我们的App在应用中几乎都需要例如进行下载图片、刷新数据等一些耗时操作,我们一般就用利用到多线程的技术,首先来说说NSThread。一个 NSThread 就代表一个线程对象。NSThread的创建一般有三个方法,下面我来通过代码说明:
1.先创建后启动
-(void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
[self test1];
}
-(void)test1
{
NSThread *newThread=[[NSThread alloc] initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(testOperaton:) object:@"Thread"];
//给新建的线程起一个别名,方便我们在出现Bug的时候可以快速排查
newThread.name=@"newThread";
//给新建的线程设置优先级,取值范围是0.0~1.0。默认是0.5(建议最好不要设置)
newThread.threadPriority=0.5;
//启动线程; 调用start方法,告诉CPU线程准备就绪;线程被 CPU 调度之后会自动执行@selector()中的方法;
[newThread start];
}
-(void)testOperaton:(NSString *)object
{
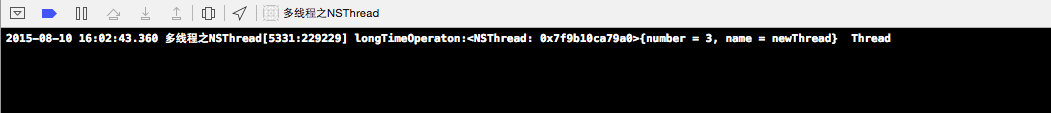
NSLog(@"longTimeOperaton:%@ %@",[NSThread currentThread],object);
}输出台的打印信息:
2. 创建完自动启动
-(void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
[self test2];
}
-(void)test2
{
//这种方式创建无法为线程设置别名
[NSThread detachNewThreadSelector:@selector(testOperaton:) toTarget:self withObject:@"newThread"];
}
-(void)testOperaton:(NSString *)object
{
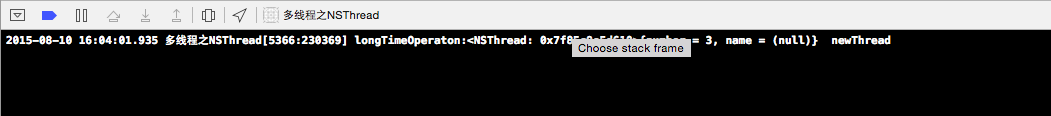
NSLog(@"longTimeOperaton:%@ %@",[NSThread currentThread],object);
}
输出台的打印信息:
3. 隐式创建(自动启动)
-(void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event
{
[self test3];
}
-(void)test3
{
[self performSelectorInBackground:@selector(testOperaton:) withObject:@"newThread"];
}
-(void)testOperaton:(NSString *)object
{
NSLog(@"longTimeOperaton:%@ %@",[NSThread currentThread],object);
}再来说下NSThread中常会用到的方法:
名字/获得主线程/获得当前线程/阻塞线程/退出线程
// 不常用: 栈区大小/优先级
1> 获得当前线程
+ (NSThread *)currentThread;
2> 获得主线程
+ (NSThread *)mainThread;
3> 睡眠(暂停)线程
+ (void)sleepUntilDate:(NSDate *)date;
+ (void)sleepForTimeInterval:(NSTimeInterval)ti;
4> 设置线程的名字
- (void)setName:(NSString *)n;
- (NSString *)name;






















 1248
1248

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








