什么是内存描述符
什么是进程?进程是正在执行的程序,是可执行程序的动态实例,它是一个承担分配系统资源的实体,但操作系统创建进程时,会为进程创建相应的内存空间,这个内存空间称为进程的地址空间,每一个进程的地址空间都是独立的!
当一个进程有了进程的地址空间,那么进程的地址空间就必须被相应的工具所管理这个工具被称为内存描述符mm_struct,它被定义在、/usr/src/kernels/include/linux/mm_types.h中,在Linux操作系统中是这样管理进程的地址空间的,如下图所示:
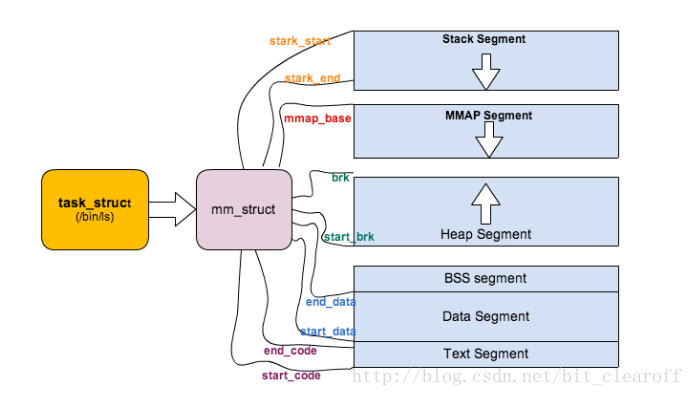
其中task_struct被称为进程描述符,当操作系统创建进程时也会一起创建它,task_struct中含有进程的相关信息,操作系统就是通过管理task_struct来达到管理进程的;
关于task_struct大家可以看看下面这篇文章:
http://blog.csdn.net/bit_clearoff/article/details/54292300
在这里,task_struct有一个mm指针指向mm_struct!
源码分析
下面我们就来解析一下mm_struct的源码:
struct mm_struct {
//mmap指向虚拟区间链表
struct vm_area_struct * mmap; /* list of VMAs */
//指向红黑树
struct rb_root mm_rb;
//指向最近的虚拟空间
struct vm_area_struct * mmap_cache; /* last find_vma result */
//
unsigned long (*get_unmapped_area) (struct file *filp,
unsigned long addr, unsigned long len,
unsigned long pgoff, unsigned long flags);
void (*unmap_area) (struct mm_struct *mm, unsigned long addr);
unsigned long mmap_base; /* base of mmap area */
unsigned long task_size; /* size of task vm space */
unsigned long cached_hole_size; /* if non-zero, the largest hole below free_area_cache */
unsigned long free_area_cache; /* first hole of size cached_hole_size or larger */
//指向进程的页目录
pgd_t * pgd;
//空间中有多少用户
atomic_t mm_users; /* How many users with user space? */
//引用计数;描述有多少指针指向当前的mm_struct
atomic_t mm_count; /* How many references to "struct mm_struct" (users count as 1) */
//虚拟区间的个数
int map_count; /* number of VMAs */
struct rw_semaphore mmap_sem;
//保护任务页表
spinlock_t page_table_lock; /* Protects page tables and some counters */
//所有mm的链表
struct list_head mmlist; /* List of maybe swapped mm's. These are globally strung
* together off init_mm.mmlist, and are protected
* by mmlist_lock
*/
/* Special counters, in some configurations protected by the
* page_table_lock, in other configurations by being atomic.
*/
mm_counter_t _file_rss;
mm_counter_t _anon_rss;
unsigned long hiwater_rss; /* High-watermark of RSS usage */
unsigned long hiwater_vm; /* High-water virtual memory usage */
unsigned long total_vm, locked_vm, shared_vm, exec_vm;
unsigned long stack_vm, reserved_vm, def_flags, nr_ptes;
//start_code:代码段的起始地址
//end_code:代码段的结束地址
//start_data:数据段起始地址
//end_data:数据段结束地址
unsigned long start_code, end_code, start_data, end_data;
//start_brk:堆的起始地址
//brk:堆的结束地址
//start_stack:栈的起始地址
unsigned long start_brk, brk, start_stack;
//arg_start,arg_end:参数段的起始和结束地址
//env_start,env_end:环境段的起始和结束地址
unsigned long arg_start, arg_end, env_start, env_end;
unsigned long saved_auxv[AT_VECTOR_SIZE]; /* for /proc/PID/auxv */
struct linux_binfmt *binfmt;
cpumask_t cpu_vm_mask;
/* Architecture-specific MM context */
mm_context_t context;
/* Swap token stuff */
/*
* Last value of global fault stamp as seen by this process.
* In other words, this value gives an indication of how long
* it has been since this task got the token.
* Look at mm/thrash.c
*/
unsigned int faultstamp;
unsigned int token_priority;
unsigned int last_interval;
unsigned long flags; /* Must use atomic bitops to access the bits */
struct core_state *core_state; /* coredumping support */
#ifdef CONFIG_AIO
spinlock_t ioctx_lock;
struct hlist_head ioctx_list;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_MM_OWNER
/*
* "owner" points to a task that is regarded as the canonical
* user/owner of this mm. All of the following must be true in
* order for it to be changed:
*
* current == mm->owner
* current->mm != mm
* new_owner->mm == mm
* new_owner->alloc_lock is held
*/
struct task_struct *owner;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_PROC_FS
/* store ref to file /proc/<pid>/exe symlink points to */
struct file *exe_file;
unsigned long num_exe_file_vmas;
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_MMU_NOTIFIER
struct mmu_notifier_mm *mmu_notifier_mm;
#endif
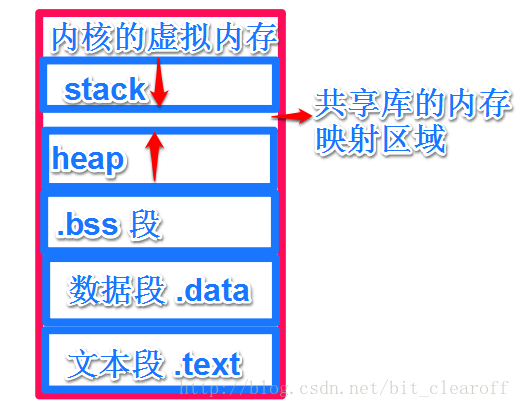
};mm_struct对进程地址空间中的虚拟空间的组织方式有下面这两种:
当虚拟区间较少时,采用单链表即mmap管理这些虚拟区间;
当虚拟区间较多时,采用红黑树管理这些虚拟区间。
并且mm_struct还把最近用到的虚拟区间放到高速缓存,由mm_struct中的mmap_cache所管理。
另外:我们还要了解一个进程中的进程地址空间由两个结构体所管理,它们分别是mm_struct和vm_ares_struct.其中mm_struct描述了整个虚拟地址空间,vm_ares_struct描述了虚拟地址空间中的一个区间;每个进程只有一个mm_struct结构,但可以有多个vm_ares_struct结构.
下面树vm_ares_struct结构的定义:
struct vm_area_struct {
struct mm_struct * vm_mm; /* The address space we belong to. */
unsigned long vm_start; /* Our start address within vm_mm. */
unsigned long vm_end; /* The first byte after our end address
within vm_mm. */
/* linked list of VM areas per task, sorted by address */
struct vm_area_struct *vm_next;
pgprot_t vm_page_prot; /* Access permissions of this VMA. */
unsigned long vm_flags; /* Flags, see mm.h. */
struct rb_node vm_rb;
/*
* For areas with an address space and backing store,
* linkage into the address_space->i_mmap prio tree, or
* linkage to the list of like vmas hanging off its node, or
* linkage of vma in the address_space->i_mmap_nonlinear list.
*/
union {
struct {
struct list_head list;
void *parent; /* aligns with prio_tree_node parent */
struct vm_area_struct *head;
} vm_set;
struct raw_prio_tree_node prio_tree_node;
} shared;
/*
* A file's MAP_PRIVATE vma can be in both i_mmap tree and anon_vma
* list, after a COW of one of the file pages. A MAP_SHARED vma
* can only be in the i_mmap tree. An anonymous MAP_PRIVATE, stack
* or brk vma (with NULL file) can only be in an anon_vma list.
*/
struct list_head anon_vma_node; /* Serialized by anon_vma->lock */
struct anon_vma *anon_vma; /* Serialized by page_table_lock */
/* Function pointers to deal with this struct. */
const struct vm_operations_struct *vm_ops;
/* Information about our backing store: */
unsigned long vm_pgoff; /* Offset (within vm_file) in PAGE_SIZE
units, *not* PAGE_CACHE_SIZE */
struct file * vm_file; /* File we map to (can be NULL). */
void * vm_private_data; /* was vm_pte (shared mem) */
unsigned long vm_truncate_count;/* truncate_count or restart_addr */
#ifndef CONFIG_MMU
struct vm_region *vm_region; /* NOMMU mapping region */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_NUMA
struct mempolicy *vm_policy; /* NUMA policy for the VMA */
#endif
};






















 2033
2033











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








