稳定性和可靠性设计策略
可靠性设计问题 (Reliability design problem)
In reliability design, the problem is to design a system that is composed of several devices connected in series.
在可靠性设计中 ,问题在于设计一个由串联连接的多个设备组成的系统。

If we imagine that r1 is the reliability of the device.
如果我们假设r1是设备的可靠性。
Then the reliability of the function can be given by πr1.
然后,函数的可靠性可以由πr1给出。
If r1 = 0.99 and n = 10 that n devices are set in a series, 1 <= i <= 10, then reliability of the whole system πri can be given as: Πri = 0.904
如果r1 = 0.99且n = 10表示将n个设备串联设置, 1 <= i <= 10 ,则整个系统的可靠性πri可表示为: Πri= 0.904
So, if we duplicate the devices at each stage then the reliability of the system can be increased.
因此,如果我们在每个阶段复制设备,则可以提高系统的可靠性。
It can be said that multiple copies of the same device type are connected in parallel through the use of switching circuits. Here, switching circuit determines which devices in any given group are functioning properly. Then they make use of such devices at each stage, that result is increase in reliability at each stage. If at each stage, there are mi similar types of devices Di, then the probability that all mi have a malfunction is (1 - ri)^mi, which is very less.
可以说,使用开关电路将相同设备类型的多个副本并联连接。 此处,开关电路确定任何给定组中的哪些设备正常工作。 然后,他们在每个阶段都使用此类设备,从而提高了每个阶段的可靠性。 如果在每个阶段都有mi个相似类型的设备Di ,则所有mi都具有故障的概率为(1- ri)^ mi ,该概率非常小。
And the reliability of the stage I becomes (1 – (1 - ri) ^mi). Thus, if ri = 0.99 and mi = 2, then the stage reliability becomes 0.9999 which is almost equal to 1. Which is much better than that of the previous case or we can say the reliability is little less than 1 - (1 - ri) ^mi because of less reliability of switching circuits.
并且阶段I的可靠性变为(1 –(1-ri)^ mi) 。 因此,如果ri = 0.99且mi = 2 ,则阶段可靠性变为0.9999 ,几乎等于1 。 这比以前的情况要好得多,或者由于开关电路的可靠性较低,所以可以说可靠性几乎不小于1-(1- ri)^ mi 。
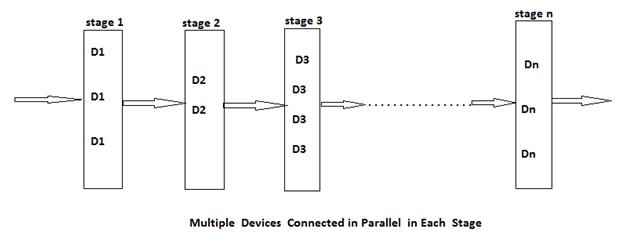
In reliability design, we try to use device duplication to maximize reliability. But this maximization should be considered along with the cost.
在可靠性设计中,我们尝试使用设备复制来最大化可靠性。 但是,这种最大化应与成本一起考虑。
Let c is the maximum allowable cost and ci be the cost of each unit of device i. Then the maximization problem can be given as follows:
令c为最大允许成本, ci为设备i的每个单位的成本。 则最大化问题可以给出如下:
Maximize π Øi (mi) for 1 <= I <= n
最大化πØi(mi)为1 <= I <= n
Subject to:
受:

mi>= 1 and integer 1 <= i <= n
mi> = 1和整数1 <= i <= n
Here, Øi (mi) denotes the reliability of the stage i.
在此, i (mi)表示阶段i的可靠性。
The reliability of the system can be given as follows:
系统的可靠性可以如下:
Π Øi (mi) for 1 <= i <= n
forØi(mi)为1 <= i <= n
If we increase the number of devices at any stage beyond the certain limit, then also only the cost will increase but the reliability could not increase.
如果我们在任何阶段增加设备数量超过一定限制,那么只会增加成本,而不会增加可靠性。
翻译自: https://www.includehelp.com/algorithms/reliability-design-problem.aspx
稳定性和可靠性设计策略







 本文探讨了可靠性设计问题,重点介绍了如何通过设备串联和并联来提高系统可靠性。当设备以串联方式连接时,整体系统的可靠性取决于每个组件的可靠性。通过在每个阶段复制设备并使用开关电路进行并联连接,可以显著提高可靠性。然而,最大化可靠性的同时需要考虑成本约束。系统可靠性与每个阶段设备的数量和类型有关,并存在一个平衡点,超过该点增加设备数量将不再提升可靠性。
本文探讨了可靠性设计问题,重点介绍了如何通过设备串联和并联来提高系统可靠性。当设备以串联方式连接时,整体系统的可靠性取决于每个组件的可靠性。通过在每个阶段复制设备并使用开关电路进行并联连接,可以显著提高可靠性。然而,最大化可靠性的同时需要考虑成本约束。系统可靠性与每个阶段设备的数量和类型有关,并存在一个平衡点,超过该点增加设备数量将不再提升可靠性。














 4230
4230

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








