排序算法中平均时间复杂度
作业排序 (Job sequencing)
Job sequencing is the set of jobs, associated with the job i where deadline di >= 0 and profit pi > 0. For any job i the profit is earned if and only if the job is completed by its deadline. To complete a job, one has to process the job on a machine for one unit of time. Only one machine is available for processing the jobs.
作业排序是与作业i相关联的一组作业,其中期限di> = 0且利润pi> 0 。 对于任何工作, 我当且仅当作业被其限期完成利润赚。 为了完成一项工作,必须在一台机器上在一个单位时间内处理该工作。 仅一台机器可用于处理作业。
Steps for performing job sequencing with deadline using greedy approach is as follows:
使用贪婪方法在截止日期之前执行作业排序的步骤如下:
Sort all the jobs based on the profit in an increasing order.
根据利润按升序对所有作业进行排序。
Let α be the maximum deadline that will define the size of array.
令α为将定义数组大小的最大截止日期。
Create a solution array S with d slots.
创建具有d个插槽的解决方案数组S。
Initialize the content of array S with zero.
用零初始化数组S的内容。
Check for all jobs.
检查所有作业。
- If scheduling is possible a lot ith slot of array s to job i.
- 如果调度是可能很多我阵列的个时隙s到工作我 。
- Otherwise look for location (i-1), (i-2)...1.
- 否则寻找位置(i-1),(i-2)... 1 。
- Schedule the job if possible else reject.
Return array S as the answer.
返回数组S作为答案。
End.
结束。
作业排序算法 (Algorithm for job sequencing)
Input: A is the array of jobs with deadline and profit S array will be the output.
输入: A是具有截止日期的职位数组,而利润S数组将是输出。
1. Begin
2. Sort all the jobs based on profit Pi so
3. P1 > P2 > P3 …………………………….>=Pn
4. d = maximum deadline of job in A
5. Create array S[1,…………………,d]
6. For i=1 to n do
7. Find the largest job x
8. For j=i to 1
9. If ((S[j] = 0) and (x deadline<= d))
10. Then
11. S[x] = i;
12. Break;
13. End if
14. End for
15. End for
16. End
时间复杂度 (Time complexity)
Job sequencing problems has the time complexity of O(n2).
作业排序问题的时间复杂度为O(n2)。
Example:
例:
Given a set of 9 jobs where each job has a deadline and profit associated to it .Each job takes 1 unit of time to complete and only one job can be scheduled at a time. We earn the profit if and only if the job is completed by its deadline. The task is to find the maximum profit and the number of jobs done.
给定一组9个工作,每个工作都有一个截止日期和与之相关的利润。每个工作需要1个时间单位才能完成,并且一次只能安排一个工作。 当且仅当工作在截止日期之前完成时,我们才能赚取利润。 任务是找到最大的利润和完成的工作数量。
Jobs Profit Deadline
J1 85 5
J2 25 4
J3 16 3
J4 40 3
J5 55 4
J6 19 5
J7 92 2
J8 80 3
J9 15 7
Step 1:
第1步:

Step 2:
第2步:

Step 3:
第三步:
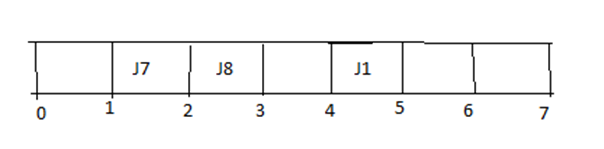
Step 4:
第4步:
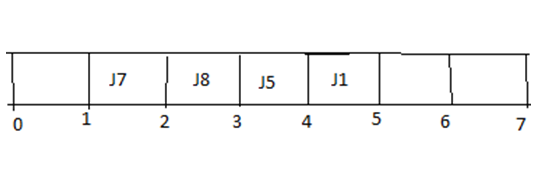
Step 5:
步骤5:
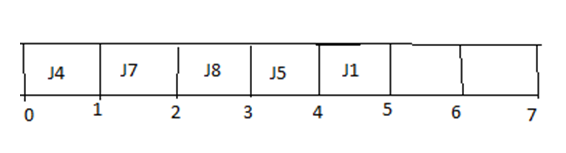
Step 6:
步骤6:

So, the maximum profit = 40 + 92 + 80 + 55 + 85 + 15 = 367
因此,最大利润= 40 + 92 + 80 + 55 + 85 + 15 = 367
翻译自: https://www.includehelp.com/operating-systems/job-sequencing.aspx
排序算法中平均时间复杂度







 本文介绍了作业排序问题,涉及如何使用贪婪方法按利润升序排列作业,并讨论了其时间复杂度为O(n^2)。通过示例解释了如何找出最大利润和完成的工作数量。
本文介绍了作业排序问题,涉及如何使用贪婪方法按利润升序排列作业,并讨论了其时间复杂度为O(n^2)。通过示例解释了如何找出最大利润和完成的工作数量。














 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








