在前面的章节中,分别介绍了 Web、App、接口自动化测试用例的生成。但是在前文中实现的效果均为在控制台打印自动化测试的用例。用例需要手动粘贴,调整之后再执行。
那么其实这个手动粘贴、执行的过程,也是可以直接通过人工智能完成的。
应用价值
- 通过人工智能代替人工操作的部分,节省时间,提升效率。
- 通过封装更多的 Tools,让 Agent 更为智能。
实践演练
实现原理
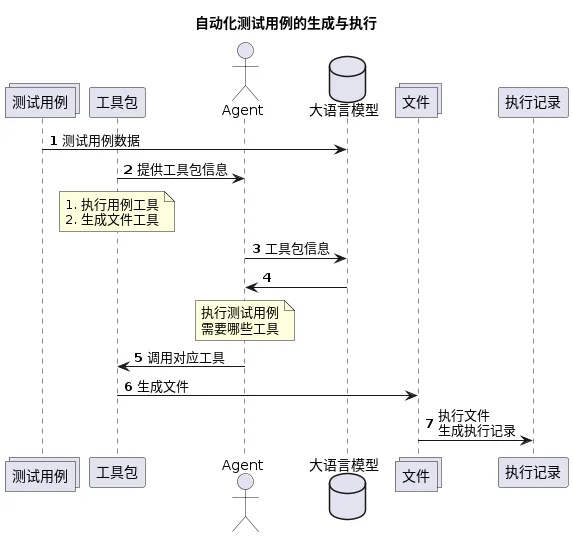
实现思路
在理解需求之后,我们可以了解到我们需要让 Agent 具备两个功能:
- 输入源码信息,生成 python 文件。
- 输入文件名,执行 pytest 测试文件功能。
如此,可以通过如下两个步骤实现需求:
- 工具包封装。
- 实现 Agent。
工具包封装
为了让工具包更易被大模型理解,我们将注释调整为英文,提升准确率。同时为了传参的时候不出现格式错误问题,通过args_schema限制参数结构与格式(tools 章节有具体讲解)。
通过 AGENT 实现需求
- 首先封装 Agent,绑定工具,输入提示词。在示例中,是在 LangChain 官方提供的
structured-chat-agent提示词基础之上修改的提示词,添加了一个code变量。目的是为了后面 code 可以由其他的 chain 的执行结果而来。
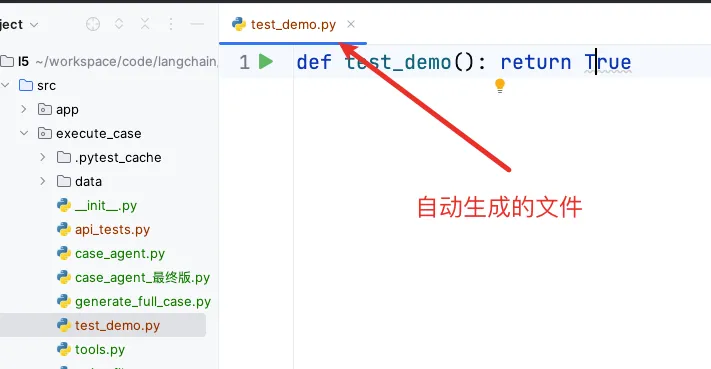
由以上的步骤,即可生成一个源码文件:
- 在生成源码文件后,可以继续补充提示词,要求Agent 执行对应的测试用例:
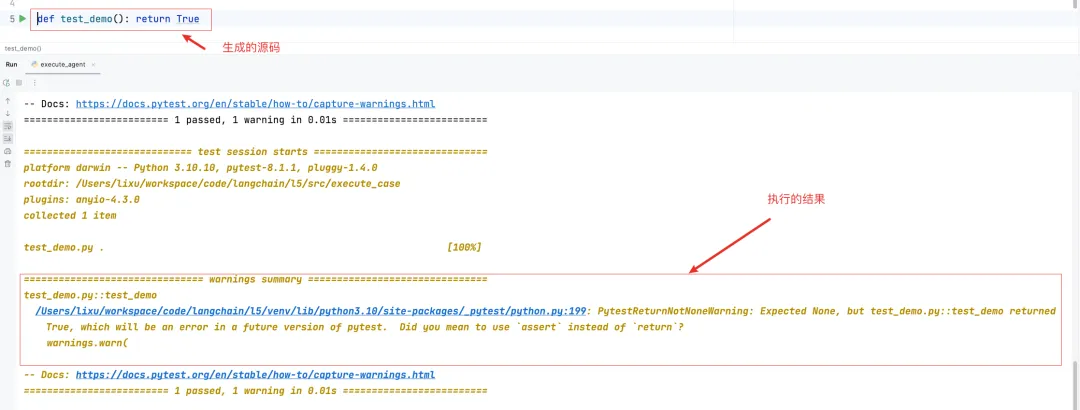
到这里,通过 Agent 就能自动生成测试用例文件,执行测试用例了。
与其他的场景结合
在前面的章节中,已经实现了自动生成接口自动化测试用例的操作。可以直接与前面的操作结合,自动生成接口自动化测试用例,并执行测试用用例。
注意:load_case 如何实现在前面章节:《基于LangChain手工测试用例转接口自动化测试生成工具》,已有对应讲解
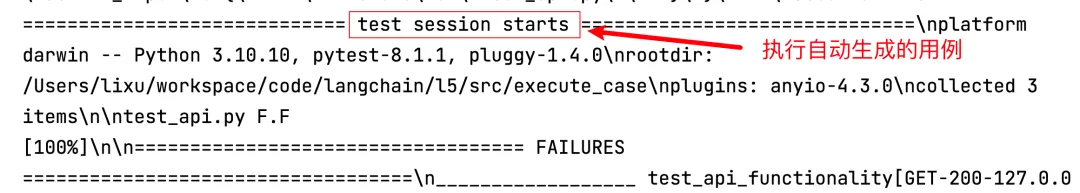
执行之后,即可在控制台看到生成的接口自动化测试用例的执行记录。
总结
- 自动化测试用例的生成与执行的实现原理。
- 自动化测试用例的生成与执行的实现思路。
- 利用 Agent 实现自动化测试用例的生成与执行。





















 1214
1214

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








