最短路径算法是一种在图中查找两个节点之间最短路径的算法。
它可以应用于很多领域,比如网络路由、地理信息系统、交通规划等。
最短路径算法可分为单源最短路径算法(求一个顶点到其他所有顶点的最短路径)
和多源最短路径算法(求任意两个顶点之间的最短路径)。
Prim算法和Dijkstra算法都是解决图中最短路径问题的算法,但是它们的约束条件不同。
Prim算法是一种用于寻找加权无向连通图中的最小生成树的贪心算法。它从任意一个节点出发,然后每次选取一条边,将其加入到当前生成树的集合中,并确保加入后生成的树仍然是一个连通图,直到包含所有节点为止。
Dijkstra算法是一种单源最短路径算法。它从一个源节点出发,计算该节点到图中其他节点的最短路径,具体算法流程是:对于图中的每一个节点,维护一个到该节点的已知最短路径和一个是否确定了该节点的最短路径(即已经找到了从起点到该节点的最短路径)的标记。然后在所有未确定最短路径的节点中,选择距离起点最近的一个节点,以该节点为中转点更新起点到所有相邻节点的距离(如果通过该节点到相邻节点的距离比现有距离更短,则更新距离,否则不变)。
虽然两种算法都与图中节点的连通性有关,但Prim算法更关注于建立图中的一棵最小生成树,而Dijkstra算法更关注于单个节点到其他节点的最短路径。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define MAX_DISTANCE 10000
/**
* The structure of a Net.
*/
typedef struct Net {
int** weights;
int numNodes;
} *NetPtr;
/**
* Initialize a Net.
*/
NetPtr initNet(int paraSize, int** paraData) {
int i, j;
NetPtr resultPtr = (NetPtr)malloc(sizeof(struct Net));
resultPtr->numNodes = paraSize;
//Two stage space allocation.
resultPtr->weights = (int**)malloc(paraSize * sizeof(int*));
for (i = 0; i < paraSize; i++) {
resultPtr->weights[i] = (int*)malloc(paraSize * sizeof(int));
for (j = 0; j < paraSize; j++) {
resultPtr->weights[i][j] = paraData[i][j];
}
}
return resultPtr;
}
/**
* The Prim algorithm for spanning tree, or the Dijkstra algorithm for nearest path.
* @param paraAlgorithm 0 for Dijkstra, 1 for Prim
* @return The total cost of the tree.
*/
int dijkstraOrPrim(NetPtr paraPtr, int paraAlgorithm) {
int i, j, minDistance, tempBestNode, resultCost;
int source = 0;
int numNodes = paraPtr->numNodes;
int* distanceArray = (int*)malloc(numNodes * sizeof(int));
int* parentArray = (int*)malloc(numNodes * sizeof(int));
//Essentially boolean
int* visitedArray = (int*)malloc(numNodes * sizeof(int));
// Step 1. Initialize. Any node can be the source.
for (i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
distanceArray[i] = paraPtr->weights[source][i];
parentArray[i] = source;
visitedArray[i] = 0;
}
distanceArray[source] = 0;
parentArray[source] = -1;
visitedArray[source] = 1;
// Step 2. Main loops.
tempBestNode = -1;
for (i = 0; i < numNodes - 1; i++) {
// Step 2.1 Find out the best next node.
minDistance = MAX_DISTANCE;
for (j = 0; j < numNodes; j++) {
// This node is visited.
if (visitedArray[j]) {
continue;
}
if (minDistance > distanceArray[j]) {
minDistance = distanceArray[j];
tempBestNode = j;
}
}
visitedArray[tempBestNode] = 1;
// Step 2.2 Prepare for the next round.
for (j = 0; j < numNodes; j++) {
// This node is visited.
if (visitedArray[j]) {
continue;
}
// This node cannot be reached.
if (paraPtr->weights[tempBestNode][j] >= MAX_DISTANCE) {
continue;
}
// Attention: the difference between Dijkstra and Prim algorithms.
if (paraAlgorithm == 0) {
if (distanceArray[j] > distanceArray[tempBestNode] + paraPtr->weights[tempBestNode][j]) {
// Change the distance.
distanceArray[j] = distanceArray[tempBestNode] + paraPtr->weights[tempBestNode][j];
// Change the parent.
parentArray[j] = tempBestNode;
}
}
else {
if (distanceArray[j] > paraPtr->weights[tempBestNode][j]) {
// Change the distance.
distanceArray[j] = paraPtr->weights[tempBestNode][j];
// Change the parent.
parentArray[j] = tempBestNode;
}
}
}
}
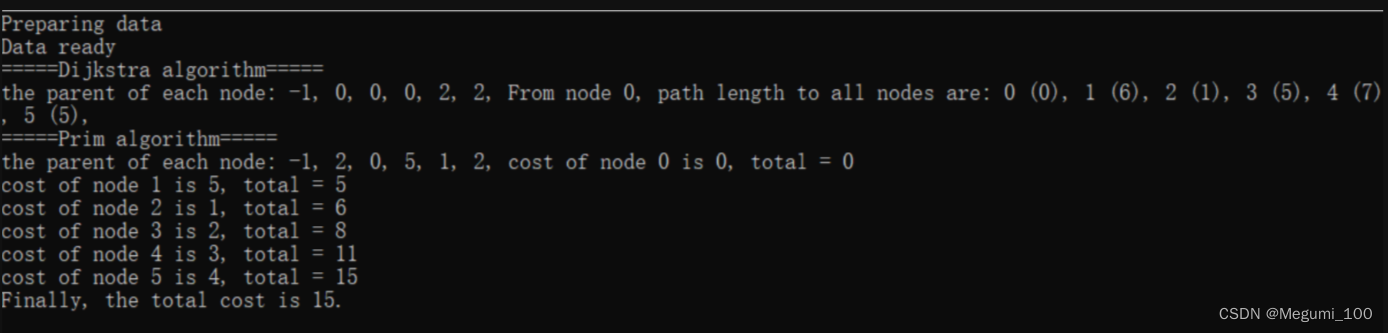
printf("the parent of each node: ");
for (i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
printf("%d, ", parentArray[i]);
}
if (paraAlgorithm == 0) {
printf("From node 0, path length to all nodes are: ");
for (i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
printf("%d (%d), ", i, distanceArray[i]);
}
}
else {
resultCost = 0;
for (i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
resultCost += distanceArray[i];
printf("cost of node %d is %d, total = %d\r\n", i, distanceArray[i], resultCost);
}
printf("Finally, the total cost is %d.\r\n ", resultCost);
}
// Step 3. Output for debug.
printf("\r\n");
return resultCost;
}
/**
* Construct a sample net.
* Revised from testGraphTranverse().
*/
NetPtr constructSampleNet() {
int i, j;
int myGraph[6][6] = {
{0, 6, 1, 5, 0, 0},
{6, 0, 5, 0, 3, 0},
{1, 5, 0, 5, 6, 4},
{5, 0, 5, 0, 0, 2},
{0, 3, 6, 0, 0, 6},
{0, 0, 4, 2, 6, 0} };
int** tempPtr;
int numNodes = 6;
printf("Preparing data\r\n");
tempPtr = (int**)malloc(numNodes * sizeof(int*));
for (i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
tempPtr[i] = (int*)malloc(numNodes * sizeof(int));
}//Of for i
for (i = 0; i < numNodes; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < numNodes; j++) {
if (myGraph[i][j] == 0) {
tempPtr[i][j] = MAX_DISTANCE;
}
else {
tempPtr[i][j] = myGraph[i][j];
}
}
}
printf("Data ready\r\n");
NetPtr resultNetPtr = initNet(numNodes, tempPtr);
return resultNetPtr;
}
/**
* Test the Prim algorithm.
*/
void testPrim() {
NetPtr tempNetPtr = constructSampleNet();
printf("=====Dijkstra algorithm=====\r\n");
dijkstraOrPrim(tempNetPtr, 0);
printf("=====Prim algorithm=====\r\n");
dijkstraOrPrim(tempNetPtr, 1);
}
/**
* The entrance.
*/
int main() {
testPrim();
return 0;
}





















 4417
4417

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








