#include< algorithm >是C++的标准模版库(STL)中最重要的头文件之一,提供了大量基于迭代器的非成员模板函数。以下将介绍几个常用的库函数:
一、max(),min()和swap()
- max(x,y) //返回两个元素中值最大的元素
- min(x,y) //返回两个元素中值最小的元素
- swap(x,y) //用来交换x和y的值
二、reverse()
反转排序指定范围中的元素,reverse(a,b) 可以将数组指针在[a,b)之间的元素或容器的迭代器在[a,ib)范围内的元素进行反转。
程序示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[10]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
reverse(a,a+6);
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
string str="abcdefgh";
reverse(str.begin()+2,str.begin()+6);
for(int j=0;j<str.length();j++){
cout<<str[j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:

三、fill()
fill() 可以把数组或容器中的某一段区间赋为某个相同的值。
程序示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
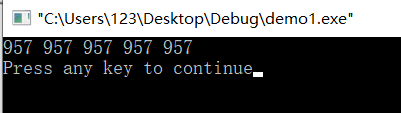
int a[5];
fill(a,a+5,957);
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
四 、 sort()
排序函数,默认为递增排序。
如果需要递减排序,需要增加一个比较函数:
bool cmp(int a,int b){
return a>b; //若a<b为递增排序
}
sort(a,a+n,cmp);
程序示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool cmp(int a,int b){
return a>b;
}
int main()
{
int i;
int a[7]={8,6,9,2,7,4,3};
cout<<"排序前数组为:";
for(i=0;i<7;i++)
{
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
sort(a,a+7);
cout<<"递增排后前数组为:";
for(i=0;i<7;i++)
{
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
sort(a,a+7,cmp);
cout<<"递减排后前数组为:";
for(i=0;i<7;i++)
{
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:

五、next_permutation()
返回给定范围中的元素组成的下一个按字典序的排列,即给出一个序列在全排列中的下一个序列。
程序示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
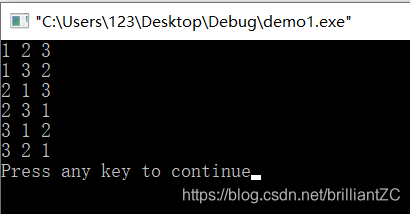
int a[5]={1,2,3};
do{
cout<<a[0]<<" "<<a[1]<<" "<<a[2]<<endl;
}while(next_permutation(a,a+3));
return 0;
}
运行结果:
六、lower_bound()和upper_bound()
lower_bound 和 upper_bound()需要用在一个有序数组或容器中。
lower_bound(first,last,val) 用来寻找在数组或容器的[first,last)范围内第一个值大于等于val元素的位置,如果是数组,返回该位置的指针;若果是容器,返回该位置的迭代器
upper_bound(first,last,val) 用来寻找在数组或容器的[first,last)范围内第一个值大于val元素的位置,如果是数组,返回该位置的指针;若果是容器,返回该位置的迭代器
程序示例:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[10]={1,2,2,3,3,4,4,5,6,7};
int *lowerPos=lower_bound(a,a+10,3);
int *upperPos=upper_bound(a,a+10,3);
cout<<"lower_bound(a,a+10,3)="<<lowerPos-a<<endl;
cout<<"upper_bound(a,a+10,3)="<<upperPos-a<<endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:

























 2327
2327

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








