reflection包下的factory包是一个对象工厂子包,该包中的类用来基于反射生产出各种对象。
该包下只提供了一个ObjectFactory接口以及其默认实现DefaultObjectFactory
ObjectFactory接口定义如下方法:
void setProperties(Properties properties);设置工厂的属性
<T> T create(Class<T> type);采用无参构造方法生成实例
<T> T create(Class<T> type, List<Class<?>> constructorArgTypes, List<Object> constructorArgs);采用有参构造方法生成实例
<T> boolean isCollection(Class<T> type);判断传入的类型是否是集合类
package com.xncoding.pos.common.dao.entity;
import lombok.Data;
@Data
public class User {
private Integer age;
private String name;
public User(){}
public User(String name,Integer age){
this.name = name;
this.age =age;
}
}
package com.xncoding.pos;
import com.xncoding.pos.common.dao.entity.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.factory.DefaultObjectFactory;
import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.factory.ObjectFactory;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.*;
@SpringBootTest
public class TestDefaultObjectFactory {
private ObjectFactory getObjectFactory(){
return new DefaultObjectFactory();
}
@Test
public void test0(){
System.out.println("无参构造生成对象————————————————————");
test1();
System.out.println("有参构造生成对象————————————————————");
test2();
System.out.println("判断是否集合类————————————————————");
test3();
}
@Test
public void test1(){
User user = this.getObjectFactory().create(User.class);
user.setName("马丁");
System.out.println("采用无参构造User对象:"+user);
}
@Test
public void test2(){
List<Class<?>> paramList = new ArrayList<>();
paramList.add(String.class);
paramList.add(Integer.class);
List<Object> valList = new ArrayList<>();
valList.add("马丁");
valList.add(20);
User user = this.getObjectFactory().create(User.class, paramList, valList);
System.out.println("采用有参构造User对象:" + user.toString());
}
@Test
public void test3(){
ObjectFactory objectFactory = this.getObjectFactory();
System.out.println("User对象是否集合:"+objectFactory.isCollection(User.class));
System.out.println("Map对象是否集合:"+objectFactory.isCollection(Map.class));
System.out.println("List对象是否集合:"+objectFactory.isCollection(List.class));
System.out.println("Set对象是否集合:"+objectFactory.isCollection(Set.class));
}
}
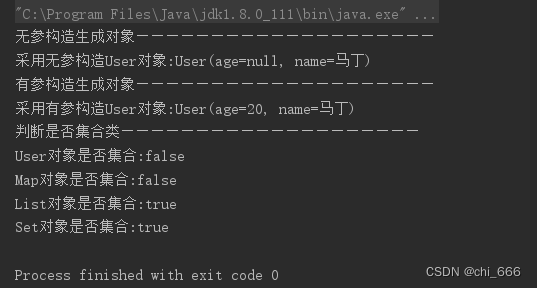
输出的结果:
DefaultObjectFactory的create方法用来生产对象,其最终都是通过instantiateClass方法基于反射来生产一个对象。其源码如下:
<T> T instantiateClass(Class<T> type, List<Class<?>> constructorArgTypes, List<Object> constructorArgs) {
try {
Constructor<T> constructor;
// 若构造器参数类型列表或参数值列表为空,则采用无参构造
if (constructorArgTypes == null || constructorArgs == null) {
constructor = type.getDeclaredConstructor();
if (!constructor.isAccessible()) {
constructor.setAccessible(true);
}
return constructor.newInstance();
}
// 构造器参数类型列表及参数值列表不为空,采用有参构造
constructor = type.getDeclaredConstructor(constructorArgTypes.toArray(new Class[constructorArgTypes.size()]));
if (!constructor.isAccessible()) {
constructor.setAccessible(true);
}
return constructor.newInstance(constructorArgs.toArray(new Object[constructorArgs.size()]));
} catch (Exception e) {
StringBuilder argTypes = new StringBuilder();
if (constructorArgTypes != null && !constructorArgTypes.isEmpty()) {
for (Class<?> argType : constructorArgTypes) {
argTypes.append(argType.getSimpleName());
argTypes.append(",");
}
argTypes.deleteCharAt(argTypes.length() - 1); // remove trailing ,
}
StringBuilder argValues = new StringBuilder();
if (constructorArgs != null && !constructorArgs.isEmpty()) {
for (Object argValue : constructorArgs) {
argValues.append(String.valueOf(argValue));
argValues.append(",");
}
argValues.deleteCharAt(argValues.length() - 1); // remove trailing ,
}
throw new ReflectionException("Error instantiating " + type + " with invalid types (" + argTypes + ") or values (" + argValues + "). Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
DefaultObjectFactory中的resolveInterface方法主要是解决当传入的目标类型是一个常见的接口(List、Map、Set、Collection等)时,给出一个符合该接口的默认实现类。这一点也是我们可以借鉴的。
protected Class<?> resolveInterface(Class<?> type) {
Class<?> classToCreate;
if (type == List.class || type == Collection.class || type == Iterable.class) {
classToCreate = ArrayList.class;
} else if (type == Map.class) {
classToCreate = HashMap.class;
} else if (type == SortedSet.class) { // issue #510 Collections Support
classToCreate = TreeSet.class;
} else if (type == Set.class) {
classToCreate = HashSet.class;
} else {
classToCreate = type;
}
return classToCreate;
}
值得注意的一点是针对于一个类中的小工具方法的访问权限我们通常设为默认权限、protected 权限、private 权限。






















 223
223











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








