什么是Handle,有什么用?
Handle主要处理线程间通信。在Android的应用启动时,会创建一个主线程,主线程会创建一个
消息队列来处理各种消息。当你创建子线程时,你可以在你的子线程中拿到父线程中
创建的Handler 对象,就可以通过该对象向父线程的消息队列发送消息了。由于Android
要求在UI线程中更新界面,因此,可以通过该方法在其它线程中更新界面。
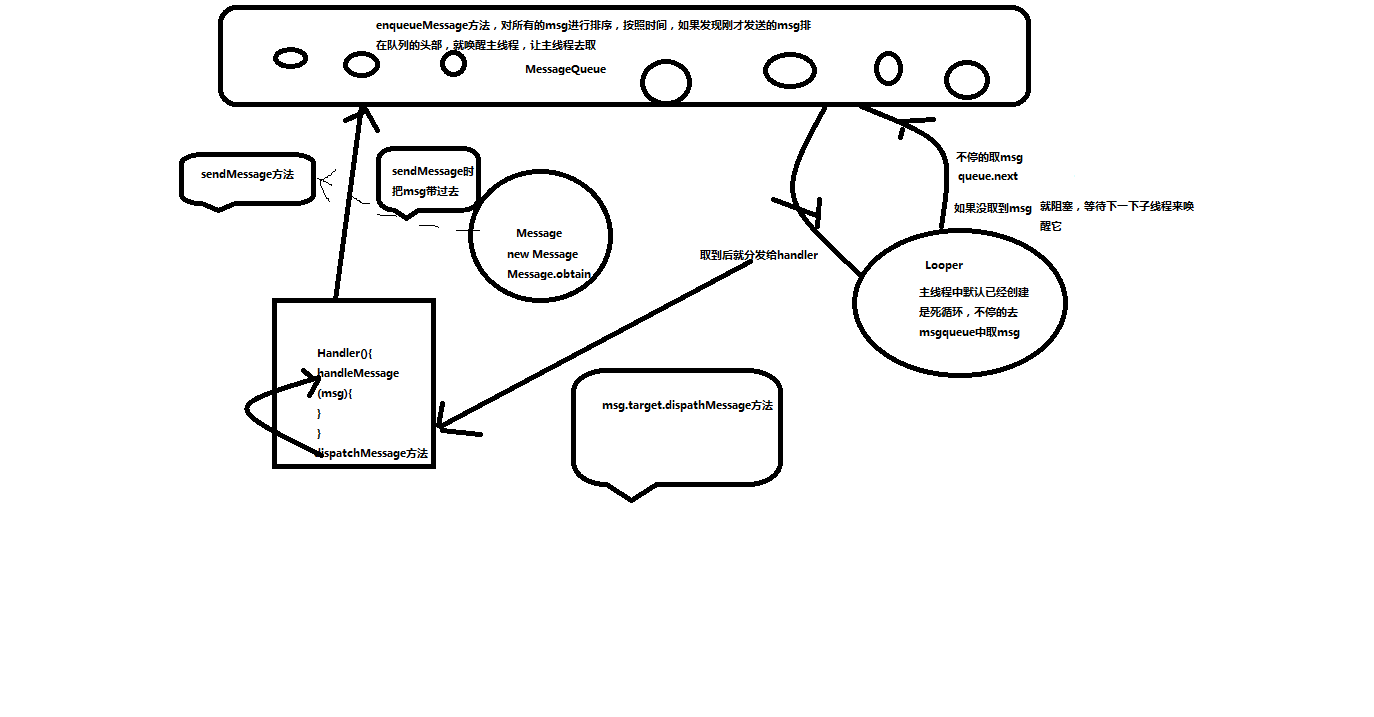
Handle的消息机制主要涉及三个核心类和一个数据结构:
Message : 消息
Message Queue:消息队列 一个数据接口。存放所有的Message,它被封装在Looper中
Looper : 一个线程可以产生一个Looper对象,由它通过死循环来管理此线程里的Message Queue
Handler : 构造Handler对象来与Looper沟通,以便push 新消息到 Message Queue里,或者
接收Looper从Message Queue 里所送来的消息。
如上三个核心类的创建与执行流程:
创建的Message的方法:
Message.obtain()//推荐这样来从消息池中获得空消息对象,而不是使用 new 。
Message msg = new Message()Handler
new Handler(){
handlerMessage(Message msg){
// 处理消息
}
}Handler的构造方法:
public Handler() {
...
// 获取looper
mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
if (mLooper == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()");
}
mQueue = mLooper.mQueue;
mCallback = null;
}主线程设置Looper,在ActivityThread类里面:
每一个线程里可含有一个 Looper 对象以及一个 Message Queue 数据结构。每个handler 对应一个线程 thread,在子线程中 handler 发送的消息会进入到 Message Queue当中去,由 looper 再来分发给 Handler 处理。
public static final void main(String[] args) {
....
// 1.主线程创建Looper
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
sMainThreadHandler = new Handler();
}
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false);
if (false) {
Looper.myLooper().setMessageLogging(new
LogPrinter(Log.DEBUG, "ActivityThread"));
}
Looper.loop();Looper:
public static final void prepare() {
if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread");
}
// 3、在主线程中设置Looper, new Looper()里面创建了一个MessageQueue
sThreadLocal.set(new Looper());//通过ThreadLocal保证了线程安全
}
//在Activity中调用的prepareMainLooper
public static final void prepareMainLooper() {
// 2、调用prepare
prepare();
setMainLooper(myLooper());
if (Process.supportsProcesses()) {
myLooper().mQueue.mQuitAllowed = false;
}
}主线程调用Looper.loop()方法,主线程就会阻塞,是一个死循环,使用管道(Pipe),是Linux中的一种进程间通信方式,使用了特殊的文件,有两个文件描述符(一个是读取,一个是写入)
应用场景;主进程拿着读取描述符等待读取,没有内容时就阻塞,另一个进程拿写入描述符去写内容,唤醒主进程,主进程拿着读取描述符读取到内容,继续执行。
Handler应用场景:Handler在主线程中创建,Looper会在死循环里等待取消息,1、没取到,就阻塞,2、一旦被子线程唤醒,取到消息,就把Message交给Handler处理。子线程用Handler去发送消息,拿写入描述符去写消息,唤醒主线程。
loop()代码如下:
public static final void loop() {
...
while (true) {
// 取消息,如果没有消息,就阻塞
Message msg = queue.next(); // might block
...
//msg.target是一个Handler
msg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);
...
}
}Handler发送消息代码
public boolean sendMessageAtTime(Message msg, long uptimeMillis)
{
....
// 把Message的target置为当前发送的Handler,以便Looper取到message后根据target把message分发给正确的Handler
//因为Message与Handler是多对一。通过Message的target这个变量保证了不会对应错
msg.target = this;
// 往队列里面添加Message
sent = queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis);
....
}MessageQueue.enqueueMessage 代码
final boolean enqueueMessage(Message msg, long when) {
...
Message p = mMessages;
if (p == null || when == 0 || when < p.when) {
// 当前发送的message需要马上被处理调,needWake唤醒状态置true
msg.next = p;
mMessages = msg;
needWake = mBlocked; // new head, might need to wake up
} else {
// 当前发送的message被排队到其他message的后面,needWake唤醒状态置false
Message prev = null;
while (p != null && p.when <= when) {
prev = p;
p = p.next;
}
msg.next = prev.next;
prev.next = msg;
needWake = false; // still waiting on head, no need to wake up
}
}
// 是否唤醒主线程
if (needWake) {
nativeWake(mPtr);
}
return true;Handler.dispatchMessage方法
public void dispatchMessage(Message msg) {
if (msg.callback != null) {
handleCallback(msg);
} else {
if (mCallback != null) {
if (mCallback.handleMessage(msg)) {
return;
}
}
// 把Message交给Handler处理
handleMessage(msg);
}
}





















 2097
2097

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








