
ECCV-2018
code pytorch:https://github.com/princeton-vl/CornerNet
跑自己的 dataset:CornerNet训练不完全指南
文章目录
1 Background and Motivation
anchor-based(原文中是 anchor box) method 的 drawback 如下:
- 需要大量的框,this creates a huge imbalance between positive and negative anchor boxes and slows down training
- introduces many hyper-parameters and design choices(numbers,ratio,scale)去设计 anchor
作者提出 anchor-free 的方法,通过预测 top-left corner 和 bottom-right corner heat-map,配合 embedding vector(点 group 成框,同一框框的左上右下embedding distance is small),确定 bounding box。

作者 hypothesize two reasons why detecting corners would work better than bounding box centers or proposals.
- 定位 centers 依赖于 4 sides,而 corner only with 2 sides,且 corner pooling 还引入了 prior knowledge about the definition of corners.
- just need O ( w h ) O(wh) O(wh) corners to represent O ( w 2 h 2 ) O(w^2h^2) O(w2h2) (两个点组合起来)possible anchor boxes.
其实关于作者说的这两点,感觉理解起来不是那么通顺!!!
2 Advantages / Contributions
- first to formulate the task of object detection as a task of detecting and grouping corners simultaneously
- corner pooling
3 Method




从 resnet 的 bottleneck 改变而来
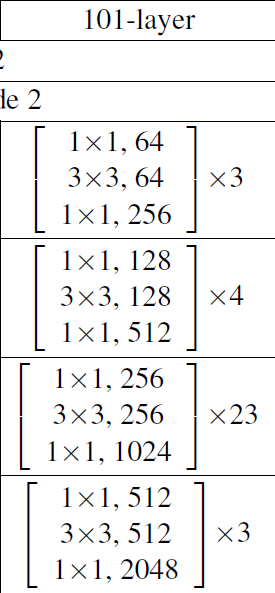
核心部分
- Heatmaps(binary mask):预测左上和右下两个点,H×W×C(categories),也就是 class-specifically
- Embeddings(1 dimension):embedding vector,group 点成框
- Offsets:refine the bounding box,让 location 更准确
- Corner Pooling
3.1 Backbone
采用的是 Hourglass Network,depth,104,堆了两个 hourglass,输入 511×511,输出 128×128,channel 变化(256,384,384,384,512),大致如下所示

图片来源:https://blog.csdn.net/u013841196/article/details/81048237
3.2 Corner Pooling

这个图可以看出,点可不是那么好 location 的哈,因为并不在 object 上(是不是间接反应了 bounding box 的局限性,哈哈哈),作者提出 corner pooling 来处理这个!
具体如下:

朝着箭头的方向,取max,然后相加

公式化表示如下

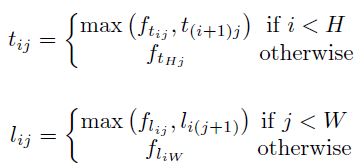
- f t f_t ft、 f l f_l fl be the feature maps that are inputs to the top-left corner pooling layer
- f t i j f_{t_{ij}} ftij、 f l i j f_{l_{ij}} flij 是 f t f_t ft、 f l f_l fl 上 location ( i , j ) (i,j) (i,j) 对应的 vectors
- t i j t_{ij} tij 是 f t f_t ft 中 ( i , j ) (i,j) (i,j) 到 ( H , j ) (H,j) (H,j) max pooling 后的结果
- l i j l_{ij} lij 是 f l f_l fl 中 ( i , j ) (i,j) (i,j) 到 ( i , W ) (i,W) (i,W) max pooling 后的结果
bottom-right 如下右所示

实话说,这么做为什么能很好的捕抓到 corner,不是特别理解!!!
3.3 Loss
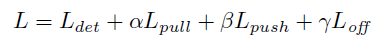
α
\alpha
α、
β
\beta
β 设置为 0.1,
γ
\gamma
γ 设置为 1
1) L d e t L_{det} Ldet
detection 的分类 loss 是改进版的 focal loss,我们先来回顾下 focal loss,参考【Focal Loss】《Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection》

画重点,well-classified examples is down-weighted,也就是削减了简单样本的权重!
这篇论文作者的分类 loss 改进如下:
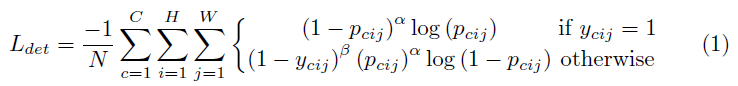
- p c i j p_{cij} pcij is the score at location ( i , j ) (i,j) (i,j) for class c c c in the predicted heatmaps
- y c i j y_{cij} ycij is ground truth heatmap augmented with the unnormalized Gaussian,这是什么意思呢?看下面的说明:
heatmap 是 binary mask,按道理哈,gt 也就两个点,一个框,其它都是 negative,作者给 gt 加了个 2D 高斯半径, σ = 1 / 3 \sigma = 1/3 σ=1/3,叫做 penalty reduction,预测的点正好对应 gt 的话(圆中心),penalty reduction y c i j y_{cij} ycij 最大, 1 − y c i j 1-y_{cij} 1−ycij 也就是 penalty 最小,离 gt 越远(离圆心越远),penalty reduction y c i j y_{cij} ycij 越小, 1 − y c i j 1-y_{cij} 1−ycij 越大。

为什么这么设计呢?请看下图

gt bounding box 是红色的框框,可以看出,gt corner 的一定范围内(橘色圆圈)group 的 bounding box 也和 gt bounding box 有很高的 IoU,所以作者才这么设计 loss!像是 cross entropy + focal loss,然后乘了个 penalty 系数
(
1
−
y
c
i
j
)
β
(1-y_{cij})^{\beta}
(1−ycij)β.
注意这里的 y c i j = 1 y_{cij} = 1 ycij=1 不是一个点,而是上面的橘色圆圈内!作者圈圈大小的设计是保证与 GT 的 IoU at least 0.7
2)
L
p
u
l
l
L_{pull}
Lpull and
L
p
u
s
h
L_{push}
Lpush
拉近同一目标两个点的距离,拉远不同目标两个点的距离,类似于类内最小,类间最大(参考目标检测论文阅读:CornerNet 的解释)!!!
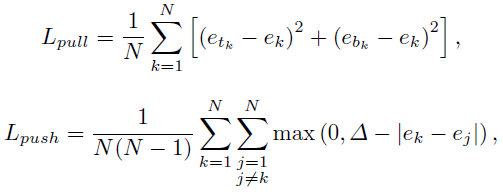
- pull loss L p u l l L_{pull} Lpull to group the corner in the same object
- push loss L p u s h L_{push} Lpush to separate the corner in the different object
- N 是 corner 的数量
- e t k e_{t_{k}} etk 是第 k k k 个 top-left corner 的 embedding(1 dimension)
- e b k e_{b_{k}} ebk 是第 k k k 个 bottom-right corner 的 embedding(1 dimension)
- e k e_k ek 是 the average of e t k e_{t_{k}} etk and e b k e_{b_{k}} ebk
- Δ = 1 \Delta = 1 Δ=1
L
p
u
s
h
L_{push}
Lpush 采用的是 hinge loss,也即,
e
k
e_k
ek 与
e
j
e_j
ej 越接近,损失越大,越大越小(最小是0)

3) L o f f L_{off} Loff
这个 loss 是更加精确的定位的,gt 的 offset 如下,显然
x
k
n
\frac{x_k}{n}
nxk 才是更准确的,而
⌊
x
k
n
⌋
\left \lfloor \frac{x_k}{n} \right \rfloor
⌊nxk⌋ 则是从原图 mapping 到 feature map 上的结果!
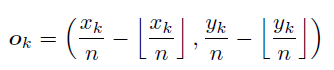
采用的是 smooth L1 loss,来学 offset
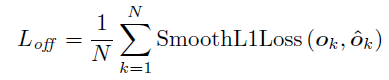
x
k
x_k
xk and
y
k
y_k
yk are the
x
x
x and
y
y
y coordinate for corner
k
k
k
4 Experiments
4.1 Datasets
MS COCO
- train+val:135k
- mini-val:5k
- test-dev:20k
4.2 Ablation Study
1)Corner Pooling
with 和 without corner pooling

可以看出,中等目标和大目标的提升比较明显。
This is expected because the topmost, bottommost, leftmost, rightmost boundaries of medium and large objects are likely to be further away from the corner locations.
2)Reducing penalty to negative locations

we see that the penalty reduction especially benefits medium and large objects.
3)Error Analysis
这个实验好骚

把 heatmaps 替换成 gt,把 heatmaps 和 offsets 都替换成 gt!效果太……恐怖!!!说明 heatmaps 和 offsets 还有很大的提升空间!
4.3 Comparisons with state-of-the-art detectors

Cascade RCNN 挺猛的哈,还有 SNIP

demo,top-left,bottom-right
5 Conclusion(owns)
- backbone 有缘的话画个草图出来,看下 hourglass 的论文
- 可以研究下 embedding,以及学习下人体姿态检测那里边的 group 点的现状
- corner pooling 如何理解呢?
下面节选一些看到不错的博客!
作者:Makalo.W
来源:CSDN
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43688730/article/details/84034604
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请附上博文链接!
Corner Pooling 的作用:作者在论文里面说,由于预测的那两个点,并不是在‘’内容‘’上面,而是在‘’内容‘’旁边,例如下图,橘色的点并不是打在人物身上,而是打在了人物旁边,但是这个地方所提供的信息并没有作用,而真正有作用的是人物,所以需要通过corner pool的方式将人物上的信息,转移到旁边来,以便模型在预测点的时候能更准确。


























 536
536











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








