固定worker工作池
服务器编程中使用最多的就是通过线程池来提升服务的并发处理能力。在Go语言编程中,一样可以轻松地构建固定数目的goroutines作为工作线程池。下面还是以计算多个整数的和为例来说明这种并发范式。
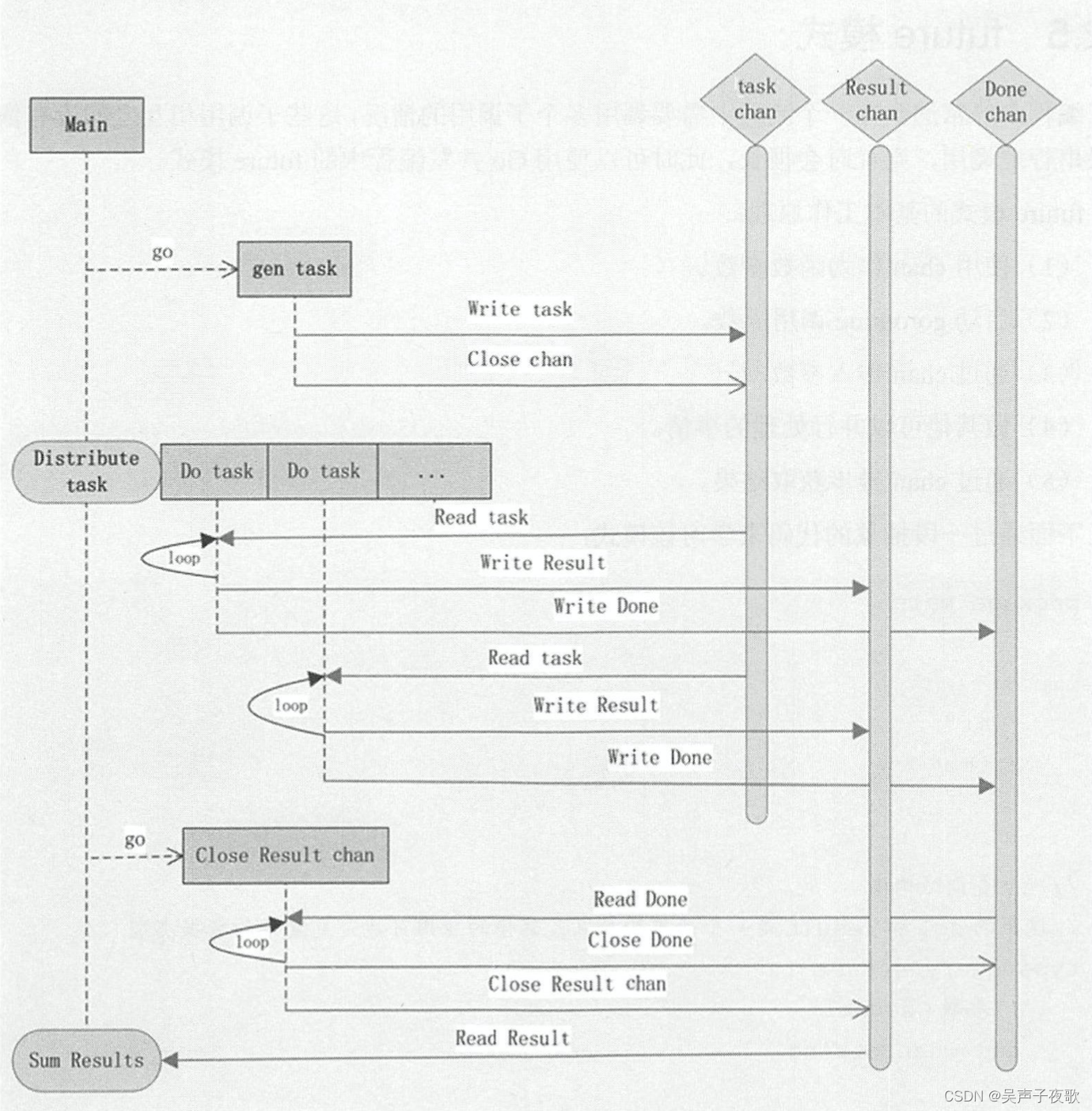
程序中除了主要的main goroutine,还开启了如下几类goroutine:
- 初始化任务的goroutine。
- 分发任务的goroutine。
- 等待所有worker结束通知,然后关闭结果通道的goroutine。
main函数负责拉起上述goroutine,并从结果通道获取最终的结果。
程序采用三个通道,分别是:
- 传递task任务的通道。
- 传递task结果的通道。
- 接收worker处理完任务后所发送通知的通道。
相关的代码如下:
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
workers := NUMBER
//工作通道
taskchan := make(chan task, 10)
//结果通道
resultchan := make(chan int, 10)
//worker信号通道
done := make(chan struct{}, 10)
//初始化task的goroutine,计算100个自然数之和
go InitTask(taskchan, resultchan, 100)
//分发任务到NUMBER个goroutine池
DistributeTask(taskchan, workers, done)
//获取各个goroutine处理完任务的通知,并关闭结果通道
go CloseResult(done, resultchan, workers)
//通过结果通道获取结果汇总
sum := ProcessResult(resultchan)
fmt.Println("sum=", sum)
}
//工作池的goroutine数目
const (
NUMBER = 10
)
//工作任务
type task struct {
begin int
end int
result chan<- int
}
//任务执行:计算begin到end的和
//执行结果写入结果chan result
func (t *task) do() {
sum := 0
for i := t.begin; i <= t.end; i++ {
sum += i
}
t.result <- sum
}
//初始化待处理task chan
func InitTask(taskchan chan<- task, r chan int, p int) {
qu := p / 10
mod := p % 10
high := qu * 10
for j := 0; j < qu; j++ {
b := 10*j + 1
e := 10 * (j + 1)
tsk := task{
begin: b,
end: e,
result: r,
}
taskchan <- tsk
}
if mod != 0 {
tsk := task{
begin: high + 1,
end: p,
result: r,
}
taskchan <- tsk
}
close(taskchan)
}
//读取task chan并分发到worker goroutine处理,总的数量是workers
func DistributeTask(taskchan <-chan task, workers int, done chan struct{}) {
for i := 0; i < workers; i++ {
go ProcessTask(taskchan, done)
}
}
//工作goroutine处理具体工作,并将处理结果发送到结果chan
func ProcessTask(taskchan <-chan task, done chan struct{}) {
for t := range taskchan {
t.do()
}
done <- struct{}{}
}
//功过done channel同步等待所有工作goroutine的结果,然后关闭结果chan
func CloseResult(done chan struct{}, resultchan chan int, workers int) {
for i := 0; i < workers; i++ {
<-done
}
close(done)
close(resultchan)
}
//读取结果通道,汇总结果
func ProcessResult(resultchan chan int) int {
sum := 0
for r := range resultchan {
sum += r
}
return sum
}
//结果
sum= 5050
程序的逻辑分析:
- 构建task并发送到task通道中。
- 分别启动n个工作线程,不停地从task通道中获取任务,然后将结果写入结果通道。如果任务通道被关闭,则负责向收敛结果的goroutine发送通知,告诉其当前worker已经完成工作。
- 收敛结果的goroutine接收到所有task已经处理完毕的信号后,主动关闭结果通道。
- main中的函数ProcessResult读取并统计所有的结果。
整个工作流程如图:






















 675
675











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








