主流的加载图片框架有UIL(Universal-Image-Loader)、Picasso、Glide、Fresco,它们之间的对比可以参照文章全面了解Android主流图片加载库。下面来介绍Picasso图片加载库。
一、简介
Picasso是一个强大的图片下载和缓存来源库。使用Picasso非常简单,只需一行代码:
使用Picasso加载图片很容易和方便,只需一行代码就够了。
Picasso.with(context).load("http://i.imgur.com/DvpvklR.png").into(imageView);
Picasso不仅实现了图片异步加载的功能,还解决了android中加载图片时需要解决的一些常见问题:
1. 在adapter中需要取消已经不在视野范围的ImageView图片资源的加载,否则会导致图片错位,Picasso已经解决了这个问题。
2. 使用复杂的图片压缩转换来尽可能的减少内存消耗;
3. 自带内存和硬盘二级缓存功能;
特性
- Adapter中下载
Adapter的重用会被自动检测到,Picasso会取消上次的加载。
@Override
public void getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
SquaredImageView view = (SquaredImageView) convertView;
if (view == null) {
view = new SquaredImageView(context);**
}
String url = getItem(position);
Picasso.with(context).load(url).into(view);
}- 图片转换
转换图片以适应布局大小并减少内存占用
Picasso.with(context)
.load(url)
.resize(50, 50)
.centerCrop()
.into(imageView);你还可以自定义转换:
public class CropSquareTransformation implements Transformation {
@Override public Bitmap transform(Bitmap source) {
int size = Math.min(source.getWidth(), source.getHeight());
int x = (source.getWidth() - size) / 2;
int y = (source.getHeight() - size) / 2;
Bitmap result = Bitmap.createBitmap(source, x, y, size, size);
if (result != source) {
source.recycle();
}
return result;
}
@Override public String key() { return "square()"; }
}
将CropSquareTransformation 的对象传递给transform 方法即可。
- Place holder
空白或者错误占位图片:picasso提供了两种占位图片,未加载完成或者加载发生错误的时需要一张图片作为提示。
Picasso.with(context)
.load(url)
.placeholder(R.drawable.user_placeholder)
.error(R.drawable.user_placeholder_error)
.into(imageView);如果加载发生错误会重复三次请求,三次都失败才会显示error Place holder
- 资源文件加载
除了加载网络图片picasso还支持加载Resources, assets, files, content providers中的资源文件。
Picasso.with(context).load(R.drawable.landing_screen).into(imageView1);
Picasso.with(context).load(new File(...)).into(imageView2);下面从图片的加载过程来分析Picasso的源码。
二、源码分析
源码的分析分为加载图片和取消加载两个部分,首先来看加载图片的过程。
2.1 加载图片
2.1.1 构造Picasso实例对象
Picasso实例对象不是通过默认的构造器来构建的,而是通过内部类Bulider方式来构建的,这样可以方便用户自定义构建Picasso对象。默认方法是通过with来创建。
/*
* 构造一个全局的Picasso实例对象,默认实现;
* 该实例自动初始化默认的配置,适用于大多数场景:
* 1,LRU内存缓存占用应用RAM的15%
* 2,磁盘缓存占用外置存储空间的2%,至少5MB,至多50MB。只在API 14以上才可以,或者是提供磁盘缓存的独立库,如OKHttp。
* 3,三个下载线程用来访问磁盘或者网络元素。
*
* 如果上面的配置满足不了你的需求,则可以通过Picasso.Builder来自定义创建一个Picasso对象。
*/
public static Picasso with(@NonNull Context context) {
if (context == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("context == null");
}
if (singleton == null) {
synchronized (Picasso.class) {
if (singleton == null) {
singleton = new Builder(context).build();
}
}
}
return singleton;
}
/*
* 创建一个Picasso实例对象
*/
public Picasso build() {
Context context = this.context;
if (downloader == null) {
//网络下载
downloader = new OkHttp3Downloader(context);
}
if (cache == null) {
//内存缓存,使用1/8的可用堆内存作为内存缓存
cache = new LruCache(context);
}
if (service == null) {
//ExecutorService服务,默认由3个线程组成
service = new PicassoExecutorService();
}
if (transformer == null) {
//请求转换器,默认是不作任何处理
transformer = RequestTransformer.IDENTITY;
}
//状态管理器
Stats stats = new Stats(cache);
//分发器
Dispatcher dispatcher = new Dispatcher(context, service, HANDLER, downloader, cache, stats);
return new Picasso(context, dispatcher, cache, listener, transformer, requestHandlers, stats,
defaultBitmapConfig, indicatorsEnabled, loggingEnabled);
}Builder可以组装构建Picasso的各种参数,例如定义内存缓存的大小。
/*
* 自定义内存缓存
*/
public Builder memoryCache(@NonNull Cache memoryCache) {
if (memoryCache == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Memory cache must not be null.");
}
if (this.cache != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Memory cache already set.");
}
this.cache = memoryCache;
return this;
}Picasso的构造函数如下:
/*
* Picasso的构造函数
*/
Picasso(Context context, Dispatcher dispatcher, Cache cache, Listener listener,
RequestTransformer requestTransformer, List<RequestHandler> extraRequestHandlers, Stats stats,
Bitmap.Config defaultBitmapConfig, boolean indicatorsEnabled, boolean loggingEnabled) {
this.context = context;
this.dispatcher = dispatcher;
this.cache = cache;
this.listener = listener;
this.requestTransformer = requestTransformer;
this.defaultBitmapConfig = defaultBitmapConfig;
int builtInHandlers = 7; // 内部处理请求的Hanlder数量
int extraCount = (extraRequestHandlers != null ? extraRequestHandlers.size() : 0);
List<RequestHandler> allRequestHandlers = new ArrayList<>(builtInHandlers + extraCount);
//ResourceRequestHandler必须放置在第一个位置
allRequestHandlers.add(new ResourceRequestHandler(context));
if (extraRequestHandlers != null) {
allRequestHandlers.addAll(extraRequestHandlers);
}
allRequestHandlers.add(new ContactsPhotoRequestHandler(context));
allRequestHandlers.add(new MediaStoreRequestHandler(context));
allRequestHandlers.add(new ContentStreamRequestHandler(context));
allRequestHandlers.add(new AssetRequestHandler(context));
allRequestHandlers.add(new FileRequestHandler(context));
allRequestHandlers.add(new NetworkRequestHandler(dispatcher.downloader, stats));
requestHandlers = Collections.unmodifiableList(allRequestHandlers);
this.stats = stats;
this.targetToAction = new WeakHashMap<>();
this.targetToDeferredRequestCreator = new WeakHashMap<>();
this.indicatorsEnabled = indicatorsEnabled;
this.loggingEnabled = loggingEnabled;
this.referenceQueue = new ReferenceQueue<>();
this.cleanupThread = new CleanupThread(referenceQueue, HANDLER);
this.cleanupThread.start();
}2.1.2 利用load方法加载图片
Picasso支持多种加载图片的方式,例如根据网络Uri来加载图片,或者是加载ResourceId指定的图片等。所以load方法被重载了,有多种实现方式:
/*
* 利用指定的Uri来加载图片
*/
public RequestCreator load(@Nullable Uri uri) {
return new RequestCreator(this, uri, 0);
}
/*
* 通过指定的图片文件来加载图片
* 等价于调用load(Uri)方法
*/
public RequestCreator load(@NonNull File file) {
if (file == null) {
return new RequestCreator(this, null, 0);
}
return load(Uri.fromFile(file));
}
/*
* 通过指定的路径来加载图片
* 该方法等价调用Load(Uri)
*/
public RequestCreator load(@Nullable String path) {
if (path == null) {
return new RequestCreator(this, null, 0);
}
if (path.trim().length() == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Path must not be empty.");
}
return load(Uri.parse(path));
}
/*
* 通过指定的ResourceID加载图片
*/
public RequestCreator load(@DrawableRes int resourceId) {
if (resourceId == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Resource ID must not be zero.");
}
return new RequestCreator(this, null, resourceId);
}可以看到,load方法最终都是返回一个RequestCreator。RequestCreator保存请求的参数,构造方法如下:
/*
* RequestCreator的构造函数
*/
RequestCreator(Picasso picasso, Uri uri, int resourceId) {
if (picasso.shutdown) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Picasso instance already shut down. Cannot submit new requests.");
}
this.picasso = picasso;
this.data = new Request.Builder(uri, resourceId, picasso.defaultBitmapConfig);
}
/*
* 存储请求的Uri和Resource Id以及Bitmap的配置
*/
Builder(Uri uri, int resourceId, Bitmap.Config bitmapConfig) {
this.uri = uri;
this.resourceId = resourceId;
this.config = bitmapConfig;
}2.1.3 into方法将ImageView传入
通过load方法加载的图片,最终都要在ImageView上显示。ImageView是通过into方法传入的。该方法在RequestCreator中实现:
public void into(ImageView target) {
into(target, null);
}
/*
* 异步执行请求,请求执行完成后回调callback
*/
public void into(ImageView target, Callback callback) {
long started = System.nanoTime();
checkMain();
if (target == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Target must not be null.");
}
//如果没有请求数据,即uri为null或者resourceID为0时,则取消请求。
if (!data.hasImage()) {
picasso.cancelRequest(target);
//加载placeHolder照片
if (setPlaceholder) {
setPlaceholder(target, getPlaceholderDrawable());
}
return;
}
if (deferred) {
if (data.hasSize()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Fit cannot be used with resize.");
}
int width = target.getWidth();
int height = target.getHeight();
if (width == 0 || height == 0 || target.isLayoutRequested()) {
if (setPlaceholder) {
setPlaceholder(target, getPlaceholderDrawable());
}
picasso.defer(target, new DeferredRequestCreator(this, target, callback));
return;
}
data.resize(width, height);
}
//创建请求以及请求的key
Request request = createRequest(started);
String requestKey = createKey(request);
//从内存缓存中加载图片
if (shouldReadFromMemoryCache(memoryPolicy)) {
Bitmap bitmap = picasso.quickMemoryCacheCheck(requestKey);
if (bitmap != null) {
picasso.cancelRequest(target);
setBitmap(target, picasso.context, bitmap, MEMORY, noFade, picasso.indicatorsEnabled);
if (picasso.loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_MAIN, VERB_COMPLETED, request.plainId(), "from " + MEMORY);
}
if (callback != null) {
callback.onSuccess();
}
return;
}
}
if (setPlaceholder) {
setPlaceholder(target, getPlaceholderDrawable());
}
//创建加载图片的Action
Action action =
new ImageViewAction(picasso, target, request, memoryPolicy, networkPolicy, errorResId,
errorDrawable, requestKey, tag, callback, noFade);
//将请求入队列,并提交执行请求
picasso.enqueueAndSubmit(action);
}RequestCretor是将Request封装成Action,然后提交请求到任务队列中,让任务异步执行。在构造请求之前,先从内存缓存中查看是否意见有图片了,如果有的话,则直接返回缓存中的图片,并回调callback接口。
2.1.4 提交任务
RequestCreator封装好任务请求后,将请求提交到任务队列中,请求入队列的过程在Picasso类中实现。
void enqueueAndSubmit(Action action) {
Object target = action.getTarget();
//取消先前的任务,并将任务将入任务队列中
if (target != null && targetToAction.get(target) != action) {
// This will also check we are on the main thread.
cancelExistingRequest(target);
targetToAction.put(target, action);
}
//提交任务
submit(action);
}
/*
* 提交任务
*/
void submit(Action action) {
dispatcher.dispatchSubmit(action);
}Dispatcher是一个分发器,根据不同的请求命令分发给不同的方法处理,是基于Handler来传递请求消息的。
void dispatchSubmit(Action action) {
handler.sendMessage(handler.obtainMessage(REQUEST_SUBMIT, action));
}
public void handleMessage(final Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case REQUEST_SUBMIT: {
Action action = (Action) msg.obj;
dispatcher.performSubmit(action);
break;
}
....
}Dispatcher最终调用performSubmit来完成任务的提交。
void performSubmit(Action action) {
performSubmit(action, true);
}
/*
* 执行提交任务
*/
void performSubmit(Action action, boolean dismissFailed) {
//暂停标志
if (pausedTags.contains(action.getTag())) {
pausedActions.put(action.getTarget(), action);
if (action.getPicasso().loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_DISPATCHER, VERB_PAUSED, action.request.logId(),
"because tag '" + action.getTag() + "' is paused");
}
return;
}
BitmapHunter hunter = hunterMap.get(action.getKey());
if (hunter != null) {
hunter.attach(action);
return;
}
//服务关闭了
if (service.isShutdown()) {
if (action.getPicasso().loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_DISPATCHER, VERB_IGNORED, action.request.logId(), "because shut down");
}
return;
}
//构建一个hunter,并提交一个任务,返回一个Future
hunter = forRequest(action.getPicasso(), this, cache, stats, action);
hunter.future = service.submit(hunter);
hunterMap.put(action.getKey(), hunter);
if (dismissFailed) {
failedActions.remove(action.getTarget());
}
if (action.getPicasso().loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_DISPATCHER, VERB_ENQUEUED, action.request.logId());
}
}
Dispatcher最终会构建一个BitmapHunter,并提交给ExecutorService来执行。BitmapHunter实现了Runnable接口,执行具体的请求操作。
@Override
public void run() {
try {
updateThreadName(data);
if (picasso.loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_HUNTER, VERB_EXECUTING, getLogIdsForHunter(this));
}
//通过hunt()方法区获取执行结果
result = hunt();
//如果执行结果不为空,则通过Dispatcher的dispatchComplete方法通知执行成功,否则通知执行失败
if (result == null) {
dispatcher.dispatchFailed(this);
} else {
dispatcher.dispatchComplete(this);
}
} catch (Downloader.ResponseException e) {
if (!e.localCacheOnly || e.responseCode != 504) {
exception = e;
}
dispatcher.dispatchFailed(this);
} catch (NetworkRequestHandler.ContentLengthException e) {
exception = e;
dispatcher.dispatchRetry(this);
} catch (IOException e) {
exception = e;
dispatcher.dispatchRetry(this);
} catch (OutOfMemoryError e) {
StringWriter writer = new StringWriter();
stats.createSnapshot().dump(new PrintWriter(writer));
exception = new RuntimeException(writer.toString(), e);
dispatcher.dispatchFailed(this);
} catch (Exception e) {
exception = e;
dispatcher.dispatchFailed(this);
} finally {
Thread.currentThread().setName(Utils.THREAD_IDLE_NAME);
}
}BitmapHunter是通过hunt方法去获取Bitmap,如果获取Bitmap成功,则通过Dispatcher的dispatchComplete方法通知加载成功,否则通过Dispatcher的dispatchFailed方法通知加载失败。下面看下hunt方法加载Bitmap的过程:
Bitmap hunt() throws IOException {
Bitmap bitmap = null;
//判断是否需要从内存缓存中读取Bitmap,如果从内存缓存中,读取成功,则直接返回,并更新stats状态
if (shouldReadFromMemoryCache(memoryPolicy)) {
bitmap = cache.get(key);
if (bitmap != null) {
stats.dispatchCacheHit();
loadedFrom = MEMORY;
if (picasso.loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_HUNTER, VERB_DECODED, data.logId(), "from cache");
}
return bitmap;
}
}
data.networkPolicy = retryCount == 0 ? NetworkPolicy.OFFLINE.index : networkPolicy;
//根据指定的请求加载图片,并将结果返回为Result
RequestHandler.Result result = requestHandler.load(data, networkPolicy);
if (result != null) {
loadedFrom = result.getLoadedFrom();
exifRotation = result.getExifOrientation();
//从result中获取bitmap结果
bitmap = result.getBitmap();
// If there was no Bitmap then we need to decode it from the stream.
if (bitmap == null) {
InputStream is = result.getStream();
try {
//从InputStream中解码出图片
bitmap = decodeStream(is, data);
} finally {
Utils.closeQuietly(is);
}
}
}
//如果bitmap不为空,则判断是否需要执行相应的转换
if (bitmap != null) {
if (picasso.loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_HUNTER, VERB_DECODED, data.logId());
}
stats.dispatchBitmapDecoded(bitmap);
if (data.needsTransformation() || exifRotation != 0) {
synchronized (DECODE_LOCK) {
// 如果bitmap需要转换的话,则通过transformResult执行相应的转换
if (data.needsMatrixTransform() || exifRotation != 0) {
bitmap = transformResult(data, bitmap, exifRotation);
if (picasso.loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_HUNTER, VERB_TRANSFORMED, data.logId());
}
}
if (data.hasCustomTransformations()) {
bitmap = applyCustomTransformations(data.transformations, bitmap);
if (picasso.loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_HUNTER, VERB_TRANSFORMED, data.logId(), "from custom transformations");
}
}
}
if (bitmap != null) {
stats.dispatchBitmapTransformed(bitmap);
}
}
}
//返回执行结果
return bitmap;
}图片的加载最终是通过RequestHandler的load方法来加载的,该方法是一个抽象方法,需要根据具体的加载策略来实现。例如从网络上加载图片,就是NetworkRequestHandler来处理,如果是根据resourceId来加载图片,则使用ResourceRequestHandler来处理。
/*
* 根据指定的request来加载图片
* @param request 加载图片的请求。
* @param networkPolicy 请求的网络加载策略
*/
public abstract Result load(Request request, int networkPolicy) throws IOException;以NetworkRequestHandler为例来说明一下图片的加载过程。
@Override
public Result load(Request request, int networkPolicy) throws IOException {
//利用下载器下载请求的Uri对应的内容
Response response = downloader.load(request.uri, request.networkPolicy);
if (response == null) {
return null;
}
//判断响应结果的来源是来自磁盘还是网络,因为Picasso不自己实现磁盘缓存,而是借助下载器的本地缓存功能,例如OkHtttp下载器就带有缓存功能。
Picasso.LoadedFrom loadedFrom = response.cached ? DISK : NETWORK;
//1.从磁盘缓存中获取Bitmap
Bitmap bitmap = response.getBitmap();
if (bitmap != null) {
return new Result(bitmap, loadedFrom);
}
//2.从网络中获取Bitmap
InputStream is = response.getInputStream();
if (is == null) {
return null;
}
// Sometimes response content length is zero when requests are being replayed. Haven't found
// root cause to this but retrying the request seems safe to do so.
if (loadedFrom == DISK && response.getContentLength() == 0) {
Utils.closeQuietly(is);
throw new ContentLengthException("Received response with 0 content-length header.");
}
if (loadedFrom == NETWORK && response.getContentLength() > 0) {
stats.dispatchDownloadFinished(response.getContentLength());
}
return new Result(is, loadedFrom);
}从上面可以看到,图片的加载过程是通过Downloader的load方法来加载的,该方法是Downloader接口中的一个方法,需要具体的加载器实现,例如OkHttpDownloader下载器。
/*
* 根据指定的Uri下载图片
*/
Response load(Uri uri, int networkPolicy) throws IOException;在load加载完图片后,会判断该图片是从磁盘缓存中加载出来的,还是从网络上获取的,并更新加载标志,返回加载的bitmap。需要注意的是Picasso没有自己实现本地磁盘缓存,而是借助下载器的本地磁盘缓存,Picasso自身只实现了内存缓存。
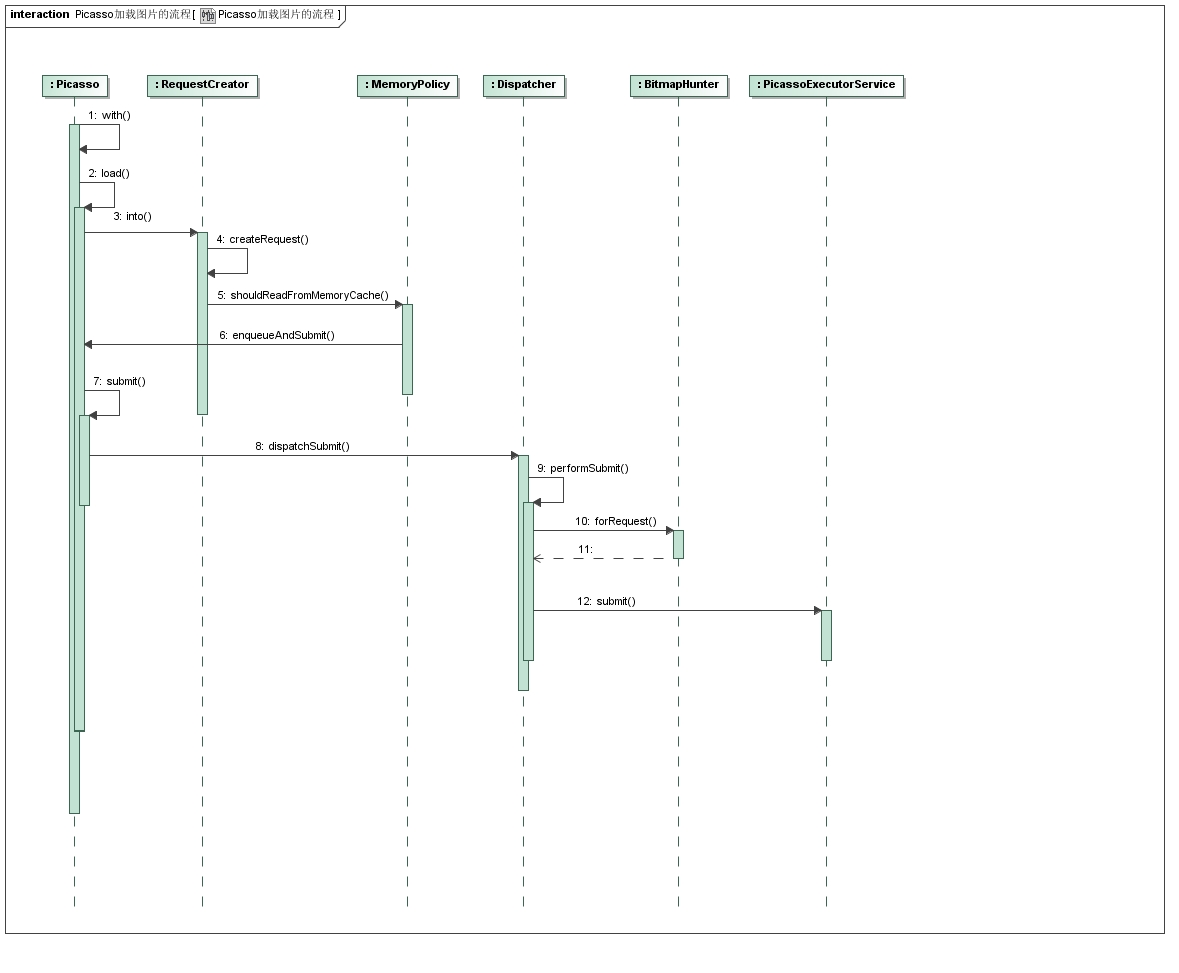
至此,一个完整的图片加载的大致流程出来了。时序图如下:
2.2 取消加载图片
一个好的图片加载库不仅需要支持灵活的加载配置,而且也要支持相应的取消操作。在某些的情况下,需要提前取消图片加载的任务,以减少系统资源的消耗。
取消加载图片的方法是通过Picasso的cancelRequest()方法来实现的,cancelRequest()方法有三种实现,分别为:
public void cancelRequest(ImageView view) {
cancelExistingRequest(view);
}
public void cancelRequest(Target target) {
cancelExistingRequest(target);
}
public void cancelRequest(RemoteViews remoteViews, int viewId) {
cancelExistingRequest(new RemoteViewsAction.RemoteViewsTarget(remoteViews, viewId));
}这三个取消方法最终都是调用到cancelExistingRequest()方法,cancelExistingRequest()方法实现如下:
private void cancelExistingRequest(Object target) {
checkMain();
//首先获取该target对应的action
Action action = targetToAction.remove(target);
if (action != null) {
action.cancel();
//调用Dispatcher的dispatchCancel方法发送取消指令
dispatcher.dispatchCancel(action);
}
//如果target是ImageView,则调用延迟请求的cancel方法
if (target instanceof ImageView) {
ImageView targetImageView = (ImageView) target;
DeferredRequestCreator deferredRequestCreator =
targetToDeferredRequestCreator.remove(targetImageView);
if (deferredRequestCreator != null) {
deferredRequestCreator.cancel();
}
}
}可以看到cancelExistingRequest的主要工作有两部分:一部分是通过Dispatcher发送取消Action操作的消息;另外一部分是针对ImageView,调用延迟请求的cancel方法。
2.2.1 Dispatcher发送取消消息
首先来看下Dispatcher的dispatchCancel方法,方法如下所示:
void dispatchCancel(Action action) {
handler.sendMessage(handler.obtainMessage(REQUEST_CANCEL, action));
}handler由DispatcherHandler内部类实现,sendMessage方法发送消息后,最终调用到handleMessage方法来处理消息:
@Override
public void handleMessage(final Message msg) {
case REQUEST_CANCEL: {
Action action = (Action) msg.obj;
dispatcher.performCancel(action);
break;
}
}
void performCancel(Action action) {
//获取action对应的key,然后根据key获取对应的BitmapHunter,BitmapHunter是一个Runnable对象
String key = action.getKey();
BitmapHunter hunter = hunterMap.get(key);
if (hunter != null) {
//将action分离,并重新计算action新的优先级
hunter.detach(action);
//调用BitmapHunter的cancel方法,最终调用Future的cancel方法。
if (hunter.cancel()) {
//移除该key对应的BitmapHunter
hunterMap.remove(key);
if (action.getPicasso().loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_DISPATCHER, VERB_CANCELED, action.getRequest().logId());
}
}
}
//如果该Action包含暂停标志,则从暂停Actions集合中移除该Action
if (pausedTags.contains(action.getTag())) {
pausedActions.remove(action.getTarget());
if (action.getPicasso().loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_DISPATCHER, VERB_CANCELED, action.getRequest().logId(),
"because paused request got canceled");
}
}
//从失败Action中移除该Action
Action remove = failedActions.remove(action.getTarget());
if (remove != null && remove.getPicasso().loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_DISPATCHER, VERB_CANCELED, remove.getRequest().logId(), "from replaying");
}
}可以看到PerformCancel方法的主要作用先分离该Action,然后调用Future的Cancel方法去真正取消任务。任务取消完成后,移除该key对应的BitmapHunter以及其他集合中包含的该Action。
BitmapHunter的Cancel方法如下:
boolean cancel() {
return action == null
&& (actions == null || actions.isEmpty())
&& future != null
&& future.cancel(false);
}action以及actions集合在BitmapHunter的detach方法被置为空了:
void detach(Action action) {
boolean detached = false;
//如果当前执行的action就是需要取消的action
if (this.action == action) {
this.action = null;
detached = true;
} else if (actions != null) {
detached = actions.remove(action);
}
// The action being detached had the highest priority. Update this
// hunter's priority with the remaining actions.
// action被分离后,需要重新计算actions集合中其他action的优先级
if (detached && action.getPriority() == priority) {
priority = computeNewPriority();
}
if (picasso.loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_HUNTER, VERB_REMOVED, action.request.logId(), getLogIdsForHunter(this, "from "));
}
}至此,cancelExistingRequest的第一部分工作完成了,发送一个取消消息,由Dispatcher真正去取消一个任。接下来看cancelExistingRequest的第二部分工作,调用延迟请求的cancel方法。
2.2.2 延迟请求的取消
当尝试调整图片的大小适应ImageView的边界,这将延迟执行该请求直至ImageView布局好了。具体在RequestCreator的fit方法中实现:
public RequestCreator fit() {
//设置deferred标志位为true
deferred = true;
return this;
}需要注意的是fit()方法只能用于ImageView,在调用into(ImageView,Callback)方法时,会根据deferred标志决定是否需要创建一个DeferredRequestCreator,into方法实现如下:
public void into(ImageView target, Callback callback) {
.....省略部分代码
if (deferred) {
if (data.hasSize()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Fit cannot be used with resize.");
}
int width = target.getWidth();
int height = target.getHeight();
if (width == 0 || height == 0) {
if (setPlaceholder) {
setPlaceholder(target, getPlaceholderDrawable());
}
//创建一个DeferredRequestCreator对象,并调用Picasso的defer方法。
picasso.defer(target, new DeferredRequestCreator(this, target, callback));
return;
}
data.resize(width, height);
}
......省略部分代码
}
void defer(ImageView view, DeferredRequestCreator request) {
targetToDeferredRequestCreator.put(view, request);
}Picasso的defer方法主要将ImageView和DeferredRequestCreator保存到一个HashMap集合中,以Key值为键值。我们再回过头来看cancelExistingRequest的延迟请求取消的部分:
private void cancelExistingRequest(Object target) {
.....省略部分代码
if (target instanceof ImageView) {
ImageView targetImageView = (ImageView) target;
//获取DeferredRequestCreator对象
DeferredRequestCreator deferredRequestCreator =
targetToDeferredRequestCreator.remove(targetImageView);
//如果DeferredRequestCreator不为空,则调用cancel方法
if (deferredRequestCreator != null) {
deferredRequestCreator.cancel();
}
}
}
void cancel() {
callback = null;
//DeferredRequestCreator持有ImageView的弱引用
ImageView target = this.target.get();
if (target == null) {
return;
}
//获取视图树的监听器
ViewTreeObserver vto = target.getViewTreeObserver();
if (!vto.isAlive()) {
return;
}
//移除OnPreDrawListener的监听
vto.removeOnPreDrawListener(this);
}在DeferredRequestCreator的构造器中,注册了监听视图树的监听,当一个视图树将要绘制时,首先回调监听函数onPreDraw函数。这样可以在ImageView绘制前,先获取ImageView的宽高,然后重新发送请求以满足ImageView的边界要求,这也是叫延迟请求的缘由了。
class DeferredRequestCreator implements ViewTreeObserver.OnPreDrawListener {
DeferredRequestCreator(RequestCreator creator, ImageView target, Callback callback) {
this.creator = creator;
this.target = new WeakReference<ImageView>(target);
this.callback = callback;
target.getViewTreeObserver().addOnPreDrawListener(this);
}
@Override
public boolean onPreDraw() {
ImageView target = this.target.get();
if (target == null) {
return true;
}
ViewTreeObserver vto = target.getViewTreeObserver();
if (!vto.isAlive()) {
return true;
}
int width = target.getWidth();
int height = target.getHeight();
if (width <= 0 || height <= 0) {
return true;
}
vto.removeOnPreDrawListener(this);
this.creator.unfit().resize(width, height).into(target, callback);
return true;
}
}至此,完成了延迟请求的取消操作了。
可以看到取消图片的加载过程,大致包含了取消当前执行的任务,以及ImageView的延迟请求取消操作。
三、Picasso关键类图
picasso开源框架中包含了内存缓存、下载器、任务执行器以及分发器等各个模块,他们之间的关系可以用类图来表示:
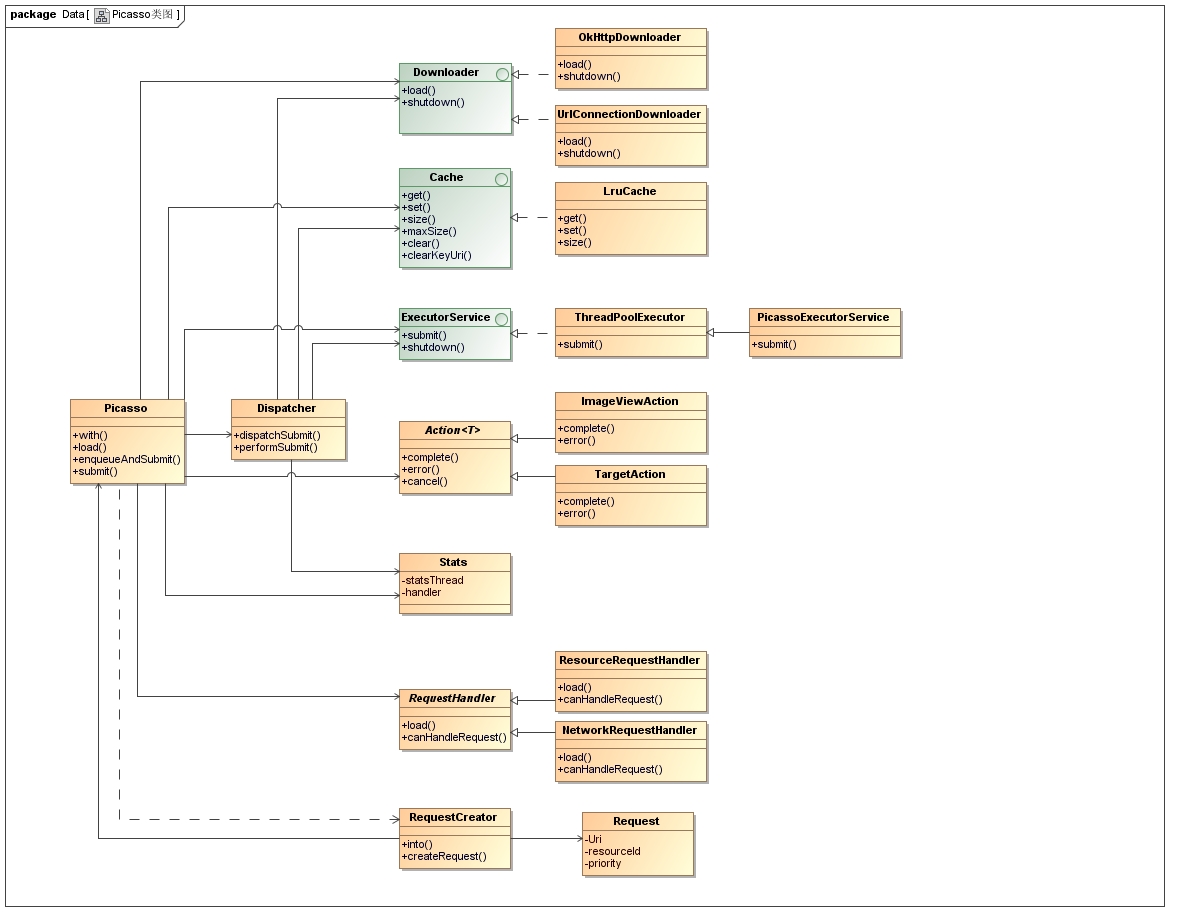
可以看到Picasso类图,大致可以分为以下几个部分:
Downloaderader:下载器,定义了下载的接口,具体的实现的有OkHttpDownloader和UrlConnectionDownloader。OkHttpDownloader是利用OkHttp来下载图片的。UrlConnectionDownloader是利用HttpURLConnection来下载图片的。也可以自定义实现下载器,只需实现loadheshutdown方法。
Cache: 缓存,定义了缓存的接口,这里的具体实现是LruCache实现的内存缓存。LruCache是基于最近使用原则来保存缓存项。也可以自定义实现缓存,只需实现Cache接口中的方法。
ExecutorService: 任务执行器,这里的具体实现是PicassoExecutorService,默认是支持3个线程同时工作,采用的优先级队列。也可以自定义实现任务执行器,只需实现ExecutorService接口中的方法。
Action:任务请求的封装,定义了任务执行的接口。这里的具体实现有ImageViewAction、RemoteViewsAction、TargetAction等。在Action中定义了任务执行完成的complete方法和任务出错的方法error。
Stats:统计任务执行状态,包括从缓存中命中图片的次数、总共下载的图片大小、平均下载图片的大小、下载次数等等。
RequestHandler:请求处理器,可以处理各种类型的请求。请求图片可以通过Uri从网络上获取,也可以通过ResourceId获取,RequestHandler是一个抽象类型,可以让用户选择处理请求的方式,目前支持7种内在类型的图片请求。ResourceRequestHandler是处理ResourceID的图片请求,NetworkRequestHandler是处理网络Uri图片请求。每个请求都通过load方法实现具体的加载逻辑。
RequestCreator:构建图片加载请求,定义into方法,最终将请求添加到任务队列中去执行。
Dispatcher:分发器,协调各个模块的运行,是整个框架的核心枢纽。通过Handler来传递消息,完成状态的流转。
四、总结
Picasso是Square公司开源的一个图片加载库,Picasso自身是不实现“本地缓存”的,需要搭配下载器来实现本地缓存,例如Square开源的OKHttp就提供了本地缓存功能。Picasso整体使用还是比较简单,源码也不是很复杂,是图片加载库的一个好的选择。






















 500
500

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








