_[ones((m, 1)), X]
correct = 0
for i in range(0, m):
prediction = argmax(theta.T.dot(X[i])) + 1
actual = y[i]
# print "prediction = %d actual = %d" % (prediction, actual)
if actual == prediction:
correct += 1
print "Accuracy: %.2f%%" % (correct * 100.0 / m )


























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








