VAAPI是什么
VAAPI是一套视频处理硬件加速的接口标准,由intel制定,视频处理包括 编码,解码,前处理,后处理。
什么是硬件加速
硬件加速就是把软件通过cpu去处理的数据交给特定的硬件去处理,减轻cpu负担同时提高处理数据的速度
以解码为例,软件解码是在cpu上跑对应的软件算法去进行解码,而硬件解码是把视频压缩数据交给特定的解码硬件设备去解码,在pc上,这个解码硬件设备就是显卡,更细的说就是显卡中集成的VPU(视频处理单元),在嵌入式系统中,一般就是指soc中集成的VPU。
目前VPU大多集成在显卡中,在规范中也都会包含的上屏显示的接口
不同厂家的硬件加速接口规范
目前来说已经有很多的硬解规范,不同系统,不同显卡都有不同的规范
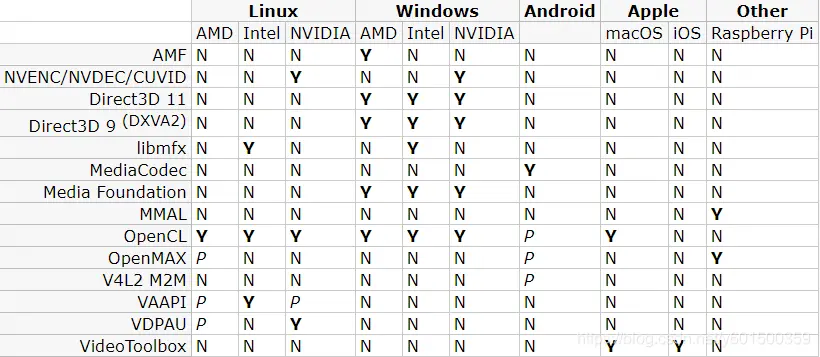
硬解码接口规范,引用知乎大神博客 注:Y 完全可用 P 部分支持 N 不可用
在linux系统中使用较多是英伟达的NVENC/NVDEC/CUVID, AMD的VDPAU, intel的VAAPI
在windows系统中一般使用windows指定的dx规范,目前解码有dxva, dxva2,d3d11va,d3d12va
VAAPI使用
由于我工作目前涉及到的是解码的部分,后面都是讲述VAAPI中解码相关的内容
应用层使用VAAPI硬解一般通过ffmpeg媒体框架去调用,在ffmpeg中已经封装好了对VAAPI接口的调用,使用ffmpeg比直接使用VAAPI要更简单
ffmpeg命令行调用VAAPI解码保存成文件
ffmpeg -hwaccel vaapi -hwaccel_output_format vaapi -i input_video -c:v <codec>_vaapi -b:v <bitrate> output_video
这里是参数的详细解释:
-hwaccel vaapi:指定使用VA-API进行硬件加速。
-hwaccel_output_format vaapi:指定硬件加速解码的输出格式为VA-API格式。
-i input_video:input_video 是要解码的输入文件。
-c:v <codec>_vaapi:<codec> 是指解码器的名称,如 h264、hevc 等,后面加上 _vaapi 表示使用VA-API进行该编解码器的硬件加速解码。
-b:v <bitrate>:指定输出视频的比特率,单位通常是 Mbps(兆比特每秒)。
此外,还有一些其他的参数可能会用到:
-vaapi_device <device>:指定VA-API设备,如 /dev/dri/renderD128,这通常与系统中的特定显卡相关联。
-vf <filter>:使用视频过滤器,如 scale_vaapi 进行视频尺寸缩放,deinterlace_vaapi 进行视频反交错处理。
比如解码h264文件位yuv:
ffmpeg -hwaccel vaapi -hwaccel_output_format vaapi -i input.mp4 -c:v h264_vaapi -b:v 5M output.yuv
调用ffmpeg接口使用VAAPI解码
#include <libavcodec/avcodec.h>
#include <libavutil/hwcontext.h>
#include <libavutil/pixfmt.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
AVFormatContext *fmt_ctx = NULL;
AVStream *video_stream = NULL;
AVCodecParameters *codecpar = NULL;
AVCodecContext *dec_ctx = NULL;
AVPacket packet;
AVFrame *frame = NULL;
AVBufferRef *hw_device_ctx = NULL;
int ret, i;
// 打开输入视频文件
if ((ret = avformat_open_input(&fmt_ctx, "input_video.mp4", NULL, NULL)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "无法打开输入文件\n");
goto end;
}
// 获取输入视频流信息
if ((ret = avformat_find_stream_info(fmt_ctx, NULL)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "无法找到流信息\n");
goto end;
}
// 遍历所有流,寻找视频流
video_stream = NULL;
for (i = 0; i < fmt_ctx->nb_streams; i++) {
if (fmt_ctx->streams[i]->codecpar->codec_type == AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO) {
video_stream = fmt_ctx->streams[i];
break;
}
}
if (!video_stream) {
fprintf(stderr, "没有找到视频流\n");
ret = AVERROR(EINVAL);
goto end;
}
codecpar = video_stream->codecpar;
dec_ctx = avcodec_alloc_context3(NULL);
if (!dec_ctx) {
ret = AVERROR(ENOMEM);
goto end;
}
// 复制流的解码参数到解码器上下文
if ((ret = avcodec_parameters_to_context(dec_ctx, codecpar)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "无法将解码参数复制到解码器上下文\n");
goto end;
}
// 查找解码器
AVCodec *codec = avcodec_find_decoder(codecpar->codec_id);
if (!codec) {
fprintf(stderr, "没有找到解码器\n");
ret = AVERROR(EINVAL);
goto end;
}
// 初始化硬件加速设备
if ((ret = av_hwdevice_ctx_alloc(&hw_device_ctx, AV_HWDEVICE_TYPE_VAAPI, "/dev/dri/renderD128", NULL, 0)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "无法初始化硬件加速设备\n");
goto end;
}
// 设置解码器的硬件加速上下文
dec_ctx->hw_device_ctx = av_buffer_ref(hw_device_ctx);
if (!dec_ctx->hw_device_ctx) {
ret = AVERROR(ENOMEM);
goto end;
}
// 打开解码器
if ((ret = avcodec_open2(dec_ctx, codec, NULL)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "无法打开解码器\n");
goto end;
}
// 分配一个帧用于解码
frame = av_frame_alloc();
if (!frame) {
ret = AVERROR(ENOMEM);
goto end;
}
// 读取和解码视频帧
while (1) {
if ((ret = av_read_frame(fmt_ctx, &packet)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "无法读取帧\n");
break;
}
if (packet.stream_index == video_stream->index) {
// 将数据包发送到解码器
if ((ret = avcodec_send_packet(dec_ctx, &packet)) < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "无法发送数据包到解码器\n");
break;
}
// 从解码器接收解码后的帧
ret = avcodec_receive_frame(dec_ctx, frame);
if (ret < 0) {
if (ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN)) {
// 需要更多的数据包
continue;
} else if (ret == AVERROR_EOF) {
// 流结束
break;
} else {
fprintf(stderr, "无法从解码器接收帧\n");
break;
}
}
// 处理解码后的帧
// ...
av_frame_unref(frame);
}
av_packet_unref(&packet);
}
end:
// 清理
av_frame_free(&frame);
avcodec_free_context(&dec_ctx);
avformat_close_input(&fmt_ctx);
av_buffer_unref(&hw_device_ctx);
return 0;
}- 使用
avformat_open_input打开输入视频文件。 - 使用
avformat_find_stream_info获取输入视频的流信息。 - 遍历所有流以找到视频流。
- 使用
av_hwdevice_ctx_alloc初始化硬件加速设备。 - 使用
avcodec_find_decoder查找解码器。 - 使用
avcodec_open2打开解码器。 - 分配一个
AVFrame结构以接收解码后的视频帧。 - 使用
av_read_frame读取输入视频的数据包。 - 使用
avcodec_send_packet将数据包发送到解码器。 - 使用
avcodec_receive_frame从解码器接收解码后的帧。 - 处理解码后的帧(在示例中省略)。
- 清理所有分配的资源。
VAAPI实现
对于使用者来说,掌握通过ffmpeg去使用VAAPI就已经基本足够应付大部分的应用场景,但是对VAAPI驱动的开发者来说,VAAPI的技术路线和接口的细节都需要掌握。这样才能将硬件的编解码功能通过VAAPI呈现给上层
VAAPI调用栈

ffmpeg或者上层应用只需要通过VA-FRONT-END(VAAPI前端库)就可以调用vaapi驱动,这个va-front有intel开发维护,可能不同版本之间有细微差异,对于应用来说不用关心是当前是哪个厂商的显卡,这就是规范的好处。
va-front会根据一定规则(后面会讲)找到当前系统使用显卡的后端库,check出api接口,应用对va-front的调用最终会转发给va-back
va-back再和自家的kernel-driver通信控制硬件进行视频处理的加速
对于vaapi驱动来说,软件层面,显卡厂商要实现就是va-back和va-kernel-driver
VAAPI前端库
va-front的作用就是方便应用层,不管使用的是哪家的显卡,应用都只需要调用va-front
自动找到对应的va-back,目前来说我们对前端的了解只需要知道,va-front是怎么样找到va-back的,找到时候是怎么check接口的。
va-front源码地址:GitHub - intel/libva: Libva is an implementation for VA-API (Video Acceleration API)
具体细节可以把代码down下来看,这里只有主要逻辑
va-front找va-back规则
前端库找后端库的办法是先获取一个名字,再根据这个名字去找后端库。比如获取到的名字是intel,那前端库会去找intel_drv_video.so,如果是景嘉微的jmgpu,就会去找jmgpu_drv_video.so。
前端库根据显示类型的不同也有很多种类,每个种类都有不同获取名字的方式。

看源码可以知道,va-front定义了好几种类型
/** \brief VA display types. */
enum {
/** \brief Mask to major identifier for VA display type. */
VA_DISPLAY_MAJOR_MASK = 0xf0,
/** \brief VA/X11 API is used, through vaGetDisplay() entry-point. */
VA_DISPLAY_X11 = 0x10,
/** \brief VA/GLX API is used, through vaGetDisplayGLX() entry-point. */
VA_DISPLAY_GLX = (VA_DISPLAY_X11 | (1 << 0)),
/** \brief VA/Android API is used, through vaGetDisplay() entry-point. */
VA_DISPLAY_ANDROID = 0x20,
/** \brief VA/DRM API is used, through vaGetDisplayDRM() entry-point. */
VA_DISPLAY_DRM = 0x30,
/** \brief VA/DRM API is used, with a render-node device path */
VA_DISPLAY_DRM_RENDERNODES = (VA_DISPLAY_DRM | (1 << 0)),
/** \brief VA/Wayland API is used, through vaGetDisplayWl() entry-point. */
VA_DISPLAY_WAYLAND = 0x40,
/** \brief VA/Win32 API is used, through vaGetDisplayWin32() entry-point. */
VA_DISPLAY_WIN32 = 0x80,
};下面是几种常用类型的前端获取名字的方式
X11前端库
X11前端库入口是vaGetDisplay
VADisplay vaGetDisplay(
Display *native_dpy /* implementation specific */
)
{
VADisplayContextP pDisplayContext;
VADriverContextP pDriverContext;
struct dri_state *dri_state;
if (!native_dpy)
return NULL;
pDisplayContext = va_newDisplayContext();
if (!pDisplayContext)
return NULL;
pDisplayContext->vaDestroy = va_DisplayContextDestroy;
pDisplayContext->vaGetDriverNames = va_DisplayContextGetDriverNames;
pDriverContext = va_newDriverContext(pDisplayContext);
if (!pDriverContext) {
free(pDisplayContext);
return NULL;
}
pDriverContext->native_dpy = (void *)native_dpy;
pDriverContext->x11_screen = XDefaultScreen(native_dpy);
pDriverContext->display_type = VA_DISPLAY_X11;
dri_state = calloc(1, sizeof(*dri_state));
if (!dri_state) {
free(pDisplayContext);
free(pDriverContext);
return NULL;
}
dri_state->base.fd = -1;
dri_state->base.auth_type = VA_NONE;
pDriverContext->drm_state = dri_state;
return (VADisplay)pDisplayContext;
}
可以看出获取driverName的接口是va_DisplayContextGetDriverNames
static VAStatus va_DisplayContextGetDriverNames(
VADisplayContextP pDisplayContext,
char **drivers, unsigned *num_drivers
)
{
VAStatus vaStatus = VA_STATUS_ERROR_UNKNOWN;
if (!getenv("LIBVA_DRI3_DISABLE"))
vaStatus = va_DRI3_GetDriverNames(pDisplayContext, drivers, num_drivers);
if (vaStatus != VA_STATUS_SUCCESS)
vaStatus = va_DRI2_GetDriverNames(pDisplayContext, drivers, num_drivers);
#ifdef HAVE_NVCTRL
if (vaStatus != VA_STATUS_SUCCESS)
vaStatus = va_NVCTRL_GetDriverNames(pDisplayContext, drivers, num_drivers);
#endif
#ifdef HAVE_FGLRX
if (vaStatus != VA_STATUS_SUCCESS)
vaStatus = va_FGLRX_GetDriverNames(pDisplayContext, drivers, num_drivers);
#endif
return vaStatus;
}
有两种方式,DRI3和DRI2,这两种都是和桌面管理通信的方式。桌面管理起来之后,加载对应显卡的桌面加速后端库,这时候会进行DRI3和DRI2的初始化并向桌面系统注册一个名字。注册之后其他的桌面客户端可以向桌面管理获取这个名字。DRI3和DRI2会有细微的差别。
如果没有LIBVA_DRI3_DISABLE,会先通过DRI3的方式找,失败了再通过DRI2的方式去找
看看DRI3的方式
VAStatus va_DRI3_GetDriverNames(
VADisplayContextP pDisplayContext,
char **drivers,
unsigned *num_drivers
)
{
VADriverContextP const ctx = pDisplayContext->pDriverContext;
struct drm_state * const drm_state = ctx->drm_state;
int fd = -1;
if (va_isDRI3Connected(ctx, &fd) && fd != -1)
return VA_STATUS_ERROR_UNKNOWN;
drm_state->fd = fd;
drm_state->auth_type = VA_DRM_AUTH_CUSTOM;
return VA_DRM_GetDriverNames(ctx, drivers, num_drivers);
}/* Returns the VA driver names and how many they are, for the active display */
VAStatus
VA_DRM_GetDriverNames(VADriverContextP ctx, char **drivers, unsigned *num_drivers)
{
#define MAX_NAMES 2 // Adjust if needed
static const struct {
const char * const drm_driver;
const char * const va_driver[MAX_NAMES];
} map[] = {
{ "xe", { "iHD" } },
{ "i915", { "iHD", "i965" } }, // Intel Media and OTC GenX
{ "pvrsrvkm", { "pvr" } }, // Intel UMG PVR
{ "radeon", { "r600", "radeonsi" } }, // Mesa Gallium
{ "amdgpu", { "radeonsi" } }, // Mesa Gallium
{ "WSL", { "d3d12" } }, // Mesa Gallium
{ "nvidia-drm", { "nvidia" } }, // Unofficial NVIDIA
};
const struct drm_state * const drm_state = ctx->drm_state;
char *drm_driver;
unsigned count = 0;
if (!drm_state || drm_state->fd < 0)
return VA_STATUS_ERROR_INVALID_DISPLAY;
drm_driver = va_DRM_GetDrmDriverName(drm_state->fd);
if (!drm_driver)
return VA_STATUS_ERROR_UNKNOWN;
/* Map vgem to WSL2 for Windows subsystem for linux */
struct utsname sysinfo = {};
if (!strncmp(drm_driver, "vgem", 4) && uname(&sysinfo) >= 0 &&
strstr(sysinfo.release, "WSL")) {
free(drm_driver);
drm_driver = strdup("WSL");
if (!drm_driver)
return VA_STATUS_ERROR_UNKNOWN;
}
for (unsigned i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE(map); i++) {
if (strcmp(map[i].drm_driver, drm_driver) == 0) {
const char * const *va_drivers = map[i].va_driver;
for (; count < MAX_NAMES && va_drivers[count] && count < *num_drivers; count++)
drivers[count] = strdup(va_drivers[count]);
break;
}
}
/* Fallback to the drm driver, if there's no va equivalent in the map. */
if (!count) {
drivers[count] = drm_driver;
count++;
} else {
free(drm_driver);
}
*num_drivers = count;
return VA_STATUS_SUCCESS;
}
这里只展示了两个关键函数,细节看源码
关键逻辑是,同过dri3的方式和桌面系统连接,将DRI3的连接句柄转化位DRM的连接句柄,再通过drm查询drm驱动的name,通过那么在数组中检索出vaapi驱动的名字,这个数组由va-front维护,在代码里面写死了。如果数组中没有就会直接把drm驱动的name给出去。
static const struct {
const char * const drm_driver;
const char * const va_driver[MAX_NAMES];
} map[] = {
{ "xe", { "iHD" } },
{ "i915", { "iHD", "i965" } }, // Intel Media and OTC GenX
{ "pvrsrvkm", { "pvr" } }, // Intel UMG PVR
{ "radeon", { "r600", "radeonsi" } }, // Mesa Gallium
{ "amdgpu", { "radeonsi" } }, // Mesa Gallium
{ "WSL", { "d3d12" } }, // Mesa Gallium
{ "nvidia-drm", { "nvidia" } }, // Unofficial NVIDIA
};那DRI2呢?
VAStatus va_DRI2_GetDriverNames(
VADisplayContextP pDisplayContext,
char **drivers,
unsigned *num_drivers
)
{
#define MAX_NAMES 2 // Adjust if needed
static const struct {
const char * const dri_driver;
const char * const va_driver[MAX_NAMES];
} map[] = {
{ "i965", { "iHD", "i965" } }, // Intel Media and OTC GenX
{ "iris", { "iHD", "i965" } }, // Intel Media and OTC GenX
{ "crocus", { "i965" } }, // OTC GenX
};
VADriverContextP ctx = pDisplayContext->pDriverContext;
char *dri_driver;
unsigned count = 0;
if (!(va_isDRI2Connected(ctx, &dri_driver) && dri_driver))
return VA_STATUS_ERROR_UNKNOWN;
for (unsigned i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE(map); i++) {
if (strcmp(map[i].dri_driver, dri_driver) == 0) {
const char * const *va_drivers = map[i].va_driver;
for (; count < MAX_NAMES && va_drivers[count] && count < *num_drivers; count++)
drivers[count] = strdup(va_drivers[count]);
break;
}
}
/* Fallback to the dri driver, if there's no va equivalent in the map. */
if (!count) {
drivers[count] = dri_driver;
count++;
} else {
free(dri_driver);
}
*num_drivers = count;
return VA_STATUS_SUCCESS;
}DRI2先从桌面系统端获取名字,再从数组中匹配检索对应的vaapi驱动名字,如果没有检索到,就会把DRI2获取到的名字直接给出去
static const struct {
const char * const dri_driver;
const char * const va_driver[MAX_NAMES];
} map[] = {
{ "i965", { "iHD", "i965" } }, // Intel Media and OTC GenX
{ "iris", { "iHD", "i965" } }, // Intel Media and OTC GenX
{ "crocus", { "i965" } }, // OTC GenX
};GLX前端库
GLX前端库的入口:
VADisplay vaGetDisplayGLX(Display *native_dpy)
{
VADisplay dpy = NULL;
VADisplayContextP pDisplayContext = NULL;
VADisplayContextGLXP pDisplayContextGLX = NULL;
VADriverContextP pDriverContext;
VADriverContextGLXP pDriverContextGLX = NULL;
dpy = vaGetDisplay(native_dpy);
if (!dpy)
return NULL;
pDisplayContext = (VADisplayContextP)dpy;
pDriverContext = pDisplayContext->pDriverContext;
pDisplayContextGLX = calloc(1, sizeof(*pDisplayContextGLX));
if (!pDisplayContextGLX)
goto error;
pDriverContextGLX = calloc(1, sizeof(*pDriverContextGLX));
if (!pDriverContextGLX)
goto error;
pDriverContext->display_type = VA_DISPLAY_GLX;
pDisplayContextGLX->vaDestroy = pDisplayContext->vaDestroy;
pDisplayContext->vaDestroy = va_DisplayContextDestroy;
pDisplayContext->opaque = pDisplayContextGLX;
pDriverContext->glx = pDriverContextGLX;
return dpy;
error:
free(pDriverContextGLX);
free(pDisplayContextGLX);
pDisplayContext->vaDestroy(pDisplayContext);
return NULL;
}明显是直接封装了vaGetDisplay,和X11是一样的。
DRM前端库
我们看下DRM前端库的入口和获取驱动name的函数:
VADisplay
vaGetDisplayDRM(int fd)
{
VADisplayContextP pDisplayContext = NULL;
VADriverContextP pDriverContext = NULL;
struct drm_state *drm_state = NULL;
int node_type;
if (fd < 0 || (node_type = drmGetNodeTypeFromFd(fd)) < 0)
return NULL;
/* Create new entry */
/* XXX: handle cache? */
drm_state = calloc(1, sizeof(*drm_state));
if (!drm_state)
goto error;
drm_state->fd = fd;
pDisplayContext = va_newDisplayContext();
if (!pDisplayContext)
goto error;
pDisplayContext->vaDestroy = va_DisplayContextDestroy;
pDisplayContext->vaGetDriverNames = va_DisplayContextGetDriverNames;
pDriverContext = va_newDriverContext(pDisplayContext);
if (!pDriverContext)
goto error;
pDriverContext->native_dpy = NULL;
pDriverContext->display_type = node_type == DRM_NODE_RENDER ?
VA_DISPLAY_DRM_RENDERNODES : VA_DISPLAY_DRM;
pDriverContext->drm_state = drm_state;
return pDisplayContext;
error:
free(pDisplayContext);
free(pDriverContext);
free(drm_state);
return NULL;
}
static VAStatus
va_DisplayContextGetDriverNames(
VADisplayContextP pDisplayContext,
char **drivers,
unsigned *num_drivers
)
{
VADriverContextP const ctx = pDisplayContext->pDriverContext;
VAStatus status = va_DisplayContextConnect(pDisplayContext);
if (status != VA_STATUS_SUCCESS)
return status;
return VA_DRM_GetDriverNames(ctx, drivers, num_drivers);
}可以看到和前面讲的DRI3获取name的方式基本一样,其实DRI3下面的支撑就是DRM
总结:这三种常用获取驱动name的获取最后到底层就是两种, DRI2和DRM, 所以对于显卡厂商来说,vaapi驱动后端的库名字按照DRI2或者DRM注册的name来命名就行了,前端库name数组中有没有都没关系。
如果没有注册呢?那是不是就不能用了呢?
实际上前端库如果根据上面的方式获取失败,还会检测用户是否设置了环境变量LIBVA_DRIVER_NAME, 和是否通过vaSetDriverName强制设置了name,所以用户知道显卡对应驱动的name的话,是可以强制指定的。
check接口流程
通过上面流程,就找到了后端库了
首先会查找后端库的入口
VADriverInit init_func = NULL;
char init_func_s[256];
int i;
struct {
int major;
int minor;
} compatible_versions[VA_MINOR_VERSION + 2];
for (i = 0; i <= VA_MINOR_VERSION; i ++) {
compatible_versions[i].major = VA_MAJOR_VERSION;
compatible_versions[i].minor = VA_MINOR_VERSION - i;
}
compatible_versions[i].major = -1;
compatible_versions[i].minor = -1;
for (i = 0; compatible_versions[i].major >= 0; i++) {
if (va_getDriverInitName(init_func_s, sizeof(init_func_s),
compatible_versions[i].major,
compatible_versions[i].minor)) {
init_func = (VADriverInit)dlsym(handle, init_func_s);
if (init_func) {
va_infoMessage(dpy, "Found init function %s\n", init_func_s);
break;
}
}入口函数名字是版本号的组合,这个版本号和前端库的版本是匹配的,后端库要支持多个版本就要有多个入口函数,入口函数名字组成规则:
static inline int
va_getDriverInitName(char *name, int namelen, int major, int minor)
{
int ret = snprintf(name, namelen, "__vaDriverInit_%d_%d", major, minor);
return ret > 0 && ret < namelen;
}函数的定义:
typedef VAStatus(*VADriverInit)(
VADriverContextP driver_context
);调用这个函数从后端库冲check出一些信息,重点是三个函数表
struct VADriverVTable *vtable = ctx->vtable;
struct VADriverVTableVPP *vtable_vpp = ctx->vtable_vpp;
struct VADriverVTableProt *vtable_prot = ctx->vtable_prot;
主函数表:struct VADriverVTable
视频处理函数表:struct VADriverVTableVPP
主要功能函数都在主函数表和视频处理函数表中
一般显卡厂家也没有实现所有接口,都是按功能去实现对应需要调用的接口,所以接下来分析也是按功能去分析。只分析主要功能。
函数接口check出来之后,前端库和后端库的通路就可以了,应用可以开始正常的对vaapi接口的调用了。
接口解析
下面是官方定义的主函数表
struct VADriverVTable {
VAStatus(*vaTerminate)(VADriverContextP ctx);
VAStatus(*vaQueryConfigProfiles)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VAProfile *profile_list, /* out */
int *num_profiles /* out */
);
VAStatus(*vaQueryConfigEntrypoints)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VAProfile profile,
VAEntrypoint *entrypoint_list, /* out */
int *num_entrypoints /* out */
);
VAStatus(*vaGetConfigAttributes)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VAProfile profile,
VAEntrypoint entrypoint,
VAConfigAttrib *attrib_list, /* in/out */
int num_attribs
);
VAStatus(*vaCreateConfig)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VAProfile profile,
VAEntrypoint entrypoint,
VAConfigAttrib *attrib_list,
int num_attribs,
VAConfigID *config_id /* out */
);
VAStatus(*vaDestroyConfig)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VAConfigID config_id
);
VAStatus(*vaQueryConfigAttributes)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VAConfigID config_id,
VAProfile *profile, /* out */
VAEntrypoint *entrypoint, /* out */
VAConfigAttrib *attrib_list, /* out */
int *num_attribs /* out */
);
VAStatus(*vaCreateSurfaces)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
int width,
int height,
int format,
int num_surfaces,
VASurfaceID *surfaces /* out */
);
VAStatus(*vaDestroySurfaces)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VASurfaceID *surface_list,
int num_surfaces
);
VAStatus(*vaCreateContext)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VAConfigID config_id,
int picture_width,
int picture_height,
int flag,
VASurfaceID *render_targets,
int num_render_targets,
VAContextID *context /* out */
);
VAStatus(*vaDestroyContext)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VAContextID context
);
VAStatus(*vaCreateBuffer)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VAContextID context, /* in */
VABufferType type, /* in */
unsigned int size, /* in */
unsigned int num_elements, /* in */
void *data, /* in */
VABufferID *buf_id
);
VAStatus(*vaBufferSetNumElements)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VABufferID buf_id, /* in */
unsigned int num_elements /* in */
);
VAStatus(*vaMapBuffer)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VABufferID buf_id, /* in */
void **pbuf /* out */
);
VAStatus(*vaUnmapBuffer)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VABufferID buf_id /* in */
);
VAStatus(*vaDestroyBuffer)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VABufferID buffer_id
);
VAStatus(*vaBeginPicture)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VAContextID context,
VASurfaceID render_target
);
VAStatus(*vaRenderPicture)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VAContextID context,
VABufferID *buffers,
int num_buffers
);
VAStatus(*vaEndPicture)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VAContextID context
);
VAStatus(*vaSyncSurface)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VASurfaceID render_target
);
VAStatus(*vaQuerySurfaceStatus)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VASurfaceID render_target,
VASurfaceStatus *status /* out */
);
VAStatus(*vaQuerySurfaceError)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VASurfaceID render_target,
VAStatus error_status,
void **error_info /*out*/
);
VAStatus(*vaPutSurface)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VASurfaceID surface,
void* draw, /* Drawable of window system */
short srcx,
short srcy,
unsigned short srcw,
unsigned short srch,
short destx,
short desty,
unsigned short destw,
unsigned short desth,
VARectangle *cliprects, /* client supplied clip list */
unsigned int number_cliprects, /* number of clip rects in the clip list */
unsigned int flags /* de-interlacing flags */
);
VAStatus(*vaQueryImageFormats)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VAImageFormat *format_list, /* out */
int *num_formats /* out */
);
VAStatus(*vaCreateImage)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VAImageFormat *format,
int width,
int height,
VAImage *image /* out */
);
VAStatus(*vaDeriveImage)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VASurfaceID surface,
VAImage *image /* out */
);
VAStatus(*vaDestroyImage)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VAImageID image
);
VAStatus(*vaSetImagePalette)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VAImageID image,
/*
* pointer to an array holding the palette data. The size of the array is
* num_palette_entries * entry_bytes in size. The order of the components
* in the palette is described by the component_order in VAImage struct
*/
unsigned char *palette
);
VAStatus(*vaGetImage)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VASurfaceID surface,
int x, /* coordinates of the upper left source pixel */
int y,
unsigned int width, /* width and height of the region */
unsigned int height,
VAImageID image
);
VAStatus(*vaPutImage)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VASurfaceID surface,
VAImageID image,
int src_x,
int src_y,
unsigned int src_width,
unsigned int src_height,
int dest_x,
int dest_y,
unsigned int dest_width,
unsigned int dest_height
);
VAStatus(*vaQuerySubpictureFormats)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VAImageFormat *format_list, /* out */
unsigned int *flags, /* out */
unsigned int *num_formats /* out */
);
VAStatus(*vaCreateSubpicture)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VAImageID image,
VASubpictureID *subpicture /* out */
);
VAStatus(*vaDestroySubpicture)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VASubpictureID subpicture
);
VAStatus(*vaSetSubpictureImage)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VASubpictureID subpicture,
VAImageID image
);
VAStatus(*vaSetSubpictureChromakey)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VASubpictureID subpicture,
unsigned int chromakey_min,
unsigned int chromakey_max,
unsigned int chromakey_mask
);
VAStatus(*vaSetSubpictureGlobalAlpha)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VASubpictureID subpicture,
float global_alpha
);
VAStatus(*vaAssociateSubpicture)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VASubpictureID subpicture,
VASurfaceID *target_surfaces,
int num_surfaces,
short src_x, /* upper left offset in subpicture */
short src_y,
unsigned short src_width,
unsigned short src_height,
short dest_x, /* upper left offset in surface */
short dest_y,
unsigned short dest_width,
unsigned short dest_height,
/*
* whether to enable chroma-keying or global-alpha
* see VA_SUBPICTURE_XXX values
*/
unsigned int flags
);
VAStatus(*vaDeassociateSubpicture)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VASubpictureID subpicture,
VASurfaceID *target_surfaces,
int num_surfaces
);
VAStatus(*vaQueryDisplayAttributes)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VADisplayAttribute *attr_list, /* out */
int *num_attributes /* out */
);
VAStatus(*vaGetDisplayAttributes)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VADisplayAttribute *attr_list, /* in/out */
int num_attributes
);
VAStatus(*vaSetDisplayAttributes)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VADisplayAttribute *attr_list,
int num_attributes
);
/* used by va trace */
VAStatus(*vaBufferInfo)(
VADriverContextP ctx, /* in */
VABufferID buf_id, /* in */
VABufferType *type, /* out */
unsigned int *size, /* out */
unsigned int *num_elements /* out */
);
/* lock/unlock surface for external access */
VAStatus(*vaLockSurface)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VASurfaceID surface,
unsigned int *fourcc, /* out for follow argument */
unsigned int *luma_stride,
unsigned int *chroma_u_stride,
unsigned int *chroma_v_stride,
unsigned int *luma_offset,
unsigned int *chroma_u_offset,
unsigned int *chroma_v_offset,
unsigned int *buffer_name, /* if it is not NULL, assign the low lever
* surface buffer name
*/
void **buffer /* if it is not NULL, map the surface buffer for
* CPU access
*/
);
VAStatus(*vaUnlockSurface)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VASurfaceID surface
);
/* DEPRECATED */
VAStatus
(*vaGetSurfaceAttributes)(
VADriverContextP dpy,
VAConfigID config,
VASurfaceAttrib *attrib_list,
unsigned int num_attribs
);
VAStatus
(*vaCreateSurfaces2)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
unsigned int format,
unsigned int width,
unsigned int height,
VASurfaceID *surfaces,
unsigned int num_surfaces,
VASurfaceAttrib *attrib_list,
unsigned int num_attribs
);
VAStatus
(*vaQuerySurfaceAttributes)(
VADriverContextP dpy,
VAConfigID config,
VASurfaceAttrib *attrib_list,
unsigned int *num_attribs
);
VAStatus
(*vaAcquireBufferHandle)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VABufferID buf_id, /* in */
VABufferInfo * buf_info /* in/out */
);
VAStatus
(*vaReleaseBufferHandle)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VABufferID buf_id /* in */
);
VAStatus(*vaCreateMFContext)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VAMFContextID *mfe_context /* out */
);
VAStatus(*vaMFAddContext)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VAMFContextID mf_context,
VAContextID context
);
VAStatus(*vaMFReleaseContext)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VAMFContextID mf_context,
VAContextID context
);
VAStatus(*vaMFSubmit)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VAMFContextID mf_context,
VAContextID *contexts,
int num_contexts
);
VAStatus(*vaCreateBuffer2)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VAContextID context, /* in */
VABufferType type, /* in */
unsigned int width, /* in */
unsigned int height, /* in */
unsigned int *unit_size, /* out */
unsigned int *pitch, /* out */
VABufferID *buf_id /* out */
);
VAStatus(*vaQueryProcessingRate)(
VADriverContextP ctx, /* in */
VAConfigID config_id, /* in */
VAProcessingRateParameter *proc_buf,/* in */
unsigned int *processing_rate /* out */
);
VAStatus
(*vaExportSurfaceHandle)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VASurfaceID surface_id, /* in */
uint32_t mem_type, /* in */
uint32_t flags, /* in */
void *descriptor /* out */
);
VAStatus(*vaSyncSurface2)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VASurfaceID surface,
uint64_t timeout_ns
);
VAStatus(*vaSyncBuffer)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VABufferID buf_id,
uint64_t timeout_ns
);
VAStatus
(*vaCopy)(
VADriverContextP ctx, /* in */
VACopyObject *dst, /* in */
VACopyObject *src, /* in */
VACopyOption option /* in */
);
VAStatus(*vaMapBuffer2)(
VADriverContextP ctx,
VABufferID buf_id, /* in */
void **pbuf, /* out */
uint32_t flags /* in */
);
/** \brief Reserved bytes for future use, must be zero */
unsigned long reserved[53];
};
接口这么多,按功能分析一下,其实在厂商实现的时候也是适配某个应用的对应功能,针对性的实现接口。当我们看不懂规范说明时,可以看下ffmpeg的调用。
解码功能接口解析
先看几个概念
| context | 上下文,标识一路解码 |
| surface | 解码表面,表示一帧解码 |
| buffer | 缓冲区,数据导入导出载体 |
| image | 一帧图像,里面实际数据存储还是buffer |
解码接口分类
| 查询类接口 | vaQueryConfigProfiles | 查询支持的质量等级,比如h264有high,main,base等 |
| vaQueryConfigEntrypoints | 查询支持的功能入口,比如解码,编码 | |
| vaGetConfigAttributes | 获取对应质量等级,功能入口支持的属性,比如rgb888,yuv420等 | |
| vaQueryConfigAttributes | 查询configId对应的属性 | |
| 资源创建类接口 | vaCreateConfig,vaDestroyConfig | 创建一个配置,包含质量等级,功能入口,属性。对应一个configId,具体内容由后端库管理 |
| vaCreateSurfaces,vaDestroySurfaces | 创建一组surfaces,一个surfaces对应一帧图片 | |
| vaCreateContext,vaDestroyContext | 创建context,表示一路数据的处理,编码,解码或vpp | |
| vaCreateBuffer,vaDestroyBuffer vaMapBuffer,vaUnmapBuffer | buffer的创建和映射,数据通过这个buffer传给后端库 | |
| 执行类接口 | vaBeginPicture | 开启一帧图片的解码工作,对应一个surface |
| vaRenderPicture | 指定几种类型用于解码的buffer数据,会有四种类型的数据buffer 1.VAPictureParameterBufferType 解码参数 h264对应VAPictureParameterBufferH264 2.VAIQMatrixBufferType 一些scalinglist参数,h264对应 VAIQMatrixBufferH264 3.VASliceParameterBufferType slice的信息。在slice流中的大小,位置等,h264对应VASliceParameterBufferH264 4.VASliceDataBufferType 压缩数据,h264对应一个bit流 | |
| vaEndPicture | 执行解码 | |
| vaSyncSurface | 等待指定surface解码完成 | |
| vaQuerySurfaceStatus | 查询surface状态 | |
| 解码结果相关接口 | VAStatus (*vaExportSurfaceHandle)( VADriverContextP ctx, VASurfaceID surface_id, /* in */ uint32_t mem_type, /* in */ uint32_t flags, /* in */ void *descriptor /* out */ ); | 获取指定surface的图像 descriptor的指针类型是VADRMPRIMESurfaceDescriptor 里面有drm的fd可以拿去用作3d显示的输入 |
|
VAStatus(*vaPutSurface)( VADriverContextP ctx, VASurfaceID surface, void* draw, /* Drawable of window system */ short srcx, short srcy, unsigned short srcw, unsigned short srch, short destx, short desty, unsigned short destw, unsigned short desth, VARectangle *cliprects, /* client supplied clip list */ unsigned int number_cliprects, /* number of clip rects in the clip list */ unsigned int flags /* de-interlacing flags */ ); | 通知vaapi将指定surface解码后的数据上屏到draw对应的窗口 | |
| VAStatus(*vaDeriveImage)( VADriverContextP ctx, VASurfaceID surface, VAImage *image /* out */ ); | 获取指定surface的图像,VAImage里面有bufferId,可以map出来直接访问,保存文件 |
接口的主体调用流程就是:
1.查询config属性,能否支持当前视频属性
2.创建资源,congtext,surface,buffer等
3.导入数据,指定资源,开始解码
4.获取解码结果
后端库解码模块实现
驱动实现分为两大块资源管理,功能逻辑封装,其他就是一些辅助接口,类似状态查询,同步,数据导入导出等,按需求实现就可以。
资源管理用来管理context,surface,buffer,image, 硬件config(包括支持的profile,entrypoint,attribute),每一种资源都有对应的操作接口。这一块的话,编码,vpp都是可以共用的。
功能逻辑封装对接硬件,核心就是将数据和参数转换成硬件寄存器值,这一块涉及到编解码算法本身,是比较复杂的。
实现时的主体软件模块图
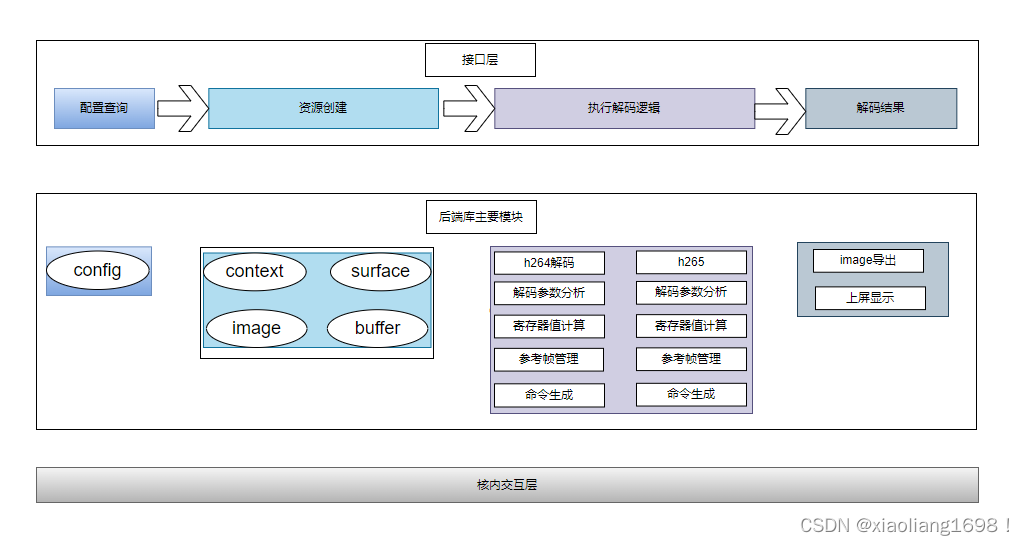
这个些模块就是支撑上面的那些分类接口。
像h264,和h265的解码逻辑都比较复杂,后面计划专门研究记录成文档。
后端库代码分析
不同厂家有不同的实现,整体上大同小异。
由于保密问题,不方便展示。
























 582
582

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








