Spring提供了几个标志接口(marker interface),这些接口用来改变容器中bean的行为;它们包括InitializingBean和DisposableBean。 实现这两个接口的bean在初始化和析构时容器会调用前者的afterPropertiesSet()方法,以及后者的destroy()方法。
在现代的Spring应用中,The JSR-250
@PostConstructand@PreDestroy接口一般认为是接收生命周期回调的最佳做法。 使用这些注解意味着bean没有耦合到Spring具体的接口。详情见Section 5.9.7, “@PostConstruct and @PreDestroy”。如果你不想使用JSR-250 注解,但你还是寻找消除耦合,考虑使用对象的init方法和destroy方法定义元数据。
Spring在内部使用 BeanPostProcessor 实现来处理它能找到的任何回调接口并调用相应的方法。如果你需要自定义特性或者生命周期行为,你可以实现自己的BeanPostProcessor 。更多信息,详情见Section 5.8, “容器拓展点”。
除了初始化和销毁回调之外,Spring管理对象可能还实现了Lifecycle接口,这些对象可以参与由容器自身驱动的启动和关闭过程。
本节中描述了生命周期回调接口。
1 初始化回调函数
实现 org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean 接口,允许容器在设置好bean的所有必要属性后,执行初始化事宜。 InitializingBean 接口仅指定了一个方法:
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception; 通常,要避免使用 InitializingBean 接口并且不鼓励使用该接口,因为这样会将代码和Spring耦合起来。 使用@PostConstruct注解或者指定一个POJO的初始化方法。 在XML配置元数据的情况下,使用 init-method 属性去指定方法名,并且该方法无参数签名。 例如,下面的定义:
<bean id="exampleInitBean" class="examples.ExampleBean" init-method="init"/>public class ExampleBean {
public void init() {
// do some initialization work
}
}下面代码和上面是完全一样的,但是没有将代码与Spring耦合在一起。
<bean id="exampleInitBean" class="examples.AnotherExampleBean"/>public class AnotherExampleBean implements InitializingBean {
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
// do some initialization work
}
}2 析构回调函数
实现 org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean 接口,允许一个bean当容器需要其销毁时获得一次回调。 DisposableBean 接口也只规定了一个方法:
void destroy() throws Exception; 建议不使用 DisposableBean 回调接口,因为会与Spring耦合。使用@PreDestroy 注解或者指定一个普通的方法,但能由bean定义支持。基于XML配置的元数据,使用 <bean/> 的 destroy-method 属性。例如,下面的定义:
<bean id="exampleInitBean" class="examples.ExampleBean" destroy-method="cleanup"/>public class ExampleBean {
public void cleanup() {
// do some destruction work (like releasing pooled connections)
}
}下面代码与上面效果相同,但是不与Spring耦合。
<bean id="exampleInitBean" class="examples.AnotherExampleBean"/>public class AnotherExampleBean implements DisposableBean {
public void destroy() {
// do some destruction work (like releasing pooled connections)
}
}3 全局的初始化和析构方法
我们可以使用 <beans/> 元素中的 default-init-method 属性和 default-destroy-method 属性来定义全局的初始化和销毁方法,代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"
default-init-method="init" default-destroy-method="destroy">
</beans>注意:
(1)如果你既定义了全局的初始化和销毁方法,又定义了基于bean的初始化方法,那么只会执行基于Bean的初始化和销毁方法。
(2)Spring容器保证在bean的所有依赖都满足后立即执行配置的初始化回调。这意味着初始化回调在原生bean上调用,这也意味着这个时候任何诸如AOP拦截器之类的将不能被应用。 一个目标bean是首先完全创建,然后才应用诸如AOP代理等拦截器链。注意,如果目标bean和代理是分开定义了,你的代码甚至可以绕开代理直接和原生bean通信。 因此,在初始化方法上使用拦截器将产生未知的结果,因为这将目标bean和它的代理/拦截器的生命周期绑定并且留下了和初始bean直接通信这样奇怪的方式。
4 组合生命周期机制
为同一个bean配置多个生命周期机制,不同的初始化方法,调用如下:
@PostConstruct元注释InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet()定义- 自定义
init()方法
销毁方法调用顺序是相同的:
@PreDestroy元注释DisposableBean的destroy()定义- 自定义
destroy()方法
如果bean存在多种的生命周期机制配置并且每种机制都配置为不同的方法名, 那所有配置的方法将会按照上面的顺利执行。然而如果配置了相同的方法名 - 例如, init()初始化方法 - 采用多种机制配置后,只会执行一次。
4.1 代码示例
4.1.1 准备Bean
package com.ws.edu.spring;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
public class Game implements InitializingBean{
public void init(){
System.out.println("Game执行初始化");
}
public void init1(){
System.out.println("Game执行初始化1");
}
public void destory(){
System.out.println("Game销毁执行!");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Game afterPropertiesSet");
}
}
package com.ws.edu.spring;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
public class Person implements InitializingBean{
public void init(){
System.out.println("Person初始化执行!");
}
public void destory(){
System.out.println("Person销毁执行!");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("Person afterPropertiesSet");
}
}
4.1.2 准备XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" default-init-method="init1">
<bean id="person" class="com.ws.edu.spring.Person" init-method="init" destroy-method="destory"/>
<bean id="game" class="com.ws.edu.spring.Game" init-method="init" destroy-method="destory"/>
</beans>4.1.3 准备启动类
package com.ws.edu.spring;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class App {
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
System.out.println(context.getBean(Person.class));
System.out.println(context.getBean(Game.class));
}
}
4.1.4 输出结果
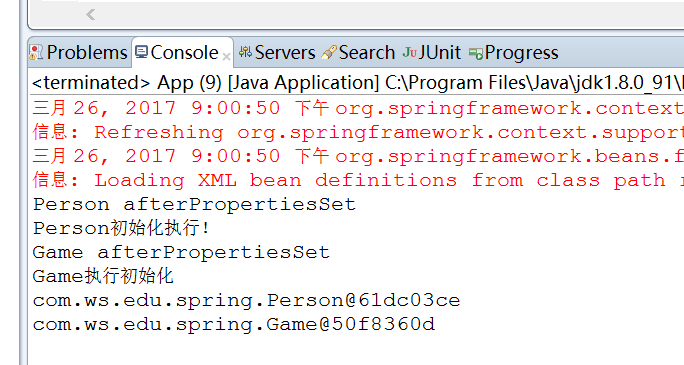
注意:@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy注解只能在注解扫描的时候才会起作用!
5 启动和关闭回调
Lifecycle 接口 为任何有它自己生命周期要求的对象定义基本方法(例如 开始和停止一些后台处理):
public interface Lifecycle {
void start();
void stop();
boolean isRunning();
} 任何Spring管理的对象可能实现那个接口。然后,当 ApplicationContext 开始和停止的时候,它会将那些调用的所有生命周期的实现 定义在这样的上下文中。通过 LifecycleProcessor :
public interface LifecycleProcessor extends Lifecycle {
void onRefresh();
void onClose();
}LifecycleProcessor 本身扩展于 Lifecycle 接口。它还增加了两个其他的方法,用于对上下文进行刷新和关闭。
启动和关闭的顺序调用也很重要。如果任何两个对象之间存在依赖关系,依赖方将会在依赖后开始,在依赖前停止。然而,有时候直接依赖关系是未知的。 你可能只知道某个类型的对象应该在另一种类型的对象之前开始。在这种情况下, SmartLifecycle 接口定义另一种选择,换句话说, 作为其超级接口,Phased 定义 getPhase()方法。
public interface Phased {
int getPhase();
}public interface SmartLifecycle extends Lifecycle, Phased {
boolean isAutoStartup();
void stop(Runnable callback);
} 当开始的时候,最低阶段的对象首先开始,并且当停止的时候,是反向的顺序。因此,实现 SmartLifecycle 接口和返回值是 Integer.MIN_VALUE 的 getPhase() 方法 的对象将在第一个开始和最后一个停止。在另一方面,相位值Integer.MAX_VALUE 将表明对象应该第一个停止和最后开始( 可能是因为它依赖于其他进程的运行)。当考虑相位值的时候,同样重要的是要知道任何没有实现 SmartLifecycle 的 Lifecycle 对象默认的相位是0。 因此,任何负相值都会显示一个对象应该在那些标准组件前开始(并且在他们之后停止),反之为任何正相位值。
正如你所看到的, SmartLifecycle 接受回调,定义了停止方法。任何实现必须调用回调的 run() 方法,在实现的关闭进程完成之后。 那使得异步关闭,在默认实现的 lifecycleprocessor 接口开始,DefaultLifecycleProcessor ,将等待其在每个阶段中的对象组的超时值来调用这个回调。 默认的 per-phase 超时时间是30秒。你可以在上下文中定义一个名为"lifecycleProcessor"的bean来重写默认生命周期处理器实例。如果你打算修改超时时间, 然后定义以下的就足够了:
<bean id="lifecycleProcessor" class="org.springframework.context.support.DefaultLifecycleProcessor">
<!-- timeout value in milliseconds -->
<property name="timeoutPerShutdownPhase" value="10000"/>
</bean> 如上所述, LifecycleProcessor 接口对于上下文的刷新和关闭定义了回调方法。如果` stop() 被显式调用,后者将简单的驱动关闭进程, 但当上下文关闭时会发生。 'refresh' 回调在另一方面来说是 `SmartLifecycle bean的另一个特点。当上下文被刷新的时候(在所有对象被实例化和 初始化之后),回调将被调用,而在这一点上,默认生命周期处理器将检查通过每一个 SmartLifecycle 对象的 isAutoStartup() 方法返回的布尔值。 如果返回 "true",这个对象将在这一点上开始,而不是等待上下文的或者本身的 start() 方法的显示调用(与上下文刷新不同,上下文开始不会 为一个标准的上下文实现自动发生)。 "phase" 值以及 "depends-on" 关系将以相同的方式确定启动顺序,如上所述。
6 在非web应用中优雅地关闭Spring IoC容器
本节仅适用于非web应用程序。在基于web的ApplicationContext实现中已有相应的代码来处理关闭web应用时如何恰当地关闭Spring IoC容器。
如果你正在一个非web应用的环境下使用Spring的IoC容器;例如在桌面富客户端环境下,你想让容器优雅的关闭,并调用singleton bean上的相应析构回调方法, 你需要在JVM里注册一个“关闭钩子”(shutdown hook)。这一点非常容易做到,并且将会确保你的Spring IoC容器被恰当关闭,以及所有由单例持有的资源都会 被释放(当然,为你的单例配置销毁回调,并正确实现销毁回调方法,依然是你的工作)。
为了注册“关闭钩子”,你只需要简单地调用在 AbstractApplicationContext 实现中的 registerShutdownHook() 方法即可。也就是:
import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public final class Boot {
public static void main(final String[] args) throws Exception {
AbstractApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
new String []{"beans.xml"});
// add a shutdown hook for the above context...
ctx.registerShutdownHook();
// app runs here...
// main method exits, hook is called prior to the app shutting down...
}
}7 ApplicationContextAware
当一个Bean实现 org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware 接口时,该Bean可以获得ApplicationContext对象。
public interface ApplicationContextAware {
void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException;
}因此,我们可以通过编程的方式手动的通过ApplicationContext对象注册一个Bean,或者通过将引用转换为该接口的已知子类,例如ConfigurableApplicationContext暴露其他功能。然而,一般来说,你应该避免它,因为它将代码耦合到Spring,并且不遵循Spring特定的规则。
8 BeanNameAware
当一个Bean实现 org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware 接口时,该Bean可以获得自己在容器中的所定义的标识符。
public interface BeanNameAware {
void setBeanName(string name) throws BeansException;
} 回调是在所有正常bean属性之后,但是在如 InitializingBean afterPropertiesSet 或者一个自定义的初始化方法 的初始化回调之前被调用。





















 702
702

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








