Problem Description
Little Q’s clock is alarming! It’s time to get up now! However, after reading the time on the clock, Little Q lies down and starts sleeping again. Well, he has 5 alarms, and it’s just the first one, he can continue sleeping for a while.
Little Q’s clock uses a standard 7-segment LCD display for all digits, plus two small segments for the ”:”, and shows all times in a 24-hour format. The ”:” segments are on at all times.
Your job is to help Little Q read the time shown on his clock.
Input
The first line of the input contains an integer T(1≤T≤1440), denoting the number of test cases.
In each test case, there is an 7×21 ASCII image of the clock screen.
All digit segments are represented by two characters, and each colon segment is represented by one character. The character ”X” indicates a segment that is on while ”.” indicates anything else. See the sample input for details.
Output
For each test case, print a single line containing a string t in the format of HH:MM, where t(00:00≤t≤23:59), denoting the time shown on the clock.
Sample Input
1
.XX…XX…..XX…XX.
X..X….X……X.X..X
X..X….X.X….X.X..X
……XX…..XX…XX.
X..X.X….X….X.X..X
X..X.X………X.X..X
.XX…XX…..XX…XX.
Sample Output
02:38
显示 有点bug 其实 图形这样的
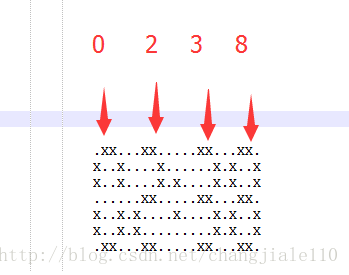
题目 给的 02:38是这样来了 我们 就是去 找 规律 找出
1-4 6-9 13-16 18-21
四个图形规律 就好 写了 2个
第一个 风格 比较 丑的 代码
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int Max = 100001;
typedef long long LL;
char a[8][22];
int main()
{
int N;
scanf("%d",&N);
while (N--)
{
memset(a,'\0',sizeof(a));
int i,j;
for (i=1;i<=7; i++)
{
for (j=1 ;j<=21; j++)
{
cin>>a[i][j];
}
getchar();
}
for (i=1; i<=21; i+=5)
{
if (a[1][i+1]=='X'&&a[1][i+2]=='X')
{
// 0 2 3 5 6 7 8 9
if (a[2][i]=='X'&&a[3][i]=='X')
{
// 0 5 6 8 9
if (a[5][i]=='X'&&a[6][i]=='X')
{
// 0 6 8
if (a[2][i+3]=='X'&&a[3][i+3]=='X')
{
// 0 8
if (a[4][i+1]=='X'&&a[4][i+2]=='X')
cout<<'8';
else
cout<<'0';
}
else
cout<<'6';
}
else
{
if (a[2][i+3]=='X'&&a[3][i+3]=='X')
cout<<'9';
else
cout<<'5';
}
}
else
{
//2 3 7
if (a[5][i]=='X'&&a[6][i]=='X')
cout<<'2';
else
{
//3 7
if (a[7][i+1]=='X'&&a[7][i+2]=='X')
cout<<'3';
else
cout<<'7';
}
}
}
else
{
//1 4
if (a[4][i+1]=='X'&&a[4][i+2]=='X')
cout<<'4';
else
cout<<'1';
}
if (i==6)
{
i += 2;
cout<<':';
}
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
第二个 在 函数里 判断
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
char m[7][22];
int fun(int x)
{
if(m[3][x]=='X'&&m[3][x+1]=='X')
{
if(m[2][x-1]=='.'&&m[1][x-1]=='.')
{
if(m[4][x-1]=='.'&&m[5][x-1]=='.')
return(3);
else return(2);
}
else
{
if(m[2][x+2]=='.'&&m[1][x+2]=='.')
{
if(m[4][x-1]=='.'&&m[5][x-1]=='.')
return(5);
else return(6);
}
else
{
if(m[4][x-1]=='.'&&m[5][x-1]=='.')
{
if(m[6][x]=='.'&&m[6][x+1]=='.')
return(4);
else return(9);
}
else return(8);
}
}
}
else
{
if(m[6][x]=='.'&&m[6][x+1]=='.')
{
if(m[0][x]=='.'&&m[0][x+1]=='.')
return(1);
else return(7);
}
else return(0);
}
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
for(int i=0;i<7;i++){
scanf("%s",m[i]);
}
int t1,t2,t3,t4;
t1=fun(1);
t2=fun(6);
t3=fun(13);
t4=fun(18);
printf("%d%d:%d%d\n",t1,t2,t3,t4);
}
return 0;
}





















 301
301











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








