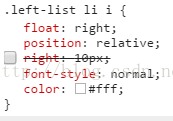
写导航栏时遇到一个有意思的问题.如图上的">", 我在float的基础上用margin-right进行调整,当时脑洞(mi)大(hu)开,想用right会有什么效果?试了一下,两者效果一样。 那么什么时候用right和margin-right呢?
翻了下MDN:
A positioned element is an element whose computed position property is either relative, absolute, fixed or sticky.
A relatively positioned element is an element whose computed position property is relative.
An absolutely positioned element is an element whose computed position property is absolute or fixed.
A stickily positioned element is an element whose computed position property is sticky.
The top, right, bottom, and left properties specify the position of positioned elements.
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/position
relatively positioned和stickily positioned 就是看是否使用对应的relative和sticky.
显然,定位元素囊括了除static之外的3种常见定位:相对定位+绝对定位+固定定位,以及sticky.
(sticky可能比较陌生, 可以看下sticky在处理页脚中的运用http://www.cssstickyfooter.com/cn/)
这3中常见定位分别可对应4种值:
相对定位即是position:relative;
绝对定位即是position:absolute 或 position:fixed
而top/right/bottom/left值只对设定这3种常见定位的元素有效.顺便说下,顺便说下,z-index也只对定位元素有效.
绝对定位元素=绝对定位+固定定位
以right为例,The right property has no effect on non-positioned elements. 排除了定位元素之外的,剩下的非定位元素应该就是static了,
static
top, right, bottom, left and z-index properties do not apply
我查了下W3school,发现也能得到同样的结论
right对static无效
| absolute | 生成绝对定位的元素,相对于 static 定位以外的第一个父元素进行定位。 元素的位置通过 "left", "top", "right" 以及 "bottom" 属性进行规定。 |
| fixed | 生成绝对定位的元素,相对于浏览器窗口进行定位。 元素的位置通过 "left", "top", "right" 以及 "bottom" 属性进行规定。 |
| relative | 生成相对定位的元素,相对于其正常位置进行定位。 因此,"left:20" 会向元素的 LEFT 位置添加 20 像素。 |
| static | 默认值。没有定位,元素出现在正常的流中(忽略 top, bottom, left, right 或者 z-index 声明)。 |
| inherit | 规定应该从父元素继承 position 属性的值。 |
总结:一般元素若是保持默认设置的static, 偏移属性和index属性对它们将不起作用。






















 461
461

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








