经典用法:
在一个无重复数字的数组中,对于每一个下标数:
-
找出在该数 左边的最近的 且 比它小的 数。
-
找出在该数 右边的最近的 且 比它小的 数。
同理可以找出:
-
找出在该数 左边的最近的 且 比它大的 数。
-
找出在该数 右边的最近的 且 比它大的 数。
操作:准备一个栈,用该栈要求从栈顶到栈底 必须遵循从大到小,,接着遍历数组,如果栈空或者栈顶数比当前数小,则直接进栈;如果栈顶数比当前数大,则将栈顶数出栈 ,记录栈顶数左右两边最近且比他小的数:左边比它小的数,就是在栈中被他压着的数,也就是出栈后的,下一个栈顶;右边比它小的数,就是当前数组中遍历到的数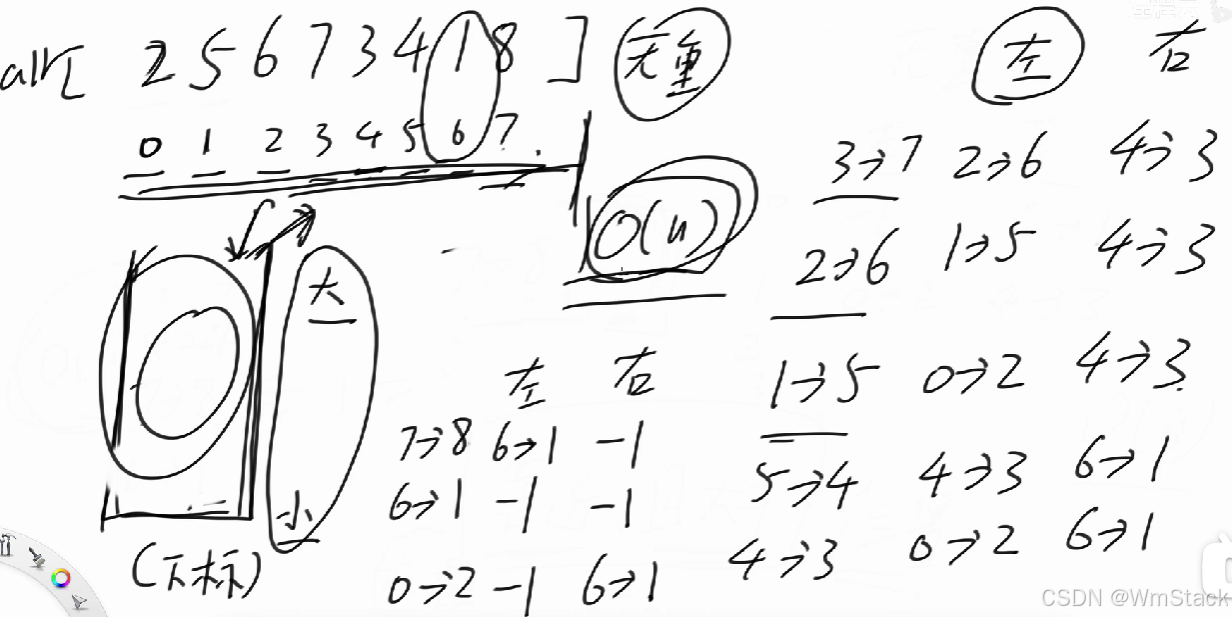
public static int MAXN = 1000001;//最大输入值
public static int[] arr = new int[MAXN];//要遍历的数组
public static int[] stack = new int[MAXN];//栈结构
public static int[][] ans = new int[MAXN][2];//结果表
public static int n, r;
public void compute(){
r=0;
int cur=0;
//遍历阶段:
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
while ( r>0&& arr[stack[r-1]]>=arr[i]){//如果栈顶的值大于等于当前值,就让栈顶出栈并结算
cur=stack[--r];//出栈
ans[cur][0]= r>0 ? stack[r-1]:-1;//当r=0时,栈空,则原栈顶左边的数不存在
ans[cur][1]= i;
}
stack[r++]=i;//栈中存下标
}
//清算阶段:
while (r>0){//这时没有右边的数了,因此ans[cur][1]都等于-1
cur=stack[--r];
ans[cur][0]=r>0?stack[r-1]:-1;
ans[cur][1]=-1;
}
//矫正阶段:
// 左侧的答案不需要修正一定是正确的因为栈是严格按照从大到小的,只有右侧答案需要修正
// 从右往左修正,n-1位置的右侧答案一定是-1,不需要修正
for (int i= arr.length-2;i>=0;i--){//当有重复数的时候存在
if (ans[i][1]!=-1&&arr[i]==arr[ans[i][1]]){
ans[i][1]=ans[ans[i][1]][1];
}
}
}
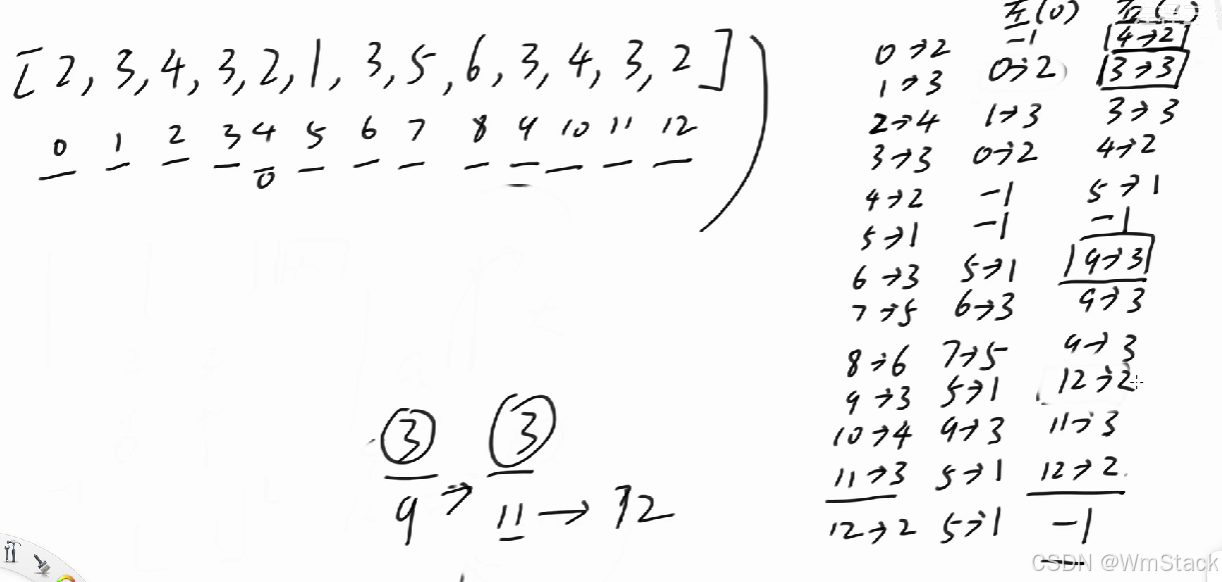
eq1
//给定一个整数数组temperatures,表示每天的温度,返回一个数组answer,其中answer[i]
// 是指对于第 i 天,下一个更高温度出现在几天后。如果气温在这之后都不会升高,请在该位置用0 来代替
//也就是求每个下标 右边的 且严格大于的 下标差值,那么栈结构就要依照从小到大
public static int maxN=100001;
public static int[] stack=new int[maxN];
public static int r;
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {
int n= temperatures.length;
int[] answer = new int[n];
r=0;
for (int i=0;i< temperatures.length;i++){
while (r>0 && temperatures[i]>temperatures[stack[r-1]]){ //stack[r-1]就是查看栈顶的值但是不对栈进行操作
int cur=stack[--r];
answer[cur]=i-cur;
}
stack[r++]=i;
}
//当只需要求一侧离自己最近的大于或者小于的值的时候,就不用进行校验阶段。
//清算阶段时右边的数字是全为-1,的右边的数字来自数组的遍历,左边的数来自栈内
return answer;
}
eq2:
//给定一个整数数组 arr,找到 min(b) 的总和,其中 b 的范围为 arr 的每个(连续)子数组。
//子数组也就是原数组中连续的一段区间。
//单调栈可以找到左右两侧离自己最近且小于自己的两个数,则这两数中间那段区间,最小值就为自己这个数,又有下标,就可以算出
//一共有多少个区间是已该数为最小值 再乘以该数即可得到这么多个区间的最小值之和
public static int mod=1000000007;
// 1000000007
public static int maxN=30001;
public static int[]stack=new int[maxN];
public static int r;
public int sumSubarrayMins(int[] arr) {
r=0;
long ans=0;
for (int i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
while(r>0 && arr[stack[r-1]]>=arr[i]){
int cur=stack[--r];
int left=r>0?stack[r-1] :-1;
ans = (ans+(long)(cur-left)*(i-cur)*arr[cur])%mod;//(cur-left)*(i-cur)得到区间的组合数 * 这些区间的最小值
}
stack[r++]=i;
}
//清算阶段:
while (r>0){
int cur=stack[--r];
int left=r>0?stack[r-1]:-1;
ans = (ans+(long) (cur-left)*(arr.length-cur)*arr[cur])%mod;
}
//不需要校验阶段,因为相同数造成的区间数的问题,总会被弥补
return (int)ans;
}
public static final int maxN=100001;
public static int[]Stack=new int[maxN];
public static int r;
//考虑每个矩阵能往左右两边扩的最大距离,其实单调栈最能得到的就是 哪一段区间的最小值或者哪一段区间的最大值!
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
r=0;
int ans=0;
for (int i=0;i<heights.length;i++){
while (r>0&&heights[i]<=heights[Stack[r-1]]){
int cur=Stack[--r];
int left=r>0?Stack[r-1] :-1 ;
ans=Math.max(heights[cur]*(i-left-1),ans);
}
Stack[r++]=i;
}
//清算阶段
while (r>0){
int cur=Stack[--r];
int left=r>0?Stack[r-1] :-1;
ans=Math.max(ans,heights[cur]*(heights.length-left-1));
}
return ans;
}
public static int maxN=201;
public static int[]Stack=new int[maxN];
public static int r;
public static int[] height=new int[maxN];
public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {
//状态压缩矩阵!
int n=matrix.length;
int m=matrix[0].length;
int ans=0;
Arrays.fill(height,0);
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
for (int j=0;j<m;j++) {
height[j] = matrix[i][j] == '0' ? 0 : height[j] + 1;
}
ans=Math.max(ans,largestRectangleArea(m));
}
return ans;
}
public int largestRectangleArea(int m){
int ans=0;
for (int i=0;i<m;i++){
while (r>0&&height[i]<=height[Stack[r-1]]){
int cur=Stack[--r];
int left=r>0?Stack[r-1] :-1;
ans=Math.max(ans,(i-left-1)*height[cur]);
}
Stack[r++]=i;
}
//清算阶段
while (r>0){
int cur=Stack[--r];
int left=r>0?Stack[r-1] :-1 ;
ans=Math.max(ans,(m-left-1)*height[cur]);
}
return ans;
}
统计最大的矩阵面积vs统计矩阵的数量,都是利用下标得到关系
// 统计全1子矩形的数量
// 给你一个 m * n 的矩阵 mat,其中只有0和1两种值
// 请你返回有多少个 子矩形 的元素全部都是1
public static int MAXM = 151;
public static int[] height = new int[MAXM];
public static int[] stack = new int[MAXM];
public static int r;
public static int numSubmat(int[][] mat) {
int n = mat.length;
int m = mat[0].length;
int ans = 0;
Arrays.fill(height, 0, m, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
height[j] = mat[i][j] == 0 ? 0 : height[j] + 1;
}
ans += countFromBottom(m);//以每一行为底统计矩阵
}
return ans;
}
// 比如
// 1
// 1
// 1 1
// 1 1 1
// 1 1 1
// 1 1 1
//
// 3 .... 6 .... 8
// left cur i
// 如上图,假设6位置从栈中弹出,6位置的高度为6(上面6个1)
// 6位置的左边、离6位置最近、且小于高度6的是3位置(left),3位置的高度是3
// 6位置的右边、离6位置最近、且小于高度6的是8位置(i),8位置的高度是4
// 此时我们求什么?
// 1) 求在4~7范围上必须以高度6作为高的矩形有几个?
// 2) 求在4~7范围上必须以高度5作为高的矩形有几个?
// 也就是说,<=4的高度一律不求,>6的高度一律不求!
// 其他位置也会从栈里弹出,等其他位置弹出的时候去求!
// 那么在4~7范围上必须以高度6作为高的矩形有几个?如下:
// 4..4 4..5 4..6 4..7
// 5..5 5..6 5..7
// 6..6 6..7
// 7..7
// 10个!什么公式?
// 4...7范围的长度为4,那么数量就是 : 4*5/2
// 同理在4~7范围上,必须以高度5作为高的矩形也是这么多
// 所以cur从栈里弹出时产生的数量 :
// (cur位置的高度-Max{left位置的高度,i位置的高度}) * ((i-left-1)*(i-left)/2)
public static int countFromBottom(int m) {
// height[0...m-1]
r = 0;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0, left, len, bottom; i < m; i++) {
while (r > 0 && height[stack[r - 1]] >= height[i]) {
int cur = stack[--r];
if (height[cur] > height[i]) {
// 只有height[cur] > height[i]才结算
// 如果是因为height[cur]==height[i]导致cur位置从栈中弹出
// 那么不结算!等i位置弹出的时候再说!
// 上一节课讲了很多这种相等时候的处理,比如"柱状图中最大的矩形"问题
left = r == 0 ? -1 : stack[r - 1];
len = i - left - 1;
bottom = Math.max(left == -1 ? 0 : height[left], height[i]);
ans += (height[cur] - bottom) * len * (len + 1) / 2;
}
}
stack[r++] = i;
}
while (r > 0) {
int cur = stack[--r];
int left = r == 0 ? -1 : stack[r - 1];
int len = m - left - 1;
int down = left == -1 ? 0 : height[left];
ans += (height[cur] - down) * len * (len + 1) / 2;
}
return ans;
}
 单调栈算法经典用法及相关操作
单调栈算法经典用法及相关操作























 7634
7634

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








