本文介绍defaultServiceManager()的流程。这里的defaultServiceManager()返回的是”IServiceManager对象”,获取”IServiceManager对象”的目的是为了和”ServiceManager进程”进行通信。例如,Server要通过”IServiceManager对象”发送请求指令注册到”ServiceManager进程”中,Client要通过”IServiceManager对象”发送请求来获取”Server对象”。
这里要搞清楚:defaultServiceManager()获取到的,不是”ServiceManager进程”,而是”IServiceManager对象”。”ServiceManager进程”是一个守护进程,而defaultServiceManager()获取到的是C++层的IServiceManager类的一个实例。当然,通过该defaultServiceManager()返回的”IServiceManager对象”是可以和ServiceManager进行通信的。注意:本文是基于Android 4.4.2版本进行介绍的!
目录
1. defaultServiceManager概述
2. defaultServiceManager流程详解
2.1. defaultServiceManager()
2.2. ProcessState::self()
2.3. ProcessState::ProcessState()
2.4. ProcessState::open_driver()
2.5. mmap()
2.6. ProcessState::getContextObject()
2.7. ProcessState::getStrongProxyForHandle()
2.8. ProcessState::lookupHandleLocked()
2.9. BpBinder::BpBinder
2.10. IPCThreadState::self()
2.11. IPCThreadState::IPCThreadState()
2.12. interface_cast()
defaultServiceManager概述
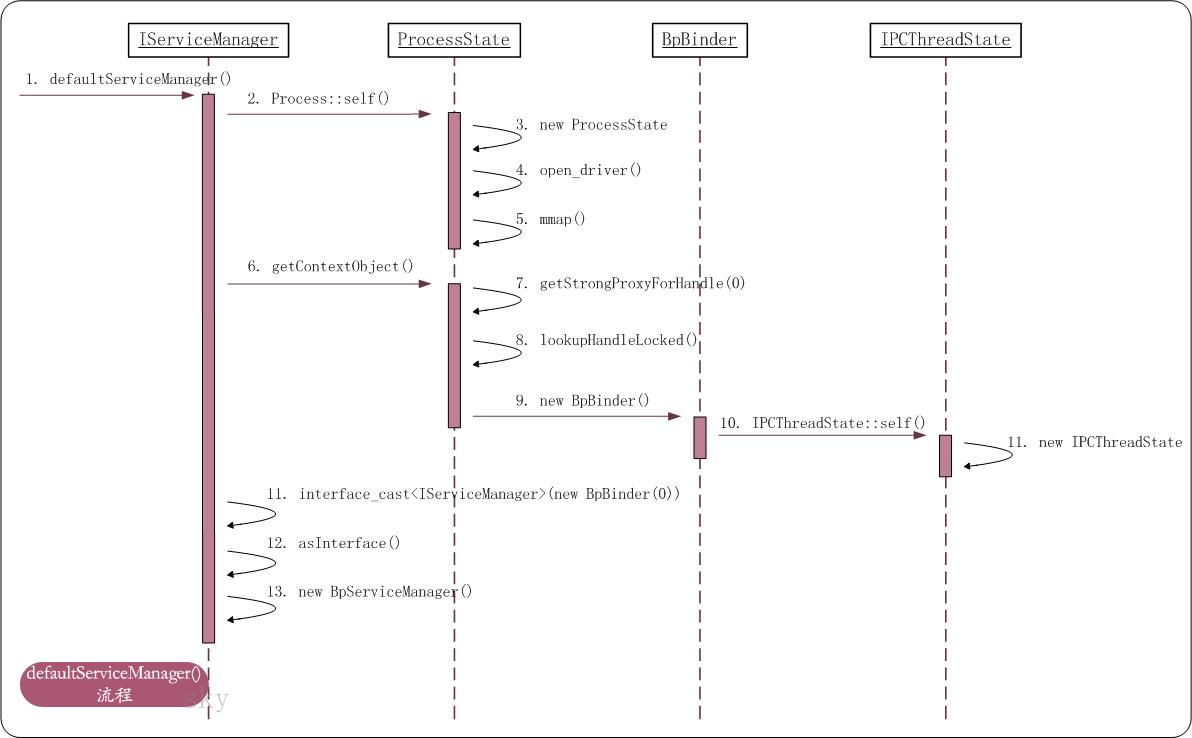
1. defaultServiceManager流程图
上面是defaultServiceManager()的时序图。
defaultServiceManager()会返回一个sp类型的对象。IServiceManager提供了addService()供MediaPlayerService等服务注册到ServiceManager中,提供了getService()供MediaPlayer等MediaPlayer等客户端获取服务。
它首先会调用ProcessState::self()获取到ProcessState对象,该ProcessState对象是采用单例模式创建的;因此,当ProcessState::self()第一次被调用时,会新建ProcessState对象。在ProcessState的构造函数中,会先通过open_driver()打开”/dev/binder”,接着调用mmap()映射内存到当前进程中。此时,ProcessState就初始化完毕,它将”/dev/binder”的文件句柄以及映射内存都保存在自己的私有成员中。
在获取到ProcessState对象之后,会通过该对象调用getContextObject()来获取一个IBinder对象。getContextObject()会调用getStrongProxyForHandle(0)来获取”句柄0的强引用代理对象”,这里的句柄0被赋予了特殊意义;它就是ServiceManager的句柄,在Binder驱动中,若获取到句柄的值是0,则会将其目标当作是ServiceManager。getStrongProxyForHandle(0)会先通过lookupHandleLocked()在”ProcessState的矢量数组mHandleToObject”中查找句柄为0的对象;找不到的话,则新建句柄为0的对象,并将其添加到mHandleToObject矢量数组中;这样,下次再通过getStrongProxyForHandle()查找时,就能快速的找到。由此可见,mHandleToObject是ProcessState中保存句柄的缓冲数组。 随后,会新建句柄0对应的BpBinder对象,BpBinder是IBinder的代理;这里就获取到了ServiceManager的BpBinder代理对象。简而言之,getContextObject()的目的就是获取ServiceManager对应的BpBinder代理对象。 在新建BpBinder时,会通过IPCThreadState::self()获取IPCThreadState对象;因为,需要通过IPCThreadState对象来与Binder驱动进行交互。
前面已经成功获取到了ServiceManager的BpBinder代理,而defaultServiceManager()返回的是IServiceManager对象。这里,使用了一个技巧,通过宏interface_cast而调用asInterface()函数,从而返回IServiceManager的代理BpServiceManager。这样,defaultServiceManager()就执行完毕了。
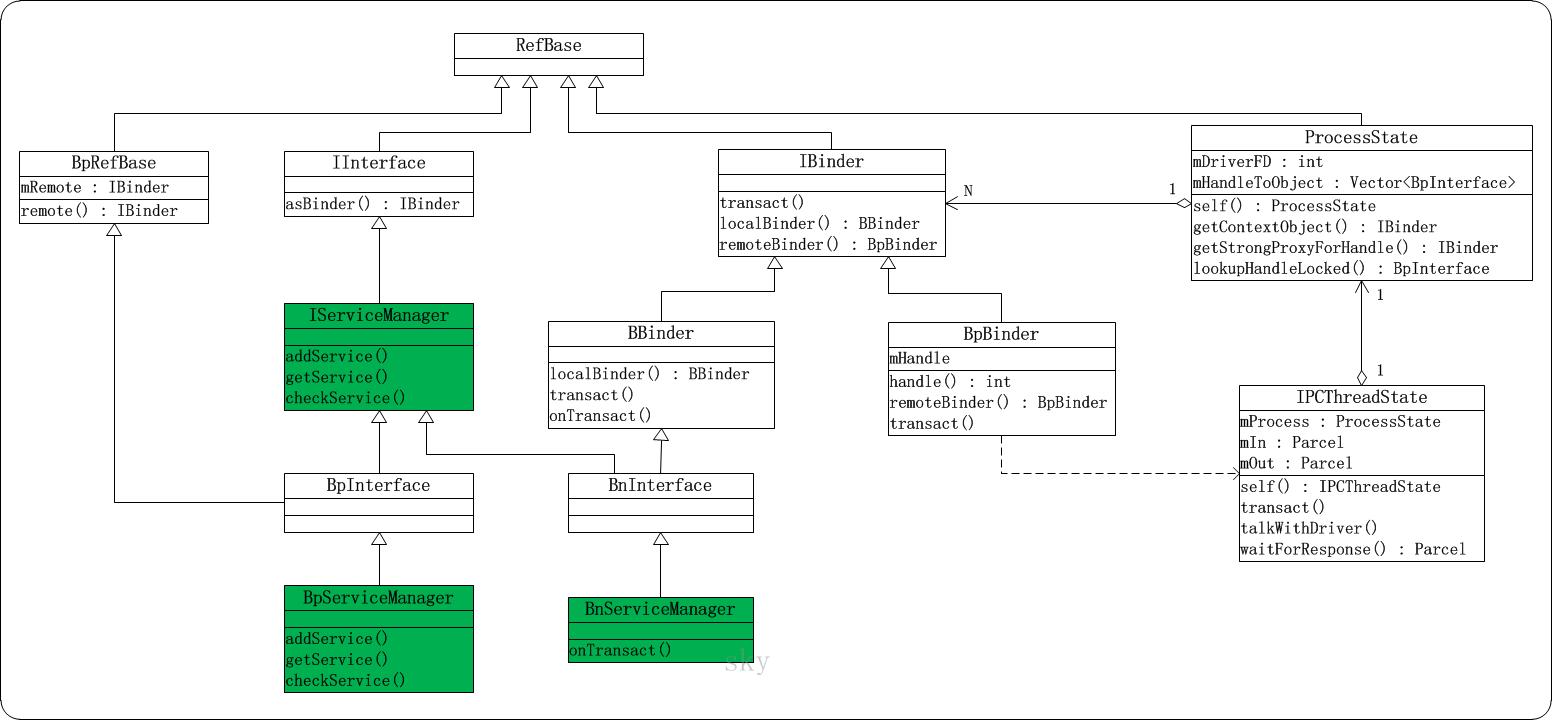
在上面的流程中,涉及到了比较多的类。下面通过类图理清它们之间的关系。
2. defaultServiceManager相关类的类图
上面是获取defaultServiceManager()时涉及到的类的类图。defaultServiceManager()虽然在IServiceManager.cpp中实现,但它并不属于IServiceManager的成员方法,而是一个全局方法。
-
RefBase
它定义在system/core/include/utils/RefBase.h中。RefBase是一个公共父类,它声明了许多常用的接口。包括增加引用计数,获取引用计数,新增对象的弱引用等接口。 -
IInterface
它定义在frameworks/native/include/binder/IInterface.h中。和RefBase类似,它也是一个公共父类,IInterface中声明了asBinder()方法,用于获取对象的IBinder对象。 -
IBinder
它定义在frameworks/native/include/binder/IBinder.h中。IBinder也是一个抽象出来的类,它包括了localBinder(), remoteBinder()和transact()等非常重要的接口。IBinder有两个直接子类类:BpBinder和BBinder。
BpBinder是Binder代理类。通过remoteBinder()可以获取BpBinder对象;而且,对于C++层而言,它相当于一个远程Binder。BpBinder的事务接口transact()会调用IPCThreadState的transact(),进而实现与Binder驱动的事务交互。此外,BpBinder中有一个mHandle句柄成员,它用来保存Server位于Binder驱动中的”Binder引用的描述”。句柄0是ServiceManager的句柄。
BBinder是本地Binder。通过localBinder()可以获取BBinder对象。当Server收到请求之后,会调用BBinder的onTransact()函数进行处理。而不同的Server会重载onTransact()函数,从而可以根据各自的情况对事务进行处理。 -
BpInterface
它定义在frameworks/native/include/binder/IInterface.h中。实际上,BpInterface是一个模板类,同时继承了BpRefBase和INTERFACE,这里的INTERFACE是模板。像IServiceManager,IMediaPlayerService等Server都是通过继承模板类是实现的。 -
BnInterface
它定义在frameworks/native/include/binder/IInterface.h中。和BpInterface类似,BnInterface也是一个模板类,它同时继承了BBinder和INTERFACE。像BnServiceManager,BnMediaPlayerService等本地Server都是通过继承模板类是实现的。 -
BpRefBase
它定义在frameworks/native/include/binder/Binder.h中。BpRefBase继承于RefBase,它有一个IBinder*类型的成员mRemote,同时提供了获取该mRemote的方法。实际上,该mRemote就是BpBinder对象。 -
ProcessState
它定义在frameworks/native/libs/binder/ProcessState.cpp中中。ProcessState的实例是采用单例模式实现的,它拥有两个非常重要的成员:mDriverFD和mHandleToObject。
mDriverFD是文件”/dev/binder”的句柄,而mHandleToObject是一个Vector矢量数组,矢量数组中的每个元素都保存了两个变量:Server的句柄,以及Server对应的BpBinder对象。实际上,Server的句柄是”Server在Binder驱动中的Binder引用的描述”;句柄0是ServiceManager的句柄。 关于Binder引用,可以回顾Android Binder机制(二) Binder中的数据结构。 -
IPCThreadState
它定义在frameworks/native/libs/binder/IPCThreadState.cpp中中。IPCThreadState的实例也是采用单例模式实现的,它是正在与Binder驱动进行交互的类。
理解上面几个类的基本概念之后,现在在从整体上对它们进行一下介绍!
对于一个Server而言,它都会存在一个”远程BpBinder对象”和”本地BBinder对象”。
(01) 远程BpBinder对象的作用,是和Binder驱动进行交互。具体的方式是,当Server要向Binder发起事务请求时,会调用BpBinder的transact()接口,而该接口会调用到IPCThreadState::transact()接口,通过IPCThreadState类来和Binder驱动交互。此外,该BpBinder在Binder驱动中的Binder引用的描述会被保存到ProcessState的mHandleToObject矢量缓冲数组中。
(02) 本地BBinder对象的作用,是Server响应Client请求的类。当Client有请求发送给Server时,都会调用到BBinder的onTransact()函数,而每个Server都会覆盖onTransact()函数。这样,每个Server就可以在onTransact()中根据自己的情况对请求进行处理。
defaultServiceManager流程详解
接下来通过源码来查看defaultServiceManager()的实现。通过源码分析,会对上面的类图有更清楚的认识!
1. defaultServiceManager()
-
sp<IServiceManager> defaultServiceManager()
-
{
-
if (gDefaultServiceManager !=
NULL)
return gDefaultServiceManager;
-
-
{
-
AutoMutex _l(gDefaultServiceManagerLock);
-
while (gDefaultServiceManager ==
NULL) {
-
gDefaultServiceManager = interface_cast<IServiceManager>(
-
ProcessState::self()->getContextObject(
NULL));
-
if (gDefaultServiceManager ==
NULL)
-
sleep(
1);
-
}
-
}
-
-
return gDefaultServiceManager;
-
}
说明:该代码定义在frameworks/native/libs/binder/IServiceManager.cpp中。它是获取IServiceManager对象,该函数的声明在frameworks/native/include/binder/IServiceManager.h中。虽然defaultServiceManager()在IServiceManager.cpp文件中实现,但是它并不是IServiceManager的一个成员方法,而是一个全局方法。
(01) gDefaultServiceManagerLock是全局互斥锁,gDefaultServiceManager是全局的IServiceManager对象。它们都定义在frameworks/native/libs/binder/Static.cpp中。
(02) gDefaultServiceManager是采用单例模式实现的,第一次调用该函数时,会创建gDefaultServiceManager对象。gDefaultServiceManager的实现可以简化为以下语句:
gDefaultServiceManager = interface_cast<IServiceManager>(ProcessState::self()->getContextObject(NULL));
下面逐个对该语句中的代码进行解析。
2. ProcessState::self()
-
sp<ProcessState> ProcessState::self()
-
{
-
Mutex::Autolock _l(gProcessMutex);
-
if (gProcess !=
NULL) {
-
return gProcess;
-
}
-
gProcess =
new ProcessState;
-
return gProcess;
-
}
说明:该代码定义在frameworks/native/libs/binder/ProcessState.cpp中,它的作用是返回gProcess对象。gProcess也是单例模式对象,它也定义在frameworks/native/libs/binder/Static.cpp中。第一次执行self()时,会新建ProcessState对象。
3. ProcessState::ProcessState()
-
ProcessState::ProcessState()
-
: mDriverFD(open_driver())
-
, mVMStart(MAP_FAILED)
-
, mManagesContexts(
false)
-
, mBinderContextCheckFunc(
NULL)
-
, mBinderContextUserData(
NULL)
-
, mThreadPoolStarted(
false)
-
, mThreadPoolSeq(
1)
-
{
-
if (mDriverFD >=
0) {
-
mVMStart = mmap(
0, BINDER_VM_SIZE, PROT_READ, MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_NORESERVE, mDriverFD,
0);
-
if (mVMStart == MAP_FAILED) {
-
// *sigh*
-
ALOGE(
"Using /dev/binder failed: unable to mmap transaction memory.\n");
-
close(mDriverFD);
-
mDriverFD =
-1;
-
}
-
}
-
...
-
}
说明:在ProcessState的构造函数中,它会进行一系列的初始化。比较重要的有如下两步。
(01) 通过open_driver()打开”/open/binder”,并将文件句柄赋值给mDriverFD。
(02) 通过调用mmap()映射内存。
下面,看看这两步的代码。
4. ProcessState::open_driver()
-
static int open_driver()
-
{
-
// 打开文件/dev/binder
-
int fd = open(
"/dev/binder", O_RDWR);
-
if (fd >=
0) {
-
fcntl(fd, F_SETFD, FD_CLOEXEC);
-
int vers;
-
// 检查/dev/binder的版本
-
status_t result = ioctl(fd, BINDER_VERSION, &vers);
-
if (result ==
-1) {
-
close(fd);
-
...
-
}
-
if (result !=
0 || vers != BINDER_CURRENT_PROTOCOL_VERSION) {
-
close(fd);
-
...
-
}
-
-
// 设置该进程最大线程数
-
size_t maxThreads =
15;
-
result = ioctl(fd, BINDER_SET_MAX_THREADS, &maxThreads);
-
if (result ==
-1) {
-
...
-
}
-
}
else {
-
...
-
}
-
return fd;
-
}
说明:
(01) open_driver()首先打开”/dev/binder”文件。它会对应执行Binder驱动的binder_open()函数,该函数在Android Binder机制(三) ServiceManager守护进程中已经详细介绍过了。
(02) 在成功打开文件之后,就会调用ioctl检查Binder版本,检查版本的部分非常简单(就是读取出版本号,判断读取的版本号与已有的版本号是否一样!),这里就不再对Binder驱动的BINDER_VERSION进行展开了。
(03) 在检查版本通过之后,在调用ioctl(,BINDER_SET_MAX_THREADS,)设置该进程的最大线程数。它会对应调用Binder驱动的binder_ioctl()函数。
注意:要区分”此处的open(“/dev/binder”,…)” 和 “ServiceManager守护进程中的open(“/dev/binder”,…)”。它们分别是属于不同的进程,本文的open(“/dev/binder”,…)是属于调用defaultServiceManager()的进程;而在ServiceManager中的open(“/dev/binder”,…)是属于ServiceManager进程的。
4.1 Binder驱动中binder_ioctl()的BINDER_SET_MAX_THREADS相关部分的源码
-
static long binder_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
-
{
-
int ret;
-
struct binder_proc *proc = filp->private_data;
-
struct binder_thread *thread;
-
unsigned
int size = _IOC_SIZE(cmd);
-
void __user *ubuf = (
void __user *)arg;
-
-
ret = wait_event_interruptible(binder_user_error_wait, binder_stop_on_user_error <
2);
-
-
// 在proc进程中查找该线程对应的binder_thread;若查找失败,则新建一个binder_thread,并添加到proc->threads中。
-
thread = binder_get_thread(proc);
-
...
-
-
switch (cmd) {
-
case BINDER_SET_MAX_THREADS:
-
if (copy_from_user(&proc->max_threads, ubuf,
sizeof(proc->max_threads))) {
-
ret = -EINVAL;
-
goto err;
-
}
-
break;
-
-
...
-
}
-
ret =
0;
-
-
...
-
return ret;
-
}
说明:BINDER_SET_MAX_THREADS的代码很简单,就是将最大线程数目从用户空间拷贝到内核空间,进而赋值给binder_proc->max_threads。
5. mmap()
在执行完open_driver()之后,将调用mmap()映射内存到当前进程的虚拟地址空间。mmap()详细代码在Android Binder机制(三) ServiceManager守护进程中已经详细分析过,这里就不再重复说明了。
到目前为止,ProcessState::self()就分析完毕。gDefaultServiceManager的赋值语句可以进一步的简化:
gDefaultServiceManager = interface_cast<IServiceManager>(ProcessState::getContextObject(NULL));
6. ProcessState::getContextObject()
-
sp<IBinder> ProcessState::getContextObject(
const sp<IBinder>& caller)
-
{
-
return getStrongProxyForHandle(
0);
-
}
说明:getContextObject()调用了getStrongProxyForHandle(0)。这里的0是代表Service Manager的句柄。
7. ProcessState::getStrongProxyForHandle()
-
sp<IBinder> ProcessState::getStrongProxyForHandle(int32_t handle)
-
{
-
sp<IBinder> result;
-
-
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
-
-
// 在矢量数组mHandleToObject中查找"句柄值为handle的handle_entry对象";
-
// 找到的话,则直接返回;找不到的话,则新建handle对应的handle_entry,并将其添加到mHandleToObject中。
-
handle_entry* e = lookupHandleLocked(handle);
-
-
if (e !=
NULL) {
-
IBinder* b = e->binder;
-
if (b ==
NULL || !e->refs->attemptIncWeak(this)) {
-
// 当handle==0(即是Service Manager的句柄)时,尝试去ping Binder驱动。
-
if (handle ==
0) {
-
Parcel data;
-
status_t status = IPCThreadState::self()->transact(
-
0, IBinder::PING_TRANSACTION, data,
NULL,
0);
-
if (status == DEAD_OBJECT)
-
return
NULL;
-
}
-
-
// 新建BpBinder代理
-
b =
new BpBinder(handle);
-
e->binder = b;
-
if (b) e->refs = b->getWeakRefs();
-
result = b;
-
}
else {
-
...
-
}
-
}
-
-
return result;
-
}
说明:getStrongProxyForHandle()的目的是返回句柄为handle的IBinder代理,这里是返回Service Manager的IBinder代理。
(01) lookupHandleLocked(),是在矢量数组mHandleToObject中查找是否有句柄为handle的handle_entry对象。有的话,则返回该handle_entry对象;没有的话,则新建handle对应的handle_entry,并将其添加到矢量数组mHandleToObject中,然后再返回。mHandleToObject是用于保存各个IBinder代理对象的矢量数组,它相当于一个缓冲。
(02) 很显然,此时e!=NULL为true,进入if(e!=NULL)中。而此时e->binder=NULL,并且handle=0;则调用IPCThreadState::self()->transact()尝试去和Binder驱动通信(尝试去ping内核中Binder驱动)。由于Binder驱动已启动,ping通信是能够成功的。ping通信涉及到”Binder机制中Server和Client的通信”,后面再专门对Server和Client的交互进行介绍;这里只要了解ping通信能够成功即可。
(03) 接着,新建BpBinder对象,并赋值给e->binder。然后,将该BpBinder对象返回。
上面对流程进行了整体介绍,下面逐个进行分析!
8. ProcessState::lookupHandleLocked()
-
ProcessState::handle_entry* ProcessState::lookupHandleLocked(
int32_t handle)
-
{
-
const
size_t N=mHandleToObject.size();
-
if (N <= (
size_t)handle) {
-
handle_entry e;
-
e.binder =
NULL;
-
e.refs =
NULL;
-
status_t err = mHandleToObject.insertAt(e, N, handle+
1-N);
-
if (err < NO_ERROR)
return
NULL;
-
}
-
return &mHandleToObject.editItemAt(handle);
-
}
说明:mHandleToObject是Vector矢量数组。mHandleToObject的初始大小为0,因此if (N <= handle)为true。接下来,就新建handle_entry,并将其添加到mHandleToObject中,然后返回该handle_entry。mHandleToObject和handle_entry的定义如下:
-
class ProcessState :
public
virtual RefBase
-
{
-
...
-
private:
-
...
-
struct handle_entry {
-
IBinder* binder;
-
RefBase::weakref_type* refs;
-
};
-
-
...
-
-
Vector<handle_entry>mHandleToObject;
-
...
-
}
说明:该代码定义在frameworks/native/include/binder/ProcessState.h中。前面说过,mHandleToObject是个缓冲矢量数组。它的成员binder是保存的Server的BpBinder对象,而refs是保存的Server在Binder驱动中的Binder引用的描述。
9. BpBinder::BpBinder
new BpBinder(0)会新建BpBinder对象,下面看看BpBinder的构造函数。
-
BpBinder::BpBinder(
int32_t handle)
-
: mHandle(handle)
-
, mAlive(
1)
-
, mObitsSent(
0)
-
, mObituaries(
NULL)
-
{
-
ALOGV(
"Creating BpBinder %p handle %d\n",
this, mHandle);
-
-
extendObjectLifetime(OBJECT_LIFETIME_WEAK);
-
IPCThreadState::self()->incWeakHandle(handle);
-
}
说明:该代码定义在frameworks/native/libs/binder/BpBinder.cpp中。主要工作是初始化。
(01) 将句柄handle保存到私有成员mHandle中。这里是将ServiceManager的句柄保存到mHandle中。
(02) 增加IPCThreadState的引用计数。IPCThreadState::self()是获取IPCThreadState对象,实际上,在前面介绍的ProcessState::getStrongProxyForHandle()中已经调用过该函数。下面看看它的代码。
10. IPCThreadState::self()
-
static
pthread_mutex_t gTLSMutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
-
static
bool gHaveTLS =
false;
-
static
pthread_key_t gTLS =
0;
-
static
bool gShutdown =
false;
-
static
bool gDisableBackgroundScheduling =
false;
-
-
IPCThreadState* IPCThreadState::self()
-
{
-
if (gHaveTLS) {
-
restart:
-
const
pthread_key_t k = gTLS;
-
IPCThreadState* st = (IPCThreadState*)pthread_getspecific(k);
-
if (st)
return st;
-
return
new IPCThreadState;
-
}
-
-
if (gShutdown)
return
NULL;
-
-
pthread_mutex_lock(&gTLSMutex);
-
if (!gHaveTLS) {
-
if (pthread_key_create(&gTLS, threadDestructor) !=
0) {
-
pthread_mutex_unlock(&gTLSMutex);
-
return
NULL;
-
}
-
gHaveTLS =
true;
-
}
-
pthread_mutex_unlock(&gTLSMutex);
-
goto restart;
-
}
说明:该代码定义在frameworks/native/libs/binder/IPCThreadState.cpp中。self()的源码比较简单,它的作用是获取IPCThreadState对象。若该对象已经存在,则直接返回;否则,新建IPCThreadState对象。
11. IPCThreadState::IPCThreadState()
-
IPCThreadState::IPCThreadState()
-
: mProcess(ProcessState::
self()),
-
mMyThreadId(androidGetTid()),
-
mStrictModePolicy(
0),
-
mLastTransactionBinderFlags(
0)
-
{
-
pthread_setspecific(gTLS, this);
-
clearCaller();
-
mIn.setDataCapacity(
256);
-
mOut.setDataCapacity(
256);
-
}
说明:
(01) 获取ProcessState对象,并将其赋值给成员mProcess。ProcessState::self()在前面已经介绍国,它是获取全局的ProcessState对象。
(02) 设置mIn和mOut的容量为256字节。IPCThreadState是和Binder驱动交互的类,mOut是用来保存”IPCThreadState需要发送给Binder驱动的内容的”,而mIn则是用来保存”Binder驱动反馈给IPCThreadState的内容的”。后面在介绍”Server和Client”通信中用到它们时,再进一步说明。
到目前为止,ProcessState::getContextObject()就分析完了。gDefaultServiceManager的赋值语句可以进一步的简化:
gDefaultServiceManager = interface_cast<IServiceManager>(new BpBinder(0));
接下来,看看interface_cast。
12. interface_cast()
-
template<
typename INTERFACE>
-
inline sp<INTERFACE> interface_cast(
const sp<IBinder>& obj)
-
{
-
return INTERFACE::asInterface(obj);
-
}
说明:该代码在frameworks/native/include/binder/IInterface.h中。它是一个模板函数,对于interface_cast而言,返回的结果是IServiceManager::asInterface()。
13. IServiceManager::asInterface()
接下来,就是查找IServiceManager::asInterface()的实现了。在IServiceManager.cpp中不存在,追踪代码,发现asInterface()是通过DECLARE_META_INTERFACE()来声明,并通过IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE()来实现的。
(01) IServiceManager中的DECLARE_META_INTERFACE()声明和IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE()实现,分别在头文件frameworks/native/include/binder/IServiceManager.h 以及 frameworks/native/libs/binder/IServiceManager.cpp中。
-
// IServiceManager.h中的声明
-
class IServiceManager : public IInterface
-
{
-
public:
-
DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(ServiceManager);
-
...
-
}
-
-
// IServiceManager.pp中的实现
-
IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE(ServiceManager,
"android.os.IServiceManager");
(02) DECLARE_META_INTERFACE()和IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE()的定义在frameworks/native/include/binder/IInterface.h中。
-
#define DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(INTERFACE) \
-
static
const android::String16 descriptor; \
-
static android::sp<I
##INTERFACE> asInterface( \
-
const android::sp<android::IBinder>& obj); \
-
virtual
const android::String16& getInterfaceDescriptor()
const; \
-
I
##INTERFACE(); \
-
virtual ~I
##INTERFACE(); \
-
-
#define IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE(INTERFACE, NAME) \
-
const android::String16 I
##INTERFACE::descriptor(NAME); \
-
const android::String16& \
-
I
##INTERFACE::getInterfaceDescriptor() const { \
-
return I
##INTERFACE::descriptor; \
-
} \
-
android::sp<I
##INTERFACE> I##INTERFACE::asInterface( \
-
const android::sp<android::IBinder>& obj) \
-
{ \
-
android::sp<I
##INTERFACE> intr; \
-
if (obj !=
NULL) { \
-
intr = static_cast<I
##INTERFACE*>( \
-
obj->queryLocalInterface( \
-
I
##INTERFACE::descriptor).get()); \
-
if (intr ==
NULL) { \
-
intr =
new Bp
##INTERFACE(obj); \
-
} \
-
} \
-
return intr; \
-
} \
-
I
##INTERFACE::I##INTERFACE() { } \
-
I
##INTERFACE::~I##INTERFACE() { } \
-
-
-
#define CHECK_INTERFACE(interface, data, reply) \
-
if (!data.checkInterface(this)) {
return PERMISSION_DENIED; } \
用ServiceManager替换INTERFACE之后,得到结果如下:IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE(ServiceManager, “android.os.IServiceManager”);
-
#define DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(IServiceManager) \
-
static const android::String16 descriptor; \
-
static android::sp<IServiceManager> asInterface( \
-
const android::sp<android::IBinder>& obj); \
-
virtual
const android::
String16& getInterfaceDescriptor() const; \
-
IServiceManager(); \
-
virtual ~IServiceManager(); \
-
-
-
#define IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE(IServiceManager, "android.os.IServiceManager") \
-
const android::String16 IServiceManager::descriptor("android.os.IServiceManager"); \
-
const android::String16& \
-
IServiceManager::getInterfaceDescriptor() const { \
-
return IServiceManager::descriptor; \
-
} \
-
android::sp<IServiceManager> IServiceManager::asInterface( \
-
const android::sp<android::IBinder>& obj) \
-
{ \
-
android::sp<IServiceManager> intr; \
-
if (obj !=
NULL) { \
-
intr =
static_cast<IServiceManager*>( \
-
obj->queryLocalInterface( \
-
IServiceManager::descriptor).get()); \
-
if (intr ==
NULL) { \
-
intr =
new BpServiceManager(obj); \
-
} \
-
} \
-
return intr; \
-
} \
-
IServiceManager::IServiceManager() { } \
-
IServiceManager::~IServiceManager() { }
因此,得到IServiceManager::asInterface()的源码如下:
-
android::sp<IServiceManager> IServiceManager::asInterface(
const android::sp<android::IBinder>& obj)
-
{
-
android::sp<IServiceManager> intr;
-
if (obj !=
NULL) {
-
intr =
static_cast<IServiceManager*>(
-
obj->queryLocalInterface(
-
IServiceManager::descriptor).get());
-
if (intr ==
NULL) {
-
intr =
new BpServiceManager(obj);
-
}
-
}
-
return intr;
-
}
说明:asInterface()的作用是获取IServiceManager接口。
(01) obj是传入的BpBinder对象,不为NULL。因此,执行obj->queryLocalInterface(“android.os.IServiceManager”)来查找名称为”android.os.IServiceManager”的本地接口,queryLocalInterface()的实现在BpBinder的父类IBinder中,具体在文件frameworks/native/libs/binder/Binder.cpp中。很显然,IServiceManager接口还没创建,因此intr=NULL。
(02) 新建BpServiceManager(obj)对象,并返回。BpServiceManager的实现在frameworks/native/libs/binder/IServiceManager.cpp中。
-
sp<IInterface> IBinder::queryLocalInterface(
const String16& descriptor)
-
{
-
return
NULL;
-
}
到目前为止,gDefaultServiceManager的创建流程就分析完了,它实际返回的是一个BpServiceManager对象,该对象包含IBinder的代理BpBinder。以下是转换后的获取gDefaultServiceManager的语句。
gDefaultServiceManager = new BpServiceManager(new BpBinder(0));






















 3281
3281

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








