我的Android Studio配置:
主要内容
一、SlideExpandableListView的基本使用
二、SlideExpandableListView的源码框架深入解析
一、SlideExpandableListView的基本使用
demo地址:http://download.csdn.net/detail/cjh_android/9436688
资源里面包括了简单的官方demo,和我打成的.arr文件
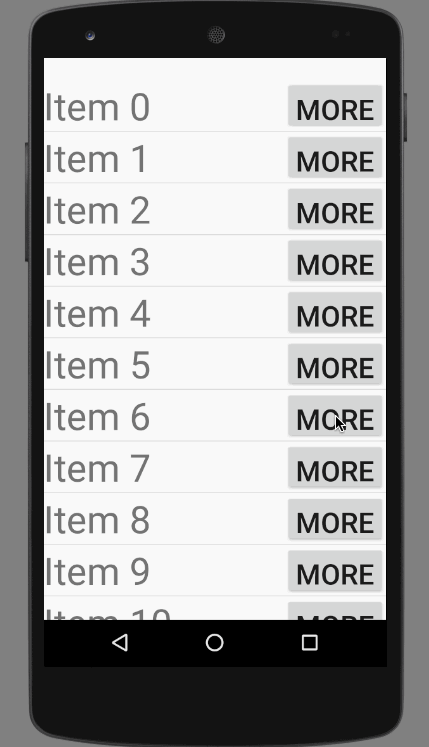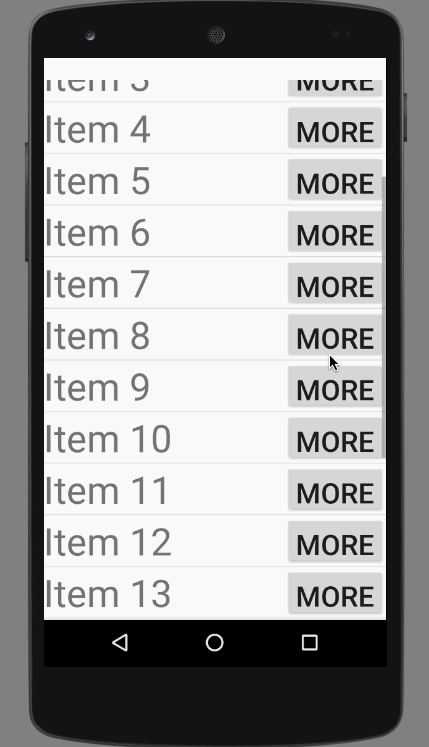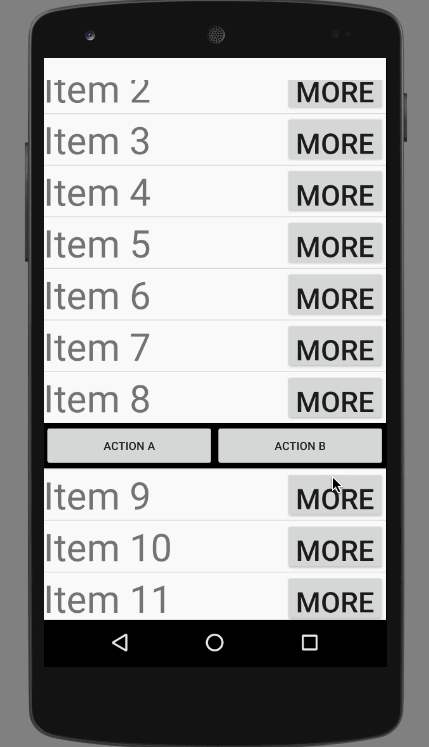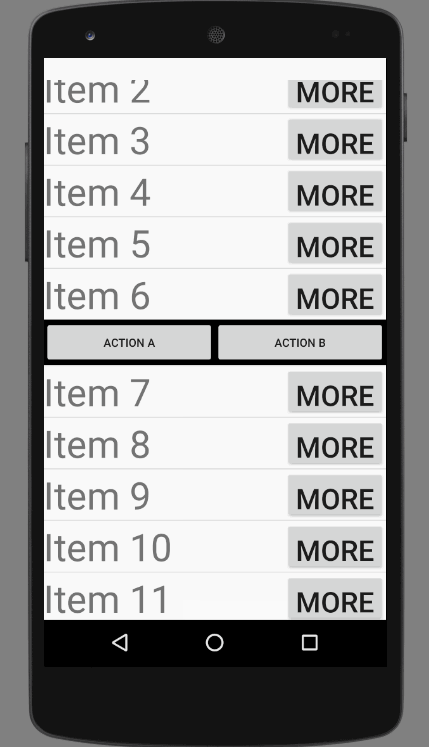
直接上效果图:
效果非常不错,其实这并不是一个ExpandableListView,这实际上是一个自定义的ListView和Adapter。
这是MainActivity的布局:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<merge
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:fitsSystemWindows="true"
tools:context="com.example.chenjiahuan.myapplication.MainActivity">
<com.tjerkw.slideexpandable.library.ActionSlideExpandableListView
android:id="@+id/lv"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
/>
</merge>
这是Item的布局:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:id="@+id/item">
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/text"
android:text="Hello World"
android:textSize="40dp"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/expandable_toggle_button"
android:text="More"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/text"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_alignTop="@id/text"
android:textSize="30dp"/>
</RelativeLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:id="@+id/expandable"
android:background="#000000">
<Button
android:id="@+id/buttonA"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="0.5"
android:text="Action A"
android:textSize="12dip"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/buttonB"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="0.5"
android:text="Action B"
android:textSize="12dip"/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>布局里面唯一要注意的就是item布局中 控制展开、收起和需要展开、收起的这两个控件的id:expandable_toggle_button,expandable。MainActivity中的代码无非就是填充数据了,这里就不浪费篇幅了。
二、SlideExpandableListView的源码框架深入解析
在MainActivity中重要的代码如下:
首先是对展开、收起控件点击事件的监听,这里使用回调的方式传入了你需要监听的控件id,:
lv.setItemActionListener(new ActionSlideExpandableListView.OnActionClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View listView, View buttonview, int position) {
String actionName = "";
if(buttonview.getId()==R.id.buttonA) {
actionName = "buttonA";
} else {
actionName = "ButtonB";
}
Toast.makeText(
MainActivity.this,
"Clicked Action: "+actionName+" in list item "+position,
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT
).show();
}
}, R.id.buttonA, R.id.buttonB);其次就是listview的数据填充了:
lv.setAdapter(buildDummyData());以上就是我们使用的时候需要去写的代码,接下来才是重点 — 效果是如何实现的。
先从整体架构出发,之前已经说到这个效果其实就是自定义的ListView+自定义的Adapter,我们先从Adapter看起。
封装的基本适配器 — WrapperListAdapterImpl:
public abstract class WrapperListAdapterImpl extends BaseAdapter implements WrapperListAdapter {
protected final ListAdapter wrapped;
public WrapperListAdapterImpl(ListAdapter wrapped) {
this.wrapped = wrapped;
}
@Override
public ListAdapter getWrappedAdapter() {
return wrapped;
}
@Override
public boolean areAllItemsEnabled() {
return wrapped.areAllItemsEnabled();
}
@Override
public boolean isEnabled(int i) {
return wrapped.isEnabled(i);
}
@Override
public void registerDataSetObserver(DataSetObserver dataSetObserver) {
wrapped.registerDataSetObserver(dataSetObserver);
}
@Override
public void unregisterDataSetObserver(DataSetObserver dataSetObserver) {
wrapped.unregisterDataSetObserver(dataSetObserver);
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return wrapped.getCount();
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int i) {
return wrapped.getItem(i);
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int i) {
return wrapped.getItemId(i);
}
@Override
public boolean hasStableIds() {
return wrapped.hasStableIds();
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View view, ViewGroup viewGroup) {
return wrapped.getView(position, view, viewGroup);
}
@Override
public int getItemViewType(int i) {
return wrapped.getItemViewType(i);
}
@Override
public int getViewTypeCount() {
return wrapped.getViewTypeCount();
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return wrapped.isEmpty();
}
@Override
public void notifyDataSetChanged() {
if (wrapped instanceof BaseAdapter) {
((BaseAdapter)wrapped).notifyDataSetChanged();
}
}
@Override
public void notifyDataSetInvalidated() {
if (wrapped instanceof BaseAdapter) {
((BaseAdapter)wrapped).notifyDataSetInvalidated();
}
}
}这是WrapperListAdapterImpl这个所有的代码,粘贴了这么多代码并不是想要占篇幅,你可以看到,在这个适配器类中它维护了一个 ListAdapter 的实例,所有有用、需要重写的方法都由 ListAdapter 的实例去实现。事实上如果不是要实现特别复杂的UI,并不一定要做这样的实现,我们可以联想到在写简单的ListView的时候,其实并没有这么多的方法需要重写。
我们来看一看 BaseAdapter 的源码:
public abstract class BaseAdapter implements ListAdapter, SpinnerAdapter {
private final DataSetObservable mDataSetObservable = new DataSetObservable();
public boolean hasStableIds() {
return false;
}
public void registerDataSetObserver(DataSetObserver observer) {
mDataSetObservable.registerObserver(observer);
}
public void unregisterDataSetObserver(DataSetObserver observer) {
mDataSetObservable.unregisterObserver(observer);
}
/**
* Notifies the attached observers that the underlying data has been changed
* and any View reflecting the data set should refresh itself.
*/
public void notifyDataSetChanged() {
mDataSetObservable.notifyChanged();
}
/**
* Notifies the attached observers that the underlying data is no longer valid
* or available. Once invoked this adapter is no longer valid and should
* not report further data set changes.
*/
public void notifyDataSetInvalidated() {
mDataSetObservable.notifyInvalidated();
}
public boolean areAllItemsEnabled() {
return true;
}
public boolean isEnabled(int position) {
return true;
}
public View getDropDownView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
return getView(position, convertView, parent);
}
public int getItemViewType(int position) {
return 0;
}
public int getViewTypeCount() {
return 1;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return getCount() == 0;
}
}我们可以看到 BaseAdapter 它是实现了 ListAdapter 的,也重写一些常用的方法,比如 getViewTypeCount,而 WrapperListAdapterImpl 是要做的事完全的继承 Adapter 功能的适配器,所以维护 ListAdapter 的实例,可以保证在需要添加被封装对象的功能的同时,其他的特性不会被影响。 就以当前项目为例,我们要做的就是在 getView 保证正常显示的同时,添加动画效果。
在ActionSlideExpandableListView中调用setAdapter其实实现的是其父类SlideExpandableListView的方法:
public void setAdapter(ListAdapter adapter) {
this.adapter = new SlideExpandableListAdapter(adapter);
super.setAdapter(this.adapter);
}可以看出,最终ListView的setAdapter的方法最终拿到的Adapter其实是SlideExpandableListAdapter。
SlideExpandableListAdapter的源码:
public class SlideExpandableListAdapter extends AbstractSlideExpandableListAdapter {
private int toggle_button_id;
private int expandable_view_id;
public SlideExpandableListAdapter(ListAdapter wrapped, int toggle_button_id, int expandable_view_id) {
super(wrapped);
this.toggle_button_id = toggle_button_id;
this.expandable_view_id = expandable_view_id;
}
public SlideExpandableListAdapter(ListAdapter wrapped) {
this(wrapped, R.id.expandable_toggle_button, R.id.expandable);
}
@Override
public View getExpandToggleButton(View parent) {
return parent.findViewById(toggle_button_id);
}
@Override
public View getExpandableView(View parent) {
return parent.findViewById(expandable_view_id);
}
}这个类中提供了两个构造方法,一个是主动设置点击控件和动画控件,另一个则是支持默认id的控件(之前item布局中需要主要的地方还记得吗,就是这个id)。另外还提供了获取这些控件的两个方法。其实这个类,就我而言,有一种为了封装而封装的感觉,真正核心的代码在它的父类 AbstractSlideExpandableListAdapter 里面,其实完全可以都写在 AbstractSlideExpandableListAdapter 里面的,纯属个人观点,敬请吐槽。
ActionSlideExpandableListView中的代码非常简单,维护了一个 listener 和重写了getView的方法,大家把demo下载下来,里面有源码的。
旁枝末节该看的都看过了,现在我们来看真正的实现AbstractSlideExpandableListAdapter:
在AbstractSlideExpandableListAdapter中维护了
/**
* Reference to the last expanded list item.
* Since lists are recycled this might be null if
* though there is an expanded list item
*/
private View lastOpen = null;
/**
* The position of the last expanded list item.
* If -1 there is no list item expanded.
* Otherwise it points to the position of the last expanded list item
*/
private int lastOpenPosition = -1;
/**
* Default Animation duration
* Set animation duration with @see setAnimationDuration
*/
private int animationDuration = 330;
/**
* A list of positions of all list items that are expanded.
* Normally only one is expanded. But a mode to expand
* multiple will be added soon.
*
* If an item onj position x is open, its bit is set
*/
private BitSet openItems = new BitSet();
/**
* We remember, for each collapsable view its height.
* So we dont need to recalculate.
* The height is calculated just before the view is drawn.
*/
private final SparseIntArray viewHeights = new SparseIntArray(10);
/**
* Will point to the ListView
*/
private ViewGroup parent;我们从上往下先说一下它们的作用,具体的一会儿看代码的时候说:
lastOpen:记录最后一个展开的View
lastOpenPosition:记录最后一个展开的View的position
animationDuration:展开、收起的动画事件
openItems:判断一个Item它是展开或者收起的状态需要一个标志来记录,这里用了这个类BitSet
parent : 这其实就是ListView的实例
viewHeights:这里用一个长度为10的SparseIntArray记录需要绘制View的高度,这样就不用每次都去重新测量高度了。
到底为止:重要的常量都已经看完了,接下来,就要看getView的方法实现了
getView:
@Override
public View getView(int position, View view, ViewGroup viewGroup) {
this.parent = viewGroup;
view = wrapped.getView(position, view, viewGroup);
enableFor(view, position);
return view;
}getView中通过封装的wrapped获取了基本功能的Item的View,传给了enableFor(view, position)这个方法,并且给 this.parent 赋了值:
public void enableFor(View parent, int position) {
View more = getExpandToggleButton(parent);
View itemToolbar = getExpandableView(parent);
itemToolbar.measure(parent.getWidth(), parent.getHeight());
enableFor(more, itemToolbar, position);
itemToolbar.requestLayout();
}enableFor(more, itemToolbar, position)这个方法里面的代码是动画所有逻辑的代码,
考虑到了动画未结束多次点击的情况:
Animation a = target.getAnimation();
if (a != null && a.hasStarted() && !a.hasEnded()) {
a.setAnimationListener(new Animation.AnimationListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationStart(Animation animation) {
}
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd(Animation animation) {
view.performClick();//performClick()这是主动响应点击事件的方法
}
@Override
public void onAnimationRepeat(Animation animation) {
}
});考虑到了比如展开和收起不是同一个控件的情况:
if (type == ExpandCollapseAnimation.EXPAND) {
if (lastOpenPosition != -1 && lastOpenPosition != position) {
if (lastOpen != null) {
animateView(lastOpen, ExpandCollapseAnimation.COLLAPSE);
notifiyExpandCollapseListener(
ExpandCollapseAnimation.COLLAPSE,
lastOpen, lastOpenPosition);
}
openItems.set(lastOpenPosition, false);
}
lastOpen = target;
lastOpenPosition = position;
} else if (lastOpenPosition == position) {
lastOpenPosition = -1;
}
animateView(target, type);在type表示当前点击的情况是要进行展开的动画
if (lastOpenPosition != -1 && lastOpenPosition != position) //这行代码表示之前有展开的view没有收起,不但做了当前item展开的动画,还进行了收起的动画
以上这些都是思想和逻辑,然后就是这种柔和展开的动画了,这个动画是在ExpandCollapseAnimation这个类里面去实现的,非常简洁的类:
public class ExpandCollapseAnimation extends Animation {
private View mAnimatedView;
private int mEndHeight;
private int mType;
public final static int COLLAPSE = 1;
public final static int EXPAND = 0;
private LinearLayout.LayoutParams mLayoutParams;
public ExpandCollapseAnimation(View view, int type) {
mAnimatedView = view;
mEndHeight = mAnimatedView.getMeasuredHeight();
mLayoutParams = ((LinearLayout.LayoutParams) view.getLayoutParams());
mType = type;
if(mType == EXPAND) {
mLayoutParams.bottomMargin = -mEndHeight;
} else {
mLayoutParams.bottomMargin = 0;
}
view.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
@Override
protected void applyTransformation(float interpolatedTime, Transformation t) {
super.applyTransformation(interpolatedTime, t);
if (interpolatedTime < 1.0f) {
if(mType == EXPAND) {
mLayoutParams.bottomMargin = -mEndHeight + (int) (mEndHeight * interpolatedTime);
} else {
mLayoutParams.bottomMargin = - (int) (mEndHeight * interpolatedTime);
}
Log.d("ExpandCollapseAnimation", "anim height " + mLayoutParams.bottomMargin);
mAnimatedView.requestLayout();
} else {
if(mType == EXPAND) {
mLayoutParams.bottomMargin = 0;
mAnimatedView.requestLayout();
} else {
mLayoutParams.bottomMargin = -mEndHeight;
mAnimatedView.setVisibility(View.GONE);
mAnimatedView.requestLayout();
}
}
}
}里面的参数我就不一一解释了,毕竟作者的命名都很规范,而且代码很少,一眼看穿!
applyTransformation这个方法是自定义动画的主要方法,这个方法里面可以看到,对展开控件的LayoutParams做了控制,然后调用了requestLayout这个方法,让expand_view的父控件对其位置重新设置。大家可以做一个小demo,会发现requestLayout的时候位置的变化不是类似于 visiable或者gone,突然出现和消失,会有画出来的效果,只不过是比较快的,即便不是 Animation也是可以做出SlideExpandableListView的效果,只不过效果比较生硬,利用 Animation 的duration使得动画效果更加柔和。
解释完动画,我们再来看看 animateView()这个方法:
private void animateView(final View target, final int type) {
Animation anim = new ExpandCollapseAnimation(
target,
type
);
anim.setDuration(getAnimationDuration());
anim.setAnimationListener(new AnimationListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationStart(Animation animation) {}
@Override
public void onAnimationRepeat(Animation animation) {}
/**
*在动画结束的时候,这里考虑到了屏幕底部展开的控件会被推到屏幕外面看不到的情况,让listView 整个向上移动了item的距离
**/
@Override
public void onAnimationEnd(Animation animation) {
if (type == ExpandCollapseAnimation.EXPAND) {
if (parent instanceof ListView) {
ListView listView = (ListView) parent;
int movement = target.getBottom();
Rect r = new Rect();
boolean visible = target.getGlobalVisibleRect(r);
Rect r2 = new Rect();
listView.getGlobalVisibleRect(r2);
if (!visible) {
listView.smoothScrollBy(movement, getAnimationDuration());
} else {
if (r2.bottom == r.bottom) {
listView.smoothScrollBy(movement, getAnimationDuration());
}
}
}
}
}
});
target.startAnimation(anim);
}总结:
到这里基本上把我理解的都讲出来了,可能还有遗漏的地方,或者大家不理解的地方,请大家指出来,谢谢啦。






















 9133
9133

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








