
Windows 10 now lets you export installed Linux environments, creating a TAR file of the root file system you can import on other PCs. Copy your configured systems between computers, share them with others, or just save a backup.
Windows 10现在允许您导出已安装Linux环境 ,从而创建可以在其他PC上导入的根文件系统的TAR文件。 在计算机之间复制已配置的系统,与他人共享它们,或仅保存备份。
运作方式 (How This Works)
The import and export features were added in the May 2019 Update—that’s Windows 10 version 1903. If you don’t have it installed yet, you won’t be able to use these command-line options.
导入和导出功能已在2019年5月更新中添加-Windows 10版本1903。如果尚未安装,则将无法使用这些命令行选项。
All you need are two new options for the Windows wsl command: --export and --import . The --export option will export a Linux distribution’s root file system as a TAR file. The --import option lets you import a Linux distribution’s root file system as a TAR file.
所有你需要的是为Windows两个新选项wsl命令: --export和--import 。 --export选项会将Linux发行版的根文件系统导出为TAR文件。 使用--import选项可以将Linux发行版的根文件系统导入为TAR文件。
如何导出(备份)Linux系统 (How to Export (Back Up) a Linux System)
The wsl command is a Windows command—wsl.exe. You’ll need to run it in a PowerShell or Command Prompt environment, not in a Windows Subsystem for Linux environment. You can open one by right-clicking the Start button or pressing Windows+x and then clicking “Windows PowerShell.”
wsl命令是Windows命令wsl.exe。 您需要在PowerShell或命令提示符环境中运行它,而不是在Linux的Windows子系统环境中运行它。 您可以通过右键单击“开始”按钮或按Windows + x,然后单击“ Windows PowerShell”来打开一个。
To list the distros installed, run the following command:
要列出已安装的发行版,请运行以下命令:
wsl --list
Now, use the following command to export a distro’s file system to a TAR file:
现在,使用以下命令将发行版的文件系统导出到TAR文件:
wsl --export distro_name file_name.tar
For example, to export out Ubuntu 18.04 system to a file named ubuntu.tar, we’d run:
例如,要将Ubuntu 18.04系统导出到名为ubuntu.tar的文件中,我们将运行:
wsl --export Ubuntu-18.04 ubuntu.tar
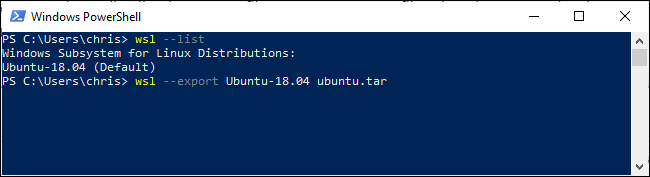
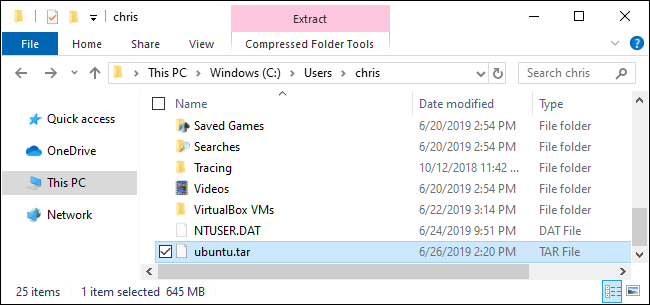
You now have a TAR file containing the Linux distribution’s file system. The file we created—based on a pretty standard Ubuntu 18.04 LTS system—was 645 MB in size. If you’ve installed more software in your distribution, it will be larger.
现在,您有了一个TAR文件,其中包含Linux发行版的文件系统。 我们基于非常标准的Ubuntu 18.04 LTS系统创建的文件大小为645 MB。 如果您在发行版中安装了更多软件,它将更大。
如何导入(还原)Linux系统 (How to Import (Restore) a Linux System)
You can use the wsl command with the --import option to import a TAR file created in this way. From a PowerShell or Command Prompt window, run the following command
可以将wsl命令与--import选项一起使用,以导入以此方式创建的TAR文件。 在PowerShell或命令提示符窗口中,运行以下命令
wsl --import distro_name install_location file_name.tar
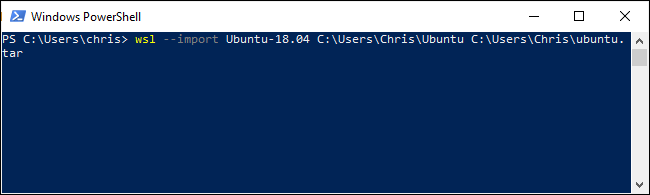
For example, let’s say you want to import a distro from a TAR file located at C:\Users\Chris\ubuntu.tar, call it “Ubuntu-18.04,” and store it at C:\Users\Chris\ubuntu. You’d run:
例如,假设您要从位于C:\ Users \ Chris \ ubuntu.tar的TAR文件导入发行版,将其命名为“ Ubuntu-18.04”,然后将其存储在C:\ Users \ Chris \ ubuntu中。 您将运行:
wsl --import Ubuntu-18.04 C:\Users\Chris\ubuntu C:\Users\Chris\ubuntu.tar
If you want to match where Windows normally installs them to by default, they’re generally in their own folder in C:\Users\NAME\AppData\Local\Packages. For example, you might want to put Ubuntu in C:\Users\NAME\AppData\Local\Packages\Ubuntu.
如果要与Windows默认情况下的默认安装位置匹配,它们通常位于C:\ Users \ NAME \ AppData \ Local \ Packages中自己的文件夹中。 例如,您可能想将Ubuntu放在C:\ Users \ NAME \ AppData \ Local \ Packages \ Ubuntu中。
Wherever you put the install location, note that you shouldn’t modify the files directly from Windows tools. Here’s how you should access the files in File Explorer instead.
请注意,无论将安装位置放在何处,都不应直接通过Windows工具修改文件。 这是您应该如何在文件资源管理器中访问文件的方法。
如何注销(删除)Linux系统 (How to Unregister (Delete) a Linux System)
You can uninstall a distro with the --unregister option along with its name. This will result in all the Linux distribution’s files being deleted.
您可以使用--unregister选项及其名称来卸载发行版。 这将导致删除所有Linux发行版的文件。
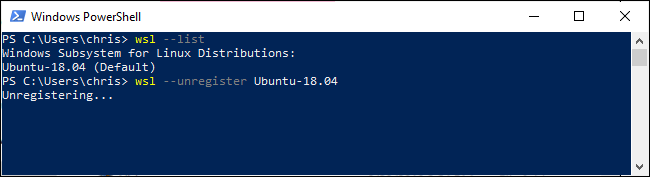
Use the following command to see all installed distributions:
使用以下命令查看所有已安装的发行版:
wsl --list
Then, specify the distribution you want to delete:
然后,指定要删除的分发:
wsl --unregister distro_name
For example, if it’s called Ubuntu-18.04, you’d run:
例如,如果它名为Ubuntu-18.04,则应运行:
wsl --unregister Ubuntu-18.04
This feature also lets you quickly and easily move installed distributions to another folder or drive. Just export the distro to a TAR file, unregister it from your system, and then import the TAR file to another location on your system.
此功能还使您可以快速轻松地将已安装的发行版移动到另一个文件夹或驱动器。 只需将发行版导出到TAR文件,从系统中注销它,然后将TAR文件导入到系统上的另一个位置。
翻译自: https://www.howtogeek.com/426562/how-to-export-and-import-your-linux-systems-on-windows-10/





















 297
297











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








