由蓝桥杯的九宫重排题改进的A算法
原文章见> http://blog.csdn.net/blue_skyrim/article/details/62418334
用启发式搜索,评价函数公式为f=g+h,g是目前为止已经发生过的耗散值,h是预计到目标需要的耗散值,这里我是与结果位置不符的数字越多,h就越大,每次搜索只需搜索评价函数最小的九宫格状态即可
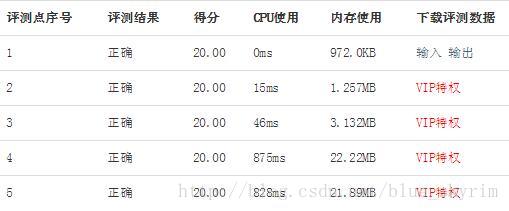
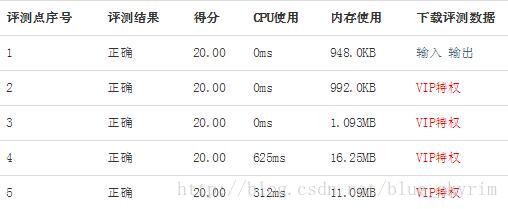
对比之前的广搜,效率明显有很大提升
bfs:
启发式搜索:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cstdio>
#include <set>
#include <math.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define MAXN 100005
#define Mod 1000000007
using namespace std;
char hajime[5][5],owali[5][5];
set<string> hsh;
struct Node
{
int x,y;
int g,h,f;
char pre;
char map[5][5];
};
struct cmp
{
bool operator()(Node a,Node b)
{
return a.f>b.f;
}
};
bool check(Node a)
{
for(int i=0; i<3; ++i)
for(int j=0; j<3; ++j)
if(a.map[i][j]!=owali[i][j])
return false;
return true;
}
bool getvis(Node a)
{
string tmp="";
for(int i=0; i<3; ++i)
for(int j=0; j<3; ++j)
{
tmp+=a.map[i][j];
}
if(hsh.find(tmp)!=hsh.end())
return false;
hsh.insert(tmp);
return true;
}
int geth(Node a)
{
int ans=0;
for(int i=0;i<3;++i)
for(int j=0;j<3;++j)
if(a.map[i][j]!=owali[i][j])
ans++;
return ans;
}
bool bfs(int x,int y)
{
Node start;
start.x=x,start.y=y;
start.pre='X';
for(int i=0; i<3; ++i)
for(int j=0; j<3; ++j)
start.map[i][j]=hajime[i][j];
start.g=0;
start.h=geth(start);
start.f=start.g+start.h;
priority_queue<Node,vector<Node>,cmp> open;
open.push(start);
while(!open.empty())
{
Node tmp=open.top(),tmp1;
open.pop();
if(check(tmp))
{
cout<<tmp.g<<endl;
return true;
}
tmp1=tmp;
if(tmp1.pre!='U'&&tmp1.x+1<3)
{
tmp1.g++;
tmp1.pre='D';
swap(tmp1.map[tmp1.x][tmp1.y],tmp1.map[tmp1.x+1][tmp1.y]);
tmp1.x++;
if(getvis(tmp1))
{
tmp1.h=geth(tmp1);
tmp1.f=tmp1.g+tmp1.h;
open.push(tmp1);
}
}
tmp1=tmp;
if(tmp1.pre!='D'&&tmp1.x-1>=0)
{
tmp1.g++;
tmp1.pre='U';
swap(tmp1.map[tmp1.x][tmp1.y],tmp1.map[tmp1.x-1][tmp1.y]);
tmp1.x--;
if(getvis(tmp1))
{
tmp1.h=geth(tmp1);
tmp1.f=tmp1.g+tmp1.h;
open.push(tmp1);
}
}
tmp1=tmp;
if(tmp1.pre!='L'&&tmp1.y+1<3)
{
tmp1.g++;
tmp1.pre='R';
swap(tmp1.map[tmp1.x][tmp1.y],tmp1.map[tmp1.x][tmp1.y+1]);
tmp1.y++;
if(getvis(tmp1))
{
tmp1.h=geth(tmp1);
tmp1.f=tmp1.g+tmp1.h;
open.push(tmp1);
}
}
tmp1=tmp;
if(tmp1.pre!='R'&&tmp1.y-1>=0)
{
tmp1.g++;
tmp1.pre='L';
swap(tmp1.map[tmp1.x][tmp1.y],tmp1.map[tmp1.x][tmp1.y-1]);
tmp1.y--;
if(getvis(tmp1))
{
tmp1.h=geth(tmp1);
tmp1.f=tmp1.g+tmp1.h;
open.push(tmp1);
}
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
char tmp[100];
scanf("%s",tmp);
int x,y;
for(int i=0; tmp[i]!='\0'; ++i)
{
hajime[i/3][i%3]=tmp[i];
if(tmp[i]=='.')
{
x=i/3;
y=i%3;
hajime[i/3][i%3]='0';
}
}
scanf("%s",tmp);
for(int i=0; tmp[i]!='\0'; ++i)
{
owali[i/3][i%3]=tmp[i];
if(tmp[i]=='.')
owali[i/3][i%3]='0';
}
if(!bfs(x,y))
cout<<-1<<endl;
return 0;
}






















 1220
1220











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








