NoSQL
No only SQL or a *database* without SQL interface, allowing people to dump data and query data.
- Scalability
- Speed
- Query and Navigational Complexity
Category
- Key-Value Store :
- Dynamo (Amazon), Voldemort (LinkedIn), Citrusleaf, Membase, Riak, Tokyo Cabinet
- Big Table Clones : (Mostly based on BigTable)
- BigTable (Google), Cassandra (Facebook), HBase, Hypertable
- Document Database : (JSON, XML files)
- CouchOne, MongoDB, Terrastore, OrientDB
- Graph Database :
- FlockDB(Twitter), AllegroGraph, DEX, InfoGrid, Neo4J, Sones
- Favors Strict Consistency over Availablity;
- Great Hadoop Integration;
- Ordered Range Partitions
- Automatically Shards/Scales
- Sparse Storage
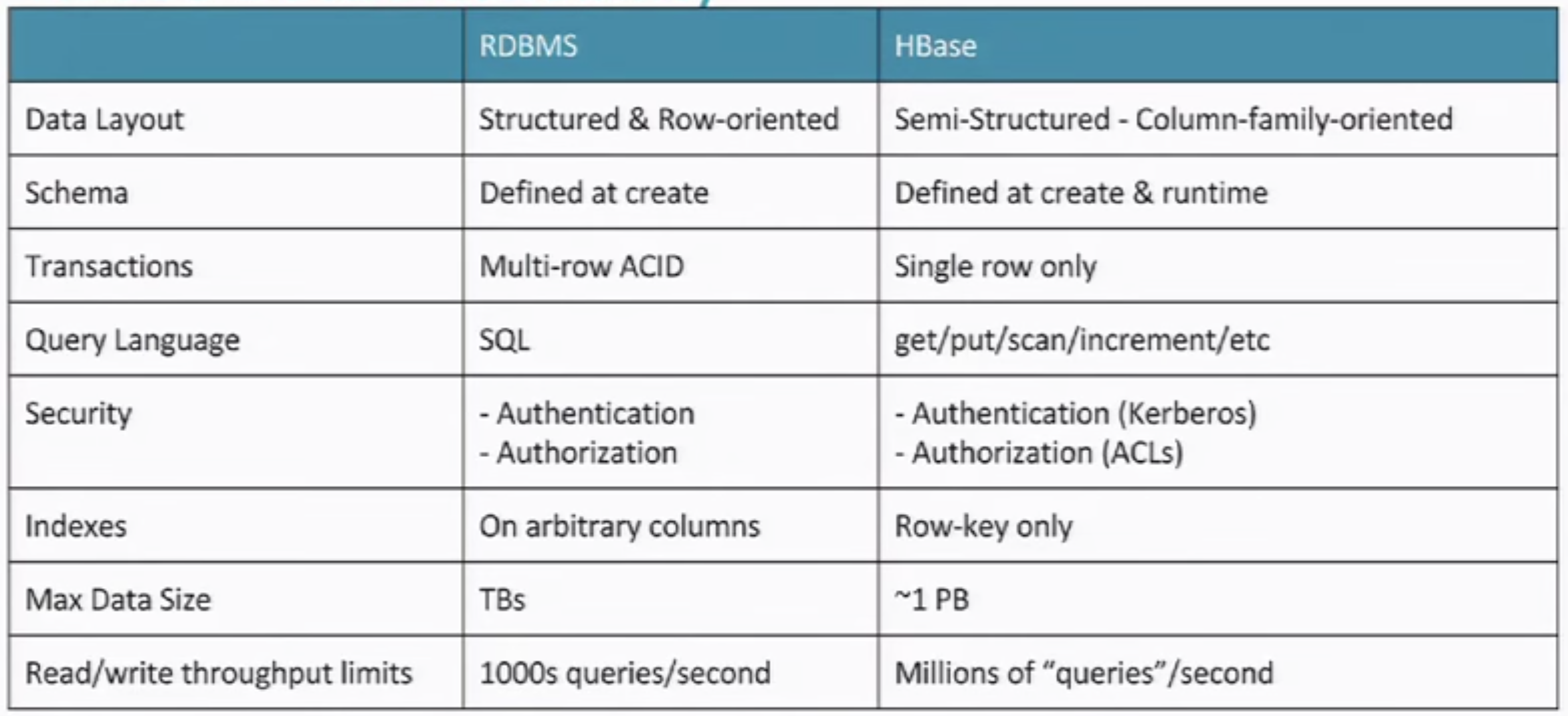
RDBMS wasn't designed for internet. As people adding in cache, denormalized data, cluster, they start to lose indexing, transacation, etc taht RDBMS prvoides.
Challenges
- Huge Data
- Fast Random Access
- Semi/UnStructured Data
- Variable Schema (additional columns)
- Need of Compression
- Need of Distribution (Sharding)
Hive Solution
- Create Data
- Insert Data
- No Update/No Delete
HBase
Distributed key/value store, where key is the combination of
- row_key/column_faily:column_qualifier/<timestamp>
design of column_family and column_qualifier is mainly to seperate the physical storage notion and logical notion. When define a table, only need to specify colum_family. column_qualifier can be specidified during run time.
timestamp : last n values (history); read history from one cell;
rows are strongly consistent. However, no transation between rows and no transactions between tables.
Storage :
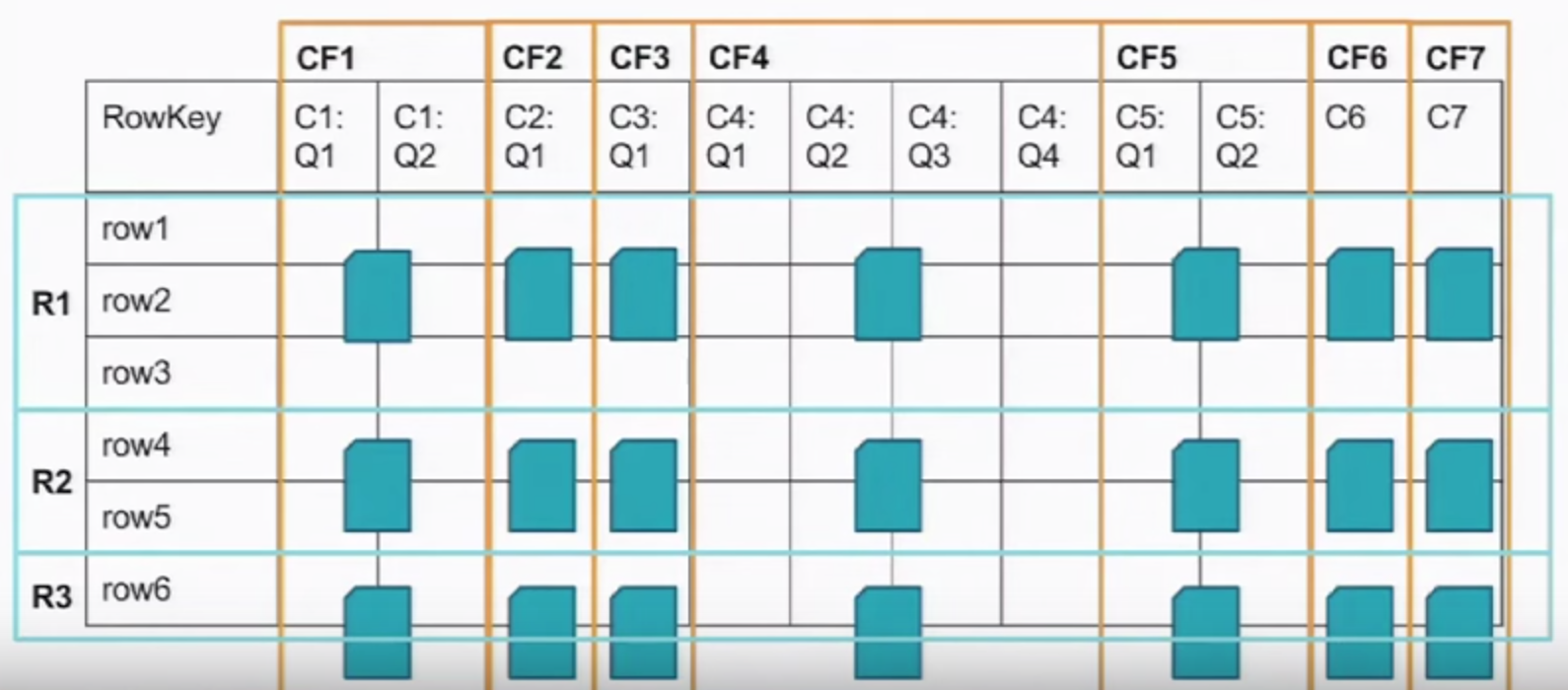
- Region : collections of rows in order
- Column Family, intersect with Region -> File -> stored on harddrive;
- It's column orientated rather than column based. It's more like hybrid approach.
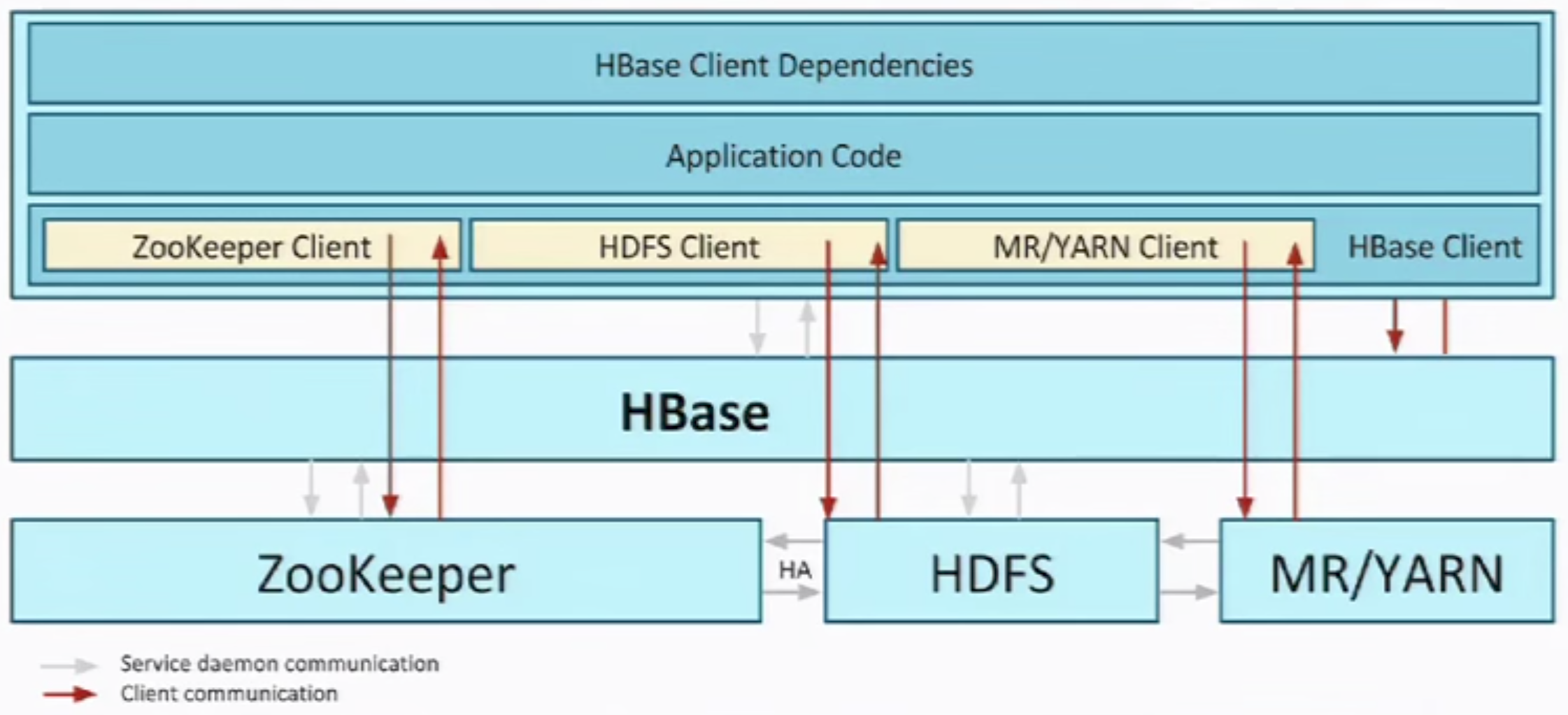
Architecture
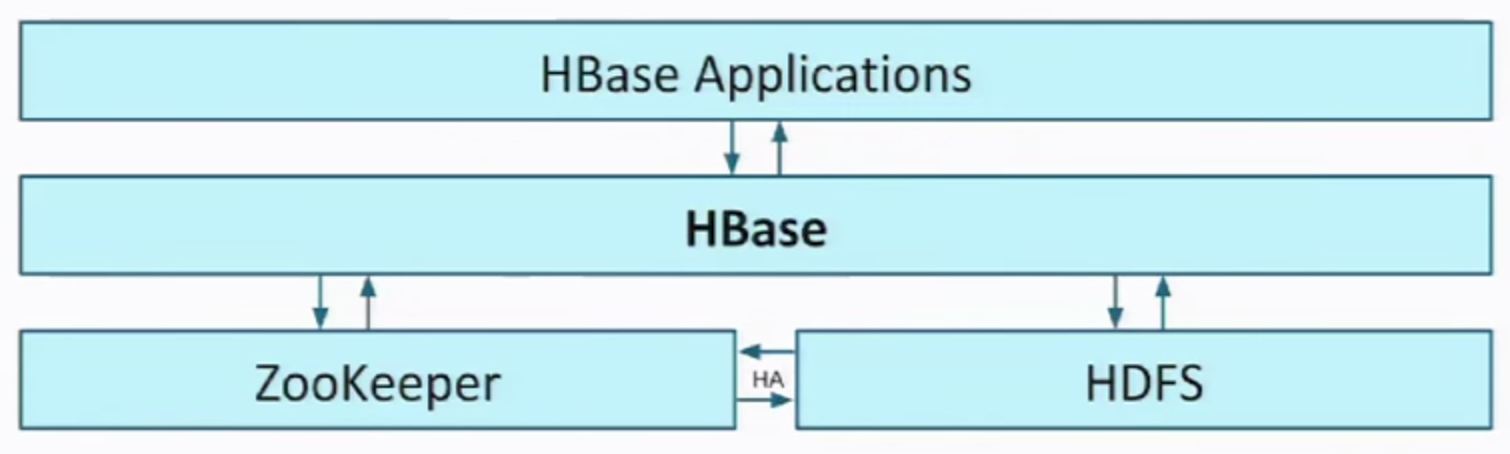
Zookeeper
- For coordination
- Source of truth / Leader Election
HDFS
- Persist HBase Data
- Data stored in HFiles (organized hierarchically by table/cf name)
- Shining Point - Fault Tolerant
- Secondary NameNode
- HA with Quorum Journaling
HBase
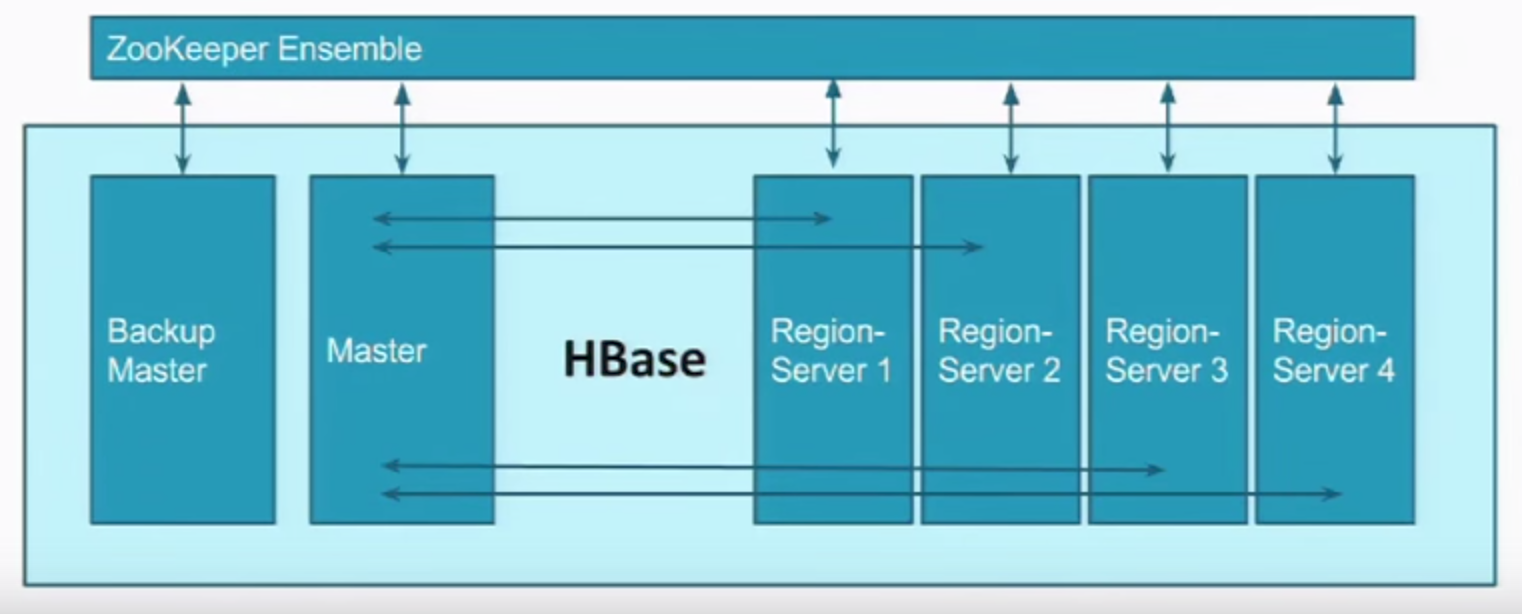
Master deal with metadata;
- Heartbeat -> Zookeeper;
Different machines/processes serving different regions;
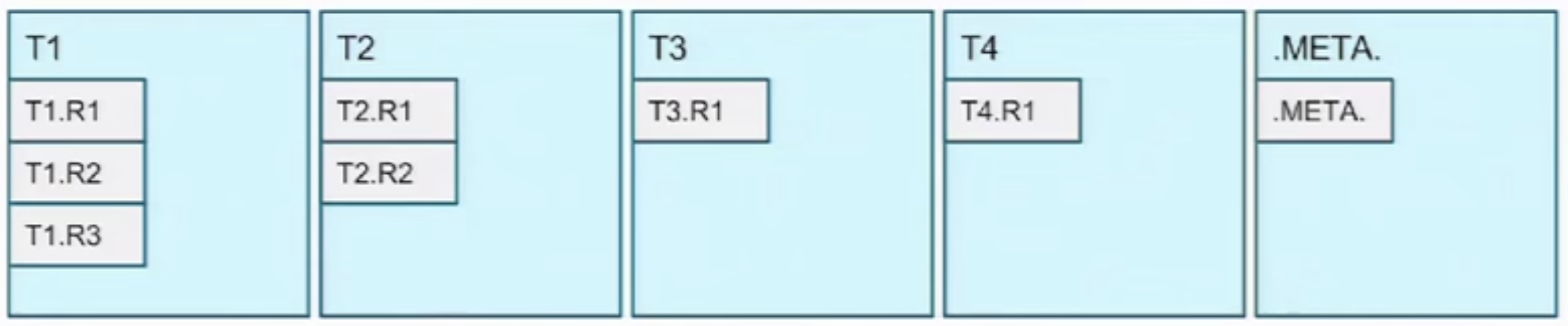
- some more bigger than others therefore need more regions;
- .meta is used for key : region, value : machine to talk to for specific regions.
- usually .meta data is kept in Zookeeper (server side)
semi-structured, allow adding fields on the fly.
- Column-oriented
- Flexible Schema, add columns on the fly
- Good with sparse tables (null value)
- Joins using MR - not optimized
- Tight integration with MR
- Horizontal scalability
- Good for semi-structured data as well as structured data
- Unstructured Data
- High Volume Data to be Stored
- High Scalability
- Column-Oriented Data
- Versioned Data
- Gnerating Data from an MR workflow
Disadvantage
- Not too many rows (cluster maintenance overhead)
- Lack RDBMS Commands (no SQL interface)
- <5 Data Nodes and replication factor is 3 (performance hit)
Commands
- hbase shell
- create table
create 'table_name',
'column_family' # a collection of columns- query tables
list
# OR
describe 'table_name'- modify table
# step 1 : disable
disable 'table_name'
# step 2 : change
alter 'table_name'. {NAME=>'cf_altered'}- drop table
# step 1 : disable
disable 'table_name'
# step 2 : drop
drop 'table_name'
- create data
put 'table_name',
'ROW_KEY', 'colum_family:column_name', 'value'
'ROW_KEY', 'colum_family:column_name2', 'value2'- query data
# whole table
scan 'table_name'
# get
get 'table_name',
'ROW_KEY'
# get multi versions (replications)
get 'table_name',
'ROW_KEY',
{COLUMN=>'column_family:column_value', VERSIONS=>3}- update data
put 'table_name',
'ROW_KEY', 'column_family:column_name', 'new_value'- delete data
delete 'table_name',
'ROW_KEY', 'column_family:column_name'Data Model
!-- row key -> column family -> column -> timestamp -> value
"emp1" : {
"personal" : {
"name" : {130222101311 : "value1"}
"age" : {1321123131 : "18"}
"school" : {1231123131 : "Shanghai",
2123123111 : "Beijing"},
"address" : {
"home" : {1231231 : "address"},
"business" : {123111111 : "asdfddd",
123111111 : "saaaaaa"}
}}
Server
Client
Master Server
Region Server (data)
API :
Restful
Java
Thrift
Java

Good :
- Random Access/short reads
- Real-time reads/writes
- Storing lots and lots of data
- Hadoop Integration
- Horizontal Scalability
- Ecosystem of projects building on top of hbase
Bad :
- Full Table Scan or Range Scan, should consider MapReduce rather than HBase (HDFS + MapReduce)
- Multi-row/Multi-table transactions (RDBMS better)
- Large Blobs (>3 GB) (HDFS better)

http://www.aboutyun.com/thread-9219-1-1.html





















 1519
1519

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








