最先进的实体对齐方法的实验研究
An Experimental Study of State-of-the-Art Entity Alignment Approaches
Xiang Zhao, Weixin Zeng, Jiuyang Tang, Wei Wang, and Fabian M. Suchanek
摘 要 摘要 摘要实体对齐 (EA) 寻找位于不同知识图谱 (KG) 中的等价实体,这是提高 KG 质量的重要步骤,因此对下游应用程序(例如,问答和推荐)具有重要意义。近年来,EA 方法迅速增加,但它们的相对性能仍不清楚,部分原因是经验评价不完整,以及比较是在不同设置(即数据集、用作输入的信息等)下进行的。在本文中,我们通过对最先进的 EA 方法进行全面评价和详细分析来填补空白。我们首先提出了一个包含所有当前方法的通用 EA 框架,然后将现有方法分为三大类。接下来,我们根据其有效性、效率和稳健性,在广泛的用例中审慎地评价这些解决方案。最后,我们构建了一个新的 EA 数据集来反映现实生活中的对齐挑战,这些挑战在很大程度上被现有文献所忽视。本研究力求清晰地展示当前 EA 方法的优缺点,以激发高质量的后续研究。
1. 简介
近年来,知识图谱 (KG) 及其应用日益增多。典型的 KG 以三元组的形式存储世界知识(即 ⟨ entity, relation, entity ⟩ \lang \text{entity, relation, entity}\rang ⟨entity, relation, entity⟩),其中实体(entity)指的是真实世界中的独特对象,而关系描述了将这些对象联系起来的关系。使用实体作为锚点,KG 中的三元组在本质上是相互关联的,因此构成了一个大的知识图谱。目前,我们有大量的 通 用 通用 通用KG(例如,DBpedia [1]、YAGO [52]、Google 的Knowledge Vault [14])和特定 领 域 领域 领域KG(例如,Medical [48] 和 Scientific KG [56])。这些 KG 已被用于增强各种下游应用,例如关键字搜索 [64]、事实检查 [30]、问答 [12] [28] 等。
在实践中,知识图谱通常由单个数据源构建,因此不太可能完全覆盖该领域 [46]。为了增加其完整性,一种流行的方法是整合来自其他 KG 的知识,这些知识可能包含额外的或补充的信息。例如,一般 KG 可能只涉及有关科学家的基本信息,而更多细节(例如个人简介和出版物列表)可以在科学领域 KG 中找到。为了巩固 KG 之间的知识,一个关键步骤是对齐不同 KG 中的等价实体,这称为 实 体 对 齐 实体对齐 实体对齐(EA) [7]、[25]。1
一般来说,当前的EA 方法主要通过假设不同 KG 中的等价实体具有相似的相邻结构,并采用表示学习方法将实体作为数据点嵌入到低维特征空间中来解决该问题。通过执行有效的(实体)嵌入,可以轻松地用数据点之间的距离来评价实体的成对差异,以确定两个实体是否匹配。
虽然该方向正在迅速发展(例如,在过去三年中发表了 20 多篇论文),但没有对这些解决方案进行系统和全面的比较。本文对最先进的 EA 方法进行经验评价,具有以下特征:
(1) 类 别 内 和 类 别 间 的 公 平 比 较 类别内和类别间的公平比较 类别内和类别间的公平比较。几乎所有最近的研究[5], [24], [38], [55], [60], [61], [62], [63], [67] 都仅限于与一部分方法进行比较。此外,不同的方法遵循不同的设置:一些仅使用 KG 结构进行对齐,而另一些还使用附加信息,一些在一轮比较中对齐 KG,而另一些则采用迭代(重新)训练策略。尽管文献中报道的这些方法的直接比较证明了解决方案的整体有效性,但更可取和更公平的做法是将这些方法分组,然后比较类别内和类别间的结果。
在这项研究中,我们对大多数最先进的方法进行横向比较,包括那些最近提出的但尚未与其他方法进行比较的方法。通过将它们分为三组,并对组内和组间评价进行详细分析,我们能够更好地定位这些方法并评价其有效性。
(2) 代 表 性 数 据 集 的 综 合 评 价 代表性数据集的综合评价 代表性数据集的综合评价。为了评价 EA 系统的性能,已经构建了几个数据集,这些数据集可以大致分为以DBP15K [53]为代表的 跨 语 言 跨语言 跨语言基准测试和以DWY100K [54] 为代表的 单 语 言 单语言 单语言基准测试。最近的一项研究 [24] 指出,以前数据集中的KG比现实生活中的要 稠 密 稠密 稠密得多,因此它创建了SRPRS数据集,其实体度数遵循 正 态 正态 正态分布。尽管有多种数据集可供选择,但现有研究仅报告他们在一个或两个特定数据集上的结果,因此难以评价它们在各种可能场景中的有效性,例如跨语言/单语言、稠密/正态、大型/中型 KG。
作为回应,本研究对包含 9 个 KG 对的所有代表性数据集(即DBP15K、DWY100K和SRPRS)进行了全面的实验评价,并在有效性、效率和稳健性方面进行了深入分析。
(3) 应 对 现 实 生 活 挑 战 的 新 数 据 集 应对现实生活挑战的新数据集 应对现实生活挑战的新数据集。对于源 KG 中的每个实体,现有的 EA 数据集在目标 KG 中仅包含一个对应实体。然而,这是一个不现实的场景。在现实生活中,一个KG 中常常包含其他 KG 不包含的实体。例如,在对齐 YAGO 4 和 IMDB 时,YAGO 4 中只有 1% 的实体与电影相关,而 YAGO 4 中其他 99% 的实体在 IMDB 中不包含匹配项。这些无法匹配的实体会增加 EA 的难度。
此外,我们观察到现有单语数据集中的不同KG 使用相同的命名约定,依赖实体名称之间字符串相似度的基线方法可以达到 100% 的准确率。然而,在现实生活中,不同 KG 中的等价实体的名称可能不相似,例如,“America”与“U.S.”。此外,KG 中的不同实体可能具有相同的名称,这对EA 构成了一个被忽视的障碍,因为无法保证源 KG 中名称为“Paris”的实体与目标 KG 中具有相同名称的实体相同——仅仅因为一个可能是法国的城市,另一个可能是德克萨斯的城市。
由于这些原因,我们认为 EA 的现有数据集过于简化了无法匹配的实体和有歧义的实体名称所面临的现实挑战。为了更好地反映这些挑战,我们提出了一个反映这些实际困难的新数据集。
贡 献 贡献 贡献。总体而言,本文既面向科学界也面向业界。这篇文章的主要贡献是:
- 据我们所知,本研究是系统和全面评价最先进的 EA 方法的首批尝试之一。这通过以下方式实现: (1) 确定现有 EA 方法的主要组成部分,并提供一个通用 EA 框架,(2)将最先进的方法分为三类,并进行详细的组内和组间评价,从而更好地定位不同的EA 解决方案, (3)在广泛的用例上检查这些方法,包括跨/单语言对齐,以及在稠密/正态、大/中规模数据上的对齐。经验结果揭示了每个解决方案的 有 效 性 有效性 有效性、 效 率 效率 效率和 稳 健 性 稳健性 稳健性。
- 我们从研究中获得的经验和见解让我们发现当前 EA 数据集的不足之处。作为补救措施,我们构建了一个新的单语数据集来反映无法匹配的实体和有歧义的实体名称的现实挑战。我们希望这个新数据集能够作为评价 EA 系统的更好基准。
组 织 组织 组织。第 2 节形式化了 EA 任务,并定义了本研究的范围。第 3 节介绍了一个包含最新 EA 方法的一般框架。第 4 节详细阐述了分类、实验设置、结果和讨论。第 5 节提供了一个新的数据集和进一步的实验,第 6 节总结了这篇文章。
2 预备知识
本节正式定义了本研究的任务和范围。
2.1 任务定义
A KG $G = (E, R, T) 是 一 个 有 向 图 , 包 括 一 组 实 体 是一个有向图,包括一组实体 是一个有向图,包括一组实体E$ 、关系 R R R和三元组 T ⊆ E × R × E T \subseteq E \times R \times E T⊆E×R×E 。三元组 ( h , r , t ) ∈ T ( h, r, t )\in T (h,r,t)∈T表示头实体 h h h通过关系 r r r连接到尾实体 t t t。每个实体被分配了一个唯一的标识符,例如DBpedia中的http://dbpedia.org/resource/Spain。
给定一个源 KG G 1 = ( E 1 , R 1 , T 1 ) G_1 = ( E_1 , R_1 , T_1 ) G1=(E1,R1,T1),目标 KG $G_2 = ( E_2 , R_2 , T_2 ) , 种 子 实 体 对 ( 训 练 集 ) , 即 ,种子实体对(训练集),即 ,种子实体对(训练集),即S = {( u, v )| u \in E_1, v_2\in E_2, u \leftrightarrow v }$ ,其中 ↔ \leftrightarrow ↔表示等价(即 u u u和 v v v指代相同的现实世界对象),EA 的任务可以定义为在测试集中发现等价的实体对。
例 1。图 1 显示了关于导演 Alfonso Cuar o ˊ n \text{Alfonso Cuar}\acute{\text o}\text n Alfonso Cuaroˊn 的部分英语 KG (KG EN _\text{EN} EN ) 和部分西班牙语 KG (KG ES _\text{ES} ES) 。给定种子实体对,即来自 KG EN _\text{EN} EN的 Mexico \verb+Mexico+ Mexico和来自 KG ES _\text{ES} ES的 Mexico \verb+Mexico+ Mexico,EA 旨在在测试集中找到等价的实体对,例如,返回KG ES _\text{ES} ES中的 Roma(ciudad) \verb+Roma(ciudad)+ Roma(ciudad) 作为KG EN _\text{EN} EN中的源实体 Roma(city) \verb+Roma(city)+ Roma(city)对应的目标实体。
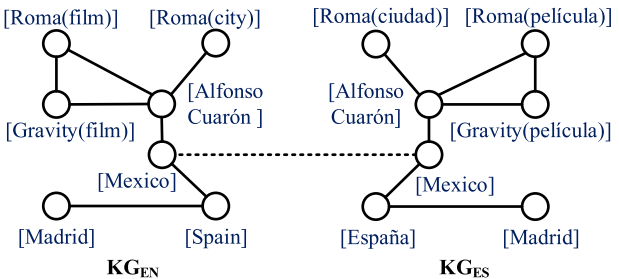
图 1. EA 示例。实体标识符放在方括号中。为清楚起见,省略了实体标识符和完整关系标识符的前缀,种子实体对由虚线连接。
2.2 范围及相关工作
虽然 EA 问题是几年前提出的,但该问题的更通用版本——识别来自不同数据源的同一现实世界实体的实体记录——已经由不同社区从不同角度进行了研究,包括实体消解 (ER) [15]、[18]、[45]、实体匹配 [13]、[42] ,记录链接 [8]、[34]、去重 [16]、实例/本体匹配 [20]、[35]、[49]、[50]、[51]、链接发现 [43]、[44],实体链接/实体消歧[11]、[29]。接下来,我们描述这项实验研究的相关工作和范围。
实 体 链 接 实体链接 实体链接。实体链接(EL)的任务也称为实体消歧。它关注识别自然语言文本中的实体提及(mention),并将它们映射到给定参考目录(大多数情况下为 KG)中的实体。例如,目标是将某些自然语言文本中的字符串“Rome”识别为实体提及,并找出它是指意大利的首都还是名字为“Rome”的众多电影中的一部。现有方法 [21]、[22]、[29]、[36]、[68] 利用大量信息,包括实体提及周围的单词、某些目标实体的先验概率、已经消歧的实体提及、维基百科等背景知识,以消除链接目标的歧义。但是,大多数信息在我们的 KG 对齐场景中不可用(例如,实体描述的嵌入,或着给定提及的实体链接的先验分布)。此外,EL 涉及自然语言文本和 KG 之间的映射。相比之下,我们的工作研究了两个 KG 之间的实体映射。








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 1725
1725











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








