4.1df命令
后面我们进入磁盘管理小节的学习,首先就是df命令
df - report file system disk space usage
[root@localhost ~]# df
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda3 16561152 1074628 15486524 7% /
devtmpfs 1927024 0 1927024 0% /dev
tmpfs 1936912 0 1936912 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 1936912 8752 1928160 1% /run
tmpfs 1936912 0 1936912 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda1 201380 115472 85908 58% /boot
tmpfs 387384 0 387384 0% /run/user/0
第一列是文件系统(分区名字),第二列磁盘总大小(K),第三列是已使用(K),第四列是可用(K),第五列是已用百分比,最后一列是挂载点。
-h选项可以根据磁盘大小适当显示单位(B, K, M, G, T)。
[root@localhost ~]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda3 16G 1.1G 15G 7% /
devtmpfs 1.9G 0 1.9G 0% /dev
tmpfs 1.9G 0 1.9G 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 1.9G 8.6M 1.9G 1% /run
tmpfs 1.9G 0 1.9G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda1 197M 113M 84M 58% /boot
tmpfs 379M 0 379M 0% /run/user/0
之前给系统分区的时候只分了三部分,/boot,/,swap,但是这里还有tmpfs和devtmpfs分区,
他表示临时的文件系统,即使你写入重启系统(断电)之后也会消失。
/dev/shm是内存,大小是物理内存的一半。
swap分区使用free命令查看。
[root@localhost ~]# free
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 3873828 140988 3549076 8752 183764 3497712
Swap: 4194300 0 4194300
-i选项可以查看分区下的inode使用情况。
[root@localhost ~]# df -i
Filesystem Inodes IUsed IFree IUse% Mounted on
/dev/sda3 8285696 31206 8254490 1% /
devtmpfs 481756 394 481362 1% /dev
tmpfs 484228 1 484227 1% /dev/shm
tmpfs 484228 459 483769 1% /run
tmpfs 484228 16 484212 1% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda1 102400 328 102072 1% /boot
tmpfs 484228 1 484227 1% /run/user/0
如果inode满了,即使还有空间也写不进去文件了。
除了-h选项,也可以使用--block-size指定显示的块的大小(k,m,g,t...)
4.2du命令
du命令用于查看一个文件的大小。
最常用的选项是-sh,du命令显示的是文件的占用空间大小。
[root@localhost ~]# du -sh /root/
40K /root/
[root@localhost ~]# du -sh /boot/
103M /boot/
[root@localhost ~]# du -sh /etc/passwd
4.0K /etc/passwd
[root@localhost ~]# ll -h /etc/passwd
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1.1K Jun 12 19:32 /etc/passwd-s选项就是总和。-h选项是合适的单位显示。
其他选项可以使用man查看。
比如-t选项(threahold)可以以文件大小过滤显示内容。
-t, --threshold=SIZE
exclude entries smaller than SIZE if positive, or entries greater than SIZE if negative
4.3/4.4磁盘分区
日常工作中,接触比较多的情景是给系统增加磁盘,增加分区,挂载。
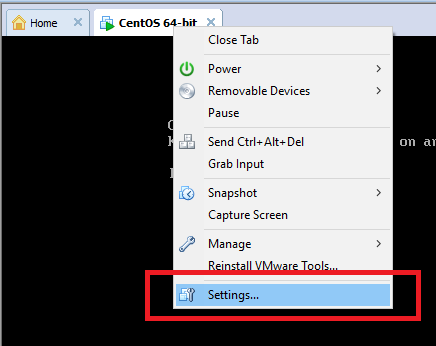
下面介绍如何增加磁盘。如果是物理机,那么关机后(虽然支持热插拔)增加磁盘然后启动就OK了,我们学习用的虚拟机也很简单,右键标签页设置
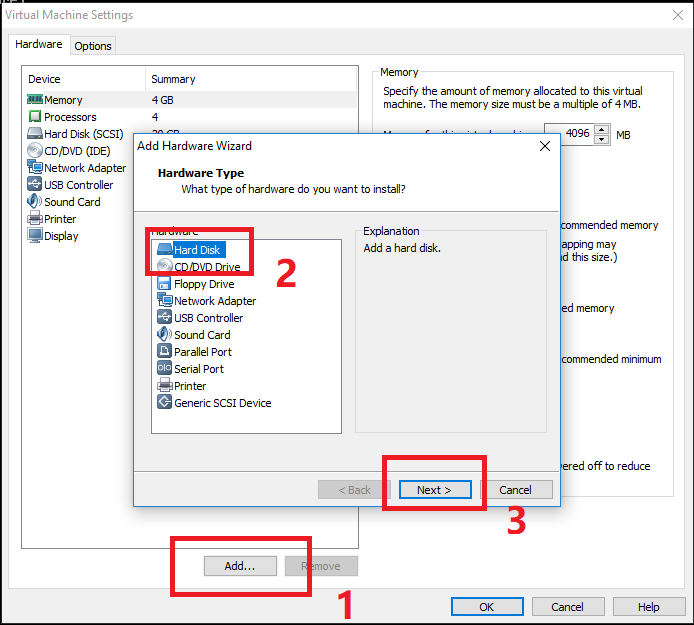
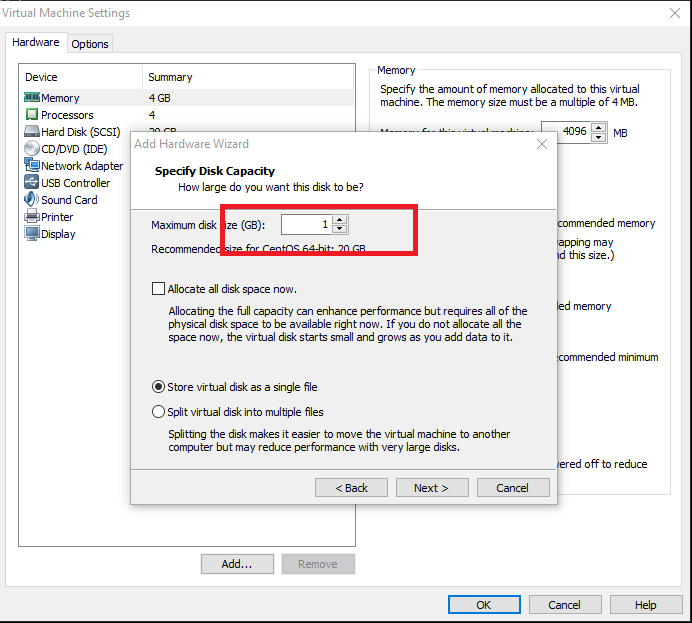
然后一直下一步,直到输入增加磁盘的大小。
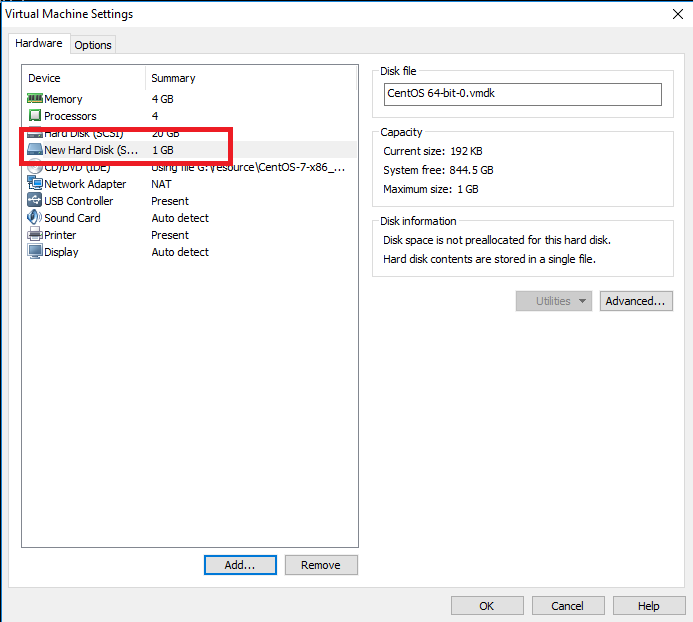
下一步,就完成了。
然后使用fdisk命令可以列出所有可以被发现的磁盘,
[root@localhost ~]# fdisk -l
Disk /dev/sda: 21.5 GB, 21474836480 bytes, 41943040 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x0009b798
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 2048 411647 204800 83 Linux
/dev/sda2 411648 8800255 4194304 82 Linux swap / Solaris
/dev/sda3 8800256 41943039 16571392 83 Linux
Disk /dev/sdb: 1073 MB, 1073741824 bytes, 2097152 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/op我们新添加的磁盘1GB就是/dev/sdb,使用fdisk+filesystem可以进入交互式界面划分分区,按m获取帮助:
Command (m for help): m
Command action
a toggle a bootable flag
b edit bsd disklabel
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition
g create a new empty GPT partition table
G create an IRIX (SGI) partition table
l list known partition types
m print this menu
n add a new partition
o create a new empty DOS partition table
p print the partition table
q quit without saving changes
s create a new empty Sun disklabel
t change a partition's system id
u change display/entry units
v verify the partition table
w write table to disk and exit
x extra functionality (experts only)n,p,w,d都是比较常用的。
输入n增加一个新的分区,会提示你选择增加分区的类型(主分区,扩展分区)
Command (m for help): n
Partition type:
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended
Select (default p):
fdisk划分的分区是mbr分区,最多2T,最多划分4个主分区,扩展分区又包括逻辑分区。主分区和扩展分区总共最多4个。扩展分区不支持格式化,它只是一个装逻辑分区的壳子,真正保存东西的是逻辑分区。
我们来划分一个主分区,分区号为1,大小200M。
Select (default p): p
Partition number (1-4, default 1): 1
First sector (2048-2097151, default 2048): 2048
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-2097151, default 2097151): +200M
Partition 1 of type Linux and of size 200 MiB is set
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 1073 MB, 1073741824 bytes, 2097152 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0xc49ecbe2
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 411647 204800 83 Linux
如果你已经划分了4个主分区了,再n一个分区会提示必须将一个主分区替换成扩展分区。
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 1073 MB, 1073741824 bytes, 2097152 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0xc49ecbe2
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 411647 204800 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 411648 821247 204800 83 Linux
/dev/sdb3 821248 1230847 204800 83 Linux
/dev/sdb4 1230848 2097151 433152 83 Linux
Command (m for help): n
If you want to create more than four partitions, you must replace a
primary partition with an extended partition first.
使用d删除
Command (m for help): d
Partition number (1-4, default 4): 4
Partition 4 is deleted然后我们new一个扩展分区
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 1073 MB, 1073741824 bytes, 2097152 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0xc49ecbe2
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 411647 204800 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 411648 821247 204800 83 Linux
/dev/sdb3 821248 1230847 204800 83 Linux
/dev/sdb4 1230848 1640447 204800 5 Extended
如果输入错误不能使用backspace删除就用Ctrl-u清空。
此时再创建分区,提示就变了
Command (m for help): n
All primary partitions are in use
Adding logical partition 5
First sector (1232896-2097151, default 1232896):
Using default value 1232896
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (1232896-2097151, default 2097151): +50M
Partition 5 of type Linux and of size 50 MiB is set
Command (m for help): p
Disk /dev/sdb: 1073 MB, 1073741824 bytes, 2097152 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0xc49ecbe2
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 411647 204800 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 411648 821247 204800 83 Linux
/dev/sdb3 821248 1230847 204800 83 Linux
/dev/sdb4 1230848 2097151 433152 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 1232896 1335295 51200 83 Linux
现在我划分了三个主分区,一个扩展分区,一个逻辑分区。
删除主分区的时候,分区号可以留空。但是删除一个逻辑分区的时候,分区号是不会留空的,所有的逻辑分区号都会前移,但是始末位置不变。逻辑分区起始是从5开始的,而且不留空。
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 411647 204800 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 411648 821247 204800 83 Linux
/dev/sdb3 821248 1230847 204800 83 Linux
/dev/sdb4 1230848 2097151 433152 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 1232896 1335295 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb6 1337344 1439743 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb7 1441792 2097151 327680 83 Linux
Command (m for help): D
Partition number (1-7, default 7): 5
Partition 5 is deleted
Command (m for help): P
Disk /dev/sdb: 1073 MB, 1073741824 bytes, 2097152 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk label type: dos
Disk identifier: 0xc49ecbe2
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 2048 411647 204800 83 Linux
/dev/sdb2 411648 821247 204800 83 Linux
/dev/sdb3 821248 1230847 204800 83 Linux
/dev/sdb4 1230848 2097151 433152 5 Extended
/dev/sdb5 1337344 1439743 51200 83 Linux
/dev/sdb6 1441792 2097151 327680 83 Linux
 Linux磁盘管理与分区详解
Linux磁盘管理与分区详解




















 1371
1371

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








