全概率......
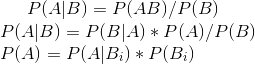
Description Problem G Output: Standard Output
N friends go to the local super market together. The probability of their buying something from the market is
InputThe input file contains at most 50 sets of inputs. The description of each set is given below:
First line of each set contains two integers N (1 ≤ N ≤ 20) and r(0 ≤ r ≤ N). Meaning of N and r are given in the problem statement. Each of the next N lines contains one floating-point number
Input is terminated by a case where the value of N and r is zero. This case should not be processes.
OutputFor each line of input produce N+1 lines of output. First line contains the serial of output. Each of the next N lines contains a floating-point number which denotes the buying probability of the i-th friend given that exactly r has bought something. These values should have six digits after the decimal point. Follow the exact format shown in output for sample input. Small precision errors will be allowed. For reasonable precision level use double precision floating-point numbers.Sample Input Output for Sample Input
Problem-setter: Shahriar Manzoor Source
Root :: AOAPC II: Beginning Algorithm Contests (Second Edition) (Rujia Liu) :: Chapter 10. Maths ::
Examples
Root :: AOAPC I: Beginning Algorithm Contests (Rujia Liu) :: Volume 6. Mathematical Concepts and Methods Root :: AOAPC I: Beginning Algorithm Contests -- Training Guide (Rujia Liu) :: Chapter 2. Mathematics :: Probability :: Exercises: Beginner Root :: Competitive Programming 2: This increases the lower bound of Programming Contests. Again (Steven & Felix Halim) :: Mathematics :: Probability Theory Root :: Prominent Problemsetters :: Shahriar Manzoor Root :: Competitive Programming: Increasing the Lower Bound of Programming Contests (Steven & Felix Halim) :: Chapter 5. Mathematics :: Probability Theory Root :: Competitive Programming 3: The New Lower Bound of Programming Contests (Steven & Felix Halim) :: Mathematics :: Probability Theory :: Standard |  |
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int n,r;
double p[50];
double ans[50];
int cot(int x)
{
int ret=0;
while(x)
{
x=x&(x-1);
ret++;
}
return ret;
}
int main()
{
int cas=1;
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&r)!=EOF)
{
if(n==0&&r==0) break;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%lf",p+i);
memset(ans,0,sizeof(ans));
double all=0.0;
for(int i=0;i<(1<<n);i++)
{
if(cot(i)==r)
{
double ppp=1.;
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(i&(1<<j)) ppp*=p[j];
else ppp*=(1-p[j]);
}
all+=ppp;
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(i&(1<<j)) ans[j]+=ppp;
}
}
}
printf("Case %d:\n",cas++);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf("%.6lf\n",ans[i]/all);
}
}
return 0;
}
























 1533
1533

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








