spring与mybatis整合
mybatis是一个持久层框架,实现了对数据库操作的封装。可以单独使用mybatis,使用mybatis主要包括以下几个部分:
1、编写各个映射文件xxMapper.xml,以及对应的各个接口文件xxMapper.java。
2、编写全局配置文件(mybatis-config.xml或mybatisConfig.xml),在mybatis全局配置文件中需要配置数据源datasource信息,管理数据库连接池,用于连接和操作数据库。
3、通过全局配置文件创建SqlSessionFactory,通过SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession,再通过SqlSession来进行增删查操作。
如下所示。
//mybatis配置文件
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
//根据配置文件获取输入流
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
//根据配置文件输入流创建会话工厂
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//根据会话工厂得到sqlsession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
//通过sqlSession获取Mapper接口,实现对数据的增删改查
UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
对于上面三部分,Spring与mybatis整合之后,依然保留第一部分,第二部分也可以保留,但是通常将mybatis配置文件中的内容放到spring配置文件(applicationContext.xml)中。第三部分则通过SqlSessionFactoryBean和SqlSessionTemplate来实现,SqlSessionFactoryBean就是对SqlSessionFactory的封装,用于创建SqlSessionTemplate,SqlSessionTemplate就是对SqlSession的封装,通过SqlSessionTemplate实现对数据的增删改查操作。
SqlSessionTemplate可以认为是spring与mybatis整合时的简单版本,后续依次出现了它的升级版本,例如SqlSessionDaoSupport、MapperFactoryBean和MapperScannerConfigurer,以及与MapperScannerConfigurer对应的注解版本@MapperScan。在springboot中也会使用@MapperScan注解,需要注意的是,@MapperScan注解是mybatis-spring中提供的,并不是mybatis-springboot-starter中提供的。
1、spring整合mybatis的简单使用
目录结构:
1.spring与mybatis整合需要引入以下依赖:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>mybatis-com.learn</artifactId>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>spring-mybatis</artifactId>
<!-- Mybatis-Spring 3.0+版本只用于Spring 6.0+,而Spring 6.0+只能在Java 17+版本运行。 -->
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<spring.version>5.3.20</spring.version>
<spring.mybatis>2.1.1</spring.mybatis>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- 使用spring提供的功能 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 使用mybatis提供的功能-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.12</version>
</dependency>
<!-- spring与mybatis整合-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>${spring.mybatis}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 使用java操作mysql数据库 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.33</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 使用druid数据库连接池 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.2.16</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 使用spring事务 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 测试 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- 日志 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 使用StringUtils等工具类 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId>
<version>3.12.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
需要在pom.xml文件中引入上述依赖,其中:
mysql-connector-java:mysql数据库驱动,用于与mysql建立连接。
datasource:数据库连接池。将建立的mysql连接维护到一个连接池中,进行连接复用。典型的连接池如druid、c3p0、tomcat-jdbc、dbcp2、hicaricp等。
mybatis:半自动的orm框架。
mybatis-spring:用于将spring与mybatis进行整合。
spring-context:使用spring提供的功能。mybatis与spring整合后,可以直接在业务层通过@Autowired注解注入Mapper,也会利用spring提供的事务管理机制。
2.编写数据库信息配置文件db.properties
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mytest?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root123
3.编写spring配置文件applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<!--创建bean-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.learn.spring.mybatis.service.UserService"/>
<!--扫描properties外部属性文件-->
<context:property-placeholder location="properties/db.properties"/>
<!-- 1.配置数据源,使用 druid 配置数据库连接池 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"
destroy-method="close" lazy-init="false">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
<property name="initialSize" value="1" />
<property name="maxActive" value="50" />
<property name="maxWait" value="30000" />
<!-- 配置扩展插件,监控统计用的filter:stat,日志用的filter:log4j,防御sql注入的filter:wall -->
<property name="filters" value="stat,wall" />
</bean>
<!--2.创建SqlSessionFactory-->
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<!--引用数据源-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<!--设置实体类别名-->
<property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="com.learn.spring.mybatis.entity"/>
<!--设置mybatis映射文件-->
<property name="mapperLocations" value="mapper/*.xml"/>
<!--设置mybatis全局配置文件路径-->
<!--<property name="configLocation" value="mybatis-config.xml"/>-->
</bean>
<!--3.利用MapperFactoryBean类扫描mapper接口,MapperFactoryBean继承SqlSessionDaoSupport-->
<bean id="factoryBean" class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperFactoryBean">
<property name="mapperInterface" value="com.learn.spring.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper"/>
<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>
<!--4.设置事务管理器-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<!--默认事务超时时间-->
<property name="defaultTimeout" value="30000"/>
<!--数据源-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
<!--提交失败的话,也进行回滚-->
<property name="rollbackOnCommitFailure" value="true"/>
</bean>
<!--开启声明式事务-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
</beans>
4.编写实体类以及创建数据表(事先已创建,此处省略)
数据表事先已创建,此处省略。
package com.learn.spring.mybatis.entity;
public class User {
private Integer userId;
private String username;
private Integer age;
// 省略get、set方法
}
5.编写mapper接口和mapper.xml映射文件
Mapper接口:
package com.learn.spring.mybatis.mapper;
import com.learn.spring.mybatis.entity.User;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Author: 倚天照海
*/
public interface UserMapper {
void createUser(User user);
void deleteUserById(Integer userId);
void updateUserById(User user);
User queryUserById(Integer userId);
User queryUserByIdWithResultType(Integer userId);
String queryNameById(Integer userId);
List<User> batchQueryByIds(List<Integer> ids);
List<String> batchQueryNameByIds(List<Integer> ids);
}
Mapper映射文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.learn.spring.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper">
<!--namespace的值必须是mapper接口的全限定名-->
<resultMap id="baseResultMap" type="com.learn.spring.mybatis.entity.User">
<result property="userId" column="user_id" jdbcType="INTEGER"/>
<result property="username" column="username" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<result property="age" column="age" jdbcType="INTEGER"/>
</resultMap>
<sql id="columnInfo">
user_id, username, age
</sql>
<insert id="createUser" parameterType="com.learn.spring.mybatis.entity.User">
insert into t_user(user_id, username, age)
values (#{userId}, #{username}, #{age})
</insert>
<delete id="deleteUserById">
delete from t_user where user_id = #{userId}
</delete>
<update id="updateUserById" parameterType="com.learn.spring.mybatis.entity.User">
update t_user
<set>
<if test="username != null">
username = #{username},
</if>
<if test="age != null">
age = #{age}
</if>
</set>
<where>
user_id = #{userId}
</where>
</update>
<select id="queryUserById" parameterType="java.lang.Integer" resultMap="baseResultMap">
select
<include refid="columnInfo"/>
from t_user
<where>
user_id = #{userId}
</where>
</select>
<!-- 上面queryUserById中结果类型用的是resultMap映射,下面查询结果类型用的是resultType,
在下面查询语句中需要使用别名将user_id映射到userId属性,否则mybatis查询到user_id字段无法给userId属性赋值。
由于resultMap中已经做了映射,所以可以不用使用别名,如果表中字段与属性名称不一致,使用resultType必须用别名转换。-->
<select id="queryUserByIdWithResultType" parameterType="java.lang.Integer" resultType="com.learn.spring.mybatis.entity.User">
select
user_id as userId, username, age
from t_user
<where>
user_id = #{userId}
</where>
</select>
<select id="queryNameById" parameterType="java.lang.Integer" resultType="java.lang.String">
select username
from t_user
<where>
user_id = #{userId}
</where>
</select>
<!-- batchQueryByIds方法的返回值类型虽然是List<User>,但是resultType或resultMap对应的是List中元素的类型,即User -->
<select id="batchQueryByIds" resultMap="baseResultMap">
select
<include refid="columnInfo"/>
from t_user
<where>
user_id in
<foreach collection="list" item="item" open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{item}
</foreach>
</where>
</select>
<!-- batchQueryNameByIds方法的返回值虽然是List<String>,但是resultType不是List,而是List中元素的类型 -->
<select id="batchQueryNameByIds" resultType="java.lang.String">
select username
from t_user
<where>
user_id in
<foreach collection="list" item="userId" open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{userId}
</foreach>
</where>
</select>
</mapper>
6.编写service
package com.learn.spring.mybatis.service;
import com.learn.spring.mybatis.entity.User;
import com.learn.spring.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
/**
* @Author: 倚天照海
*/
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
public void saveUser(User user) {
userMapper.createUser(user);
}
public void deleteUser(Integer id) {
userMapper.deleteUserById(id);
}
public void updateUser(User user) {
userMapper.updateUserById(user);
}
public User queryUserById(Integer id) {
return userMapper.queryUserById(id);
}
}
7.编写单元测试
import com.learn.spring.mybatis.entity.User;
import com.learn.spring.mybatis.service.UserService;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
/**
* @Author: 倚天照海
*/
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = { "classpath:spring/applicationContext.xml" })
public class SpringMybatisTest {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Test
public void saveUser() {
User user = buildUser(1, "张三");
userService.saveUser(user);
User queryUser = userService.queryUserById(1);
Assert.assertEquals(user.getUsername(), queryUser.getUsername());
}
@Test
public void updateUser() {
User user = buildUser(1, "李四");
userService.updateUser(user);
User queryUser = userService.queryUserById(1);
Assert.assertEquals("李四", queryUser.getUsername());
}
@Test
public void deleteUser() {
userService.deleteUser(1);
User queryUser = userService.queryUserById(1);
Assert.assertNull(queryUser);
}
private User buildUser(Integer id, String name) {
User user = new User();
user.setUserId(id);
user.setUsername(name);
return user;
}
}
测试结果:
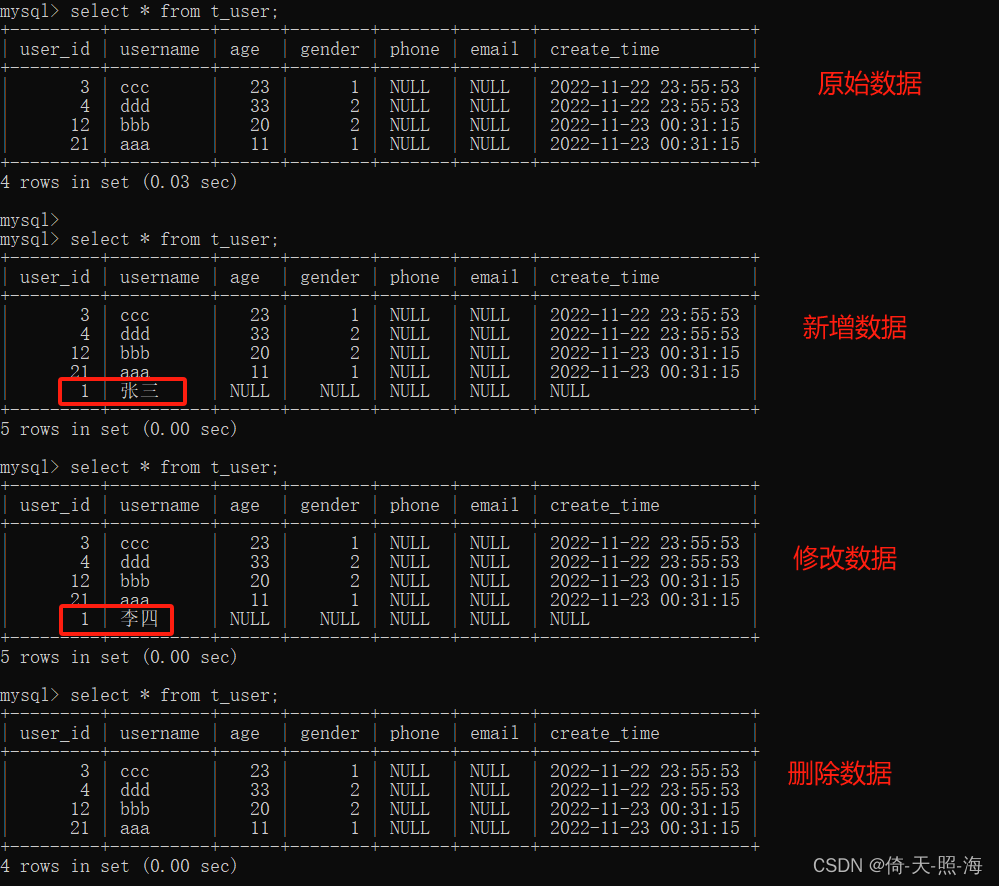
Spring整合mybatis过程中遇到的问题:
问题1:
Error:(5, 52) java: 无法访问org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired
错误的类文件: /D:/ repository/org/springframework/spring-beans/6.0.11/spring-beans-6.0.11.jar!/org/springframework/beans/factory/annotation/Autowired.class
类文件具有错误的版本 61.0, 应为 52.0
请删除该文件或确保该文件位于正确的类路径子目录中。
解决方法:原来引入的spring-context、spring-core等依赖是6.0.11版本的,而Spring 6.0+只能在Java 17+版本运行,我的环境是JDK 1.8。将spring相关依赖的版本改成5.3.20之后就没有上述错误了。
问题2:
java.lang.UnsupportedClassVersionError: org/mybatis/spring/SqlSessionFactoryBean has been compiled by a more recent version of the Java Runtime (class file version 61.0), this version of the Java Runtime only recognizes class file versions up to 52.0
解决方法:Mybatis-Spring 3.0+版本只只用于Spring 6.0+,而Spring 6.0+只能在Java 17+版本运行。如果项目使用Spring 5.x版本,就将Mybatis-Spring依赖版本更改为2.x版本。原来引入的mybatis-spring依赖是3.0.2版本的,改成2.1.1版本之后就没有上述错误了。
2、spring整合mybatis的几种方式
2.1、SqlSessionFactoryBean
首先看一下SqlSessionFactory。
在单独使用mybatis时,SqlSessionFactory和SqlSession是mybatis的核心,SqlSessionFactory用于生成SqlSession。Spring与mybatis整合之后,通过SqlSessionFactoryBean创建SqlSessionFactory,SqlSessionFactoryBean的部分源码如下所示。
public class SqlSessionFactoryBean
implements FactoryBean<SqlSessionFactory>, InitializingBean, ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {
private Resource configLocation;
private Configuration configuration;
private Resource[] mapperLocations;
private DataSource dataSource;
private TransactionFactory transactionFactory;
private Properties configurationProperties;
private SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
private Class<?>[] typeAliases;
private String typeAliasesPackage;
private Class<?> typeAliasesSuperType;
public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {
if (dataSource instanceof TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy) {
this.dataSource = ((TransactionAwareDataSourceProxy) dataSource).getTargetDataSource();
} else {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
notNull(dataSource, "Property 'dataSource' is required");
notNull(sqlSessionFactoryBuilder, "Property 'sqlSessionFactoryBuilder' is required");
state((configuration == null && configLocation == null) || !(configuration != null && configLocation != null),
"Property 'configuration' and 'configLocation' can not specified with together");
this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory();
}
protected SqlSessionFactory buildSqlSessionFactory() throws Exception {
final Configuration targetConfiguration;
XMLConfigBuilder xmlConfigBuilder = null;
if (this.configuration != null) {
targetConfiguration = this.configuration;
if (targetConfiguration.getVariables() == null) {
targetConfiguration.setVariables(this.configurationProperties);
} else if (this.configurationProperties != null) {
targetConfiguration.getVariables().putAll(this.configurationProperties);
}
} else if (this.configLocation != null) {
xmlConfigBuilder = new XMLConfigBuilder(this.configLocation.getInputStream(), null, this.configurationProperties);
targetConfiguration = xmlConfigBuilder.getConfiguration();
} else {
LOGGER.debug(
() -> "Property 'configuration' or 'configLocation' not specified, using default MyBatis Configuration");
targetConfiguration = new Configuration();
Optional.ofNullable(this.configurationProperties).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setVariables);
}
Optional.ofNullable(this.objectFactory).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setObjectFactory);
Optional.ofNullable(this.objectWrapperFactory).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setObjectWrapperFactory);
Optional.ofNullable(this.vfs).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setVfsImpl);
if (hasLength(this.typeAliasesPackage)) {
scanClasses(this.typeAliasesPackage, this.typeAliasesSuperType).stream()
.filter(clazz -> !clazz.isAnonymousClass()).filter(clazz -> !clazz.isInterface())
.filter(clazz -> !clazz.isMemberClass()).forEach(targetConfiguration.getTypeAliasRegistry()::registerAlias);
}
if (!isEmpty(this.typeAliases)) {
Stream.of(this.typeAliases).forEach(typeAlias -> {
targetConfiguration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAlias(typeAlias);
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Registered type alias: '" + typeAlias + "'");
});
}
if (!isEmpty(this.plugins)) {
Stream.of(this.plugins).forEach(plugin -> {
targetConfiguration.addInterceptor(plugin);
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Registered plugin: '" + plugin + "'");
});
}
if (hasLength(this.typeHandlersPackage)) {
scanClasses(this.typeHandlersPackage, TypeHandler.class).stream().filter(clazz -> !clazz.isAnonymousClass())
.filter(clazz -> !clazz.isInterface()).filter(clazz -> !Modifier.isAbstract(clazz.getModifiers()))
.forEach(targetConfiguration.getTypeHandlerRegistry()::register);
}
if (!isEmpty(this.typeHandlers)) {
Stream.of(this.typeHandlers).forEach(typeHandler -> {
targetConfiguration.getTypeHandlerRegistry().register(typeHandler);
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Registered type handler: '" + typeHandler + "'");
});
}
targetConfiguration.setDefaultEnumTypeHandler(defaultEnumTypeHandler);
if (!isEmpty(this.scriptingLanguageDrivers)) {
Stream.of(this.scriptingLanguageDrivers).forEach(languageDriver -> {
targetConfiguration.getLanguageRegistry().register(languageDriver);
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Registered scripting language driver: '" + languageDriver + "'");
});
}
Optional.ofNullable(this.defaultScriptingLanguageDriver)
.ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setDefaultScriptingLanguage);
if (this.databaseIdProvider != null) {// fix #64 set databaseId before parse mapper xmls
try {
targetConfiguration.setDatabaseId(this.databaseIdProvider.getDatabaseId(this.dataSource));
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new IOException("Failed getting a databaseId", e);
}
}
Optional.ofNullable(this.cache).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::addCache);
if (xmlConfigBuilder != null) {
try {
xmlConfigBuilder.parse();
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Parsed configuration file: '" + this.configLocation + "'");
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new IOException("Failed to parse config resource: " + this.configLocation, ex);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
targetConfiguration.setEnvironment(new Environment(this.environment,
this.transactionFactory == null ? new SpringManagedTransactionFactory() : this.transactionFactory,
this.dataSource));
if (this.mapperLocations != null) {
if (this.mapperLocations.length == 0) {
LOGGER.warn(() -> "Property 'mapperLocations' was specified but matching resources are not found.");
} else {
for (Resource mapperLocation : this.mapperLocations) {
if (mapperLocation == null) {
continue;
}
try {
XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(mapperLocation.getInputStream(),
targetConfiguration, mapperLocation.toString(), targetConfiguration.getSqlFragments());
xmlMapperBuilder.parse();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new IOException("Failed to parse mapping resource: '" + mapperLocation + "'", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Parsed mapper file: '" + mapperLocation + "'");
}
}
} else {
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Property 'mapperLocations' was not specified.");
}
return this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(targetConfiguration);
}
}
SqlSessionFactoryBean实现了FactoryBean和InitializingBean接口,在重写的afterPropertiesSet方法中创建了SqlSessionFactory。需要显式的为SqlSessionFactoryBean的dataSource属性引用一个数据源配置。
Spring与mybatis整合后,在spring的核心配置文件applicationContext.xml中进行如下配置:
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<!--引用数据源-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<!--设置实体类别名-->
<property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="com.learn.spring.mybatis.entity"/>
<!--设置mybatis映射文件-->
<property name="mapperLocations" value="mapper/*.xml"/>
<!--设置mybatis全局配置文件路径-->
<!--<property name="configLocation" value="mybatis-config.xml"/>-->
</bean>
2.2、SqlSessionTemplate
SqlSessionTemplate 是 mybatis-spring 的核心,其实现了SqlSession接口,且线程安全。使用SqlSessionTemplate之后,不再需要通过SqlSessionFactory.openSession()方法来创建SqlSession实例,使用完成之后,也不要调用SqlSession.close()方法进行关闭。另外,对于事务,SqlSessionTemplate 将会保证使用的 SqlSession 是和当前 Spring 的事务相关的。
SqlSessionTemplate依赖于SqlSessionFactory,在applicationContext.xml中配置方式如下所示:
<bean id="sqlSessionTemplate" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate">
<constructor-arg ref="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>
在上面的样例中,简单修改UserService.java,将SqlSessionTemplate注入进来,通过SqlSessionTemplate获取UserMapper,或者直接调用SqlSessionTemplate的方法。
package com.learn.spring.mybatis.service;
import com.learn.spring.mybatis.entity.User;
import com.learn.spring.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
/**
* @Author: 倚天照海
* 此处UserService类上没有@Service注解,而是通过spring的配置文件applicationContext.xml注入到spring容器中的
*/
public class UserService {
/*@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;*/
private static final String NAMESPACE = "com.learn.spring.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper.";
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Autowired
private SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate;
@PostConstruct
public void initUserMapper() {
this.userMapper = sqlSessionTemplate.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
}
public void saveUser(User user) {
sqlSessionTemplate.insert(NAMESPACE + "createUser", user);
// userMapper.createUser(user);
}
public void deleteUser(Integer id) {
sqlSessionTemplate.delete(NAMESPACE + "deleteUserById", id);
// userMapper.deleteUserById(id);
}
public void updateUser(User user) {
sqlSessionTemplate.update(NAMESPACE + "updateUserById", user);
// userMapper.updateUserById(user);
}
public User queryUserById(Integer id) {
return sqlSessionTemplate.selectOne(NAMESPACE + "queryUserById", id);
// return userMapper.queryUserById(id);
}
}
2.3、SqlSessionDaoSupport
除了直接注入SqlSessionTemplate,也可以编写一个Dao类继承SqlSessionDaoSupport,调用其getSqlSession()方法来返回 SqlSessionTemplate。SqlSessionDaoSupport 需要设置 sqlSessionFactory 或 sqlSessionTemplate 属性。如果两者都被设置了 , 那么SqlSessionFactory是被忽略的。事实上,如果提供的是一个SqlSessionFactory,SqlSessionDaoSupport内部也会使用其来构造一个SqlSessionTemplate实例。
由于SqlSessionDaoSupport是一个抽象类,所以不能直接通过<bean>标签生成其对象,需要创建一个子类继承它,通过<bean>标签创建子类对象。如果在applicationContext.xml中进行如下配置创建bean对象,会报错。
<bean id="sqlSessionDaoSupport" class="org.mybatis.spring.support.SqlSessionDaoSupport">
<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory" />
</bean>
创建UserDao继承SqlSessionDaoSupport,并在applicationContext.xml中创建UserDao。
package com.learn.spring.mybatis.dao;
import com.learn.spring.mybatis.entity.User;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate;
import org.mybatis.spring.support.SqlSessionDaoSupport;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
/**
* @Author: 倚天照海
*/
public class UserDao extends SqlSessionDaoSupport {
private static final String NAMESPACE = "com.learn.spring.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper.";
private SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
sqlSessionTemplate = (SqlSessionTemplate) getSqlSession();
}
public void saveUser(User user) {
sqlSessionTemplate.insert(NAMESPACE + "createUser", user);
}
public void deleteUser(Integer id) {
sqlSessionTemplate.delete(NAMESPACE + "deleteUserById", id);
}
public void updateUser(User user) {
sqlSessionTemplate.update(NAMESPACE + "updateUserById", user);
}
public User queryUserById(Integer id) {
return sqlSessionTemplate.selectOne(NAMESPACE + "queryUserById", id);
}
}
<bean id="userDao" class="com.learn.spring.mybatis.dao.UserDao">
<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory" />
</bean>
2.4、MapperFactoryBean
Mybatis提供了MapperFactoryBean,MapperFactoryBean继承了SqlSessionDaoSupport类,其部分源码如下所示。
public class MapperFactoryBean<T> extends SqlSessionDaoSupport implements FactoryBean<T> {
private Class<T> mapperInterface;
private boolean addToConfig = true;
public MapperFactoryBean() {
// intentionally empty
}
public MapperFactoryBean(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
protected void checkDaoConfig() {
super.checkDaoConfig();
notNull(this.mapperInterface, "Property 'mapperInterface' is required");
Configuration configuration = getSqlSession().getConfiguration();
if (this.addToConfig && !configuration.hasMapper(this.mapperInterface)) {
try {
configuration.addMapper(this.mapperInterface);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Error while adding the mapper '" + this.mapperInterface + "' to configuration.", e);
throw new IllegalArgumentException(e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
}
}
在spring的applicationContext.xml文件中配置MapperFactoryBean,通过mapperInterface属性指定Mapper接口,MapperFactoryBean就会针对指定的Mapper接口创建一个代理对象,并将其变成spring的一个bean,在需要使用Mapper接口时通过@Autowired注入即可。
<bean id="factoryBean" class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperFactoryBean">
<property name="mapperInterface" value="com.learn.spring.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper"/>
<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>
@Autowired
private UserMapper usermapper;2.5、MapperScannerConfigurer
通过MapperFactoryBean配置,已经是mybatis与spring整合比较理想的方式了,可以简单的通过@Autowired注解注入相关的Mapper对象。但是如果有许多的Mapper接口要配置,针对每个接口都配置一个MapperFactoryBean,会使得applicationContext.xml配置文件很臃肿。关于这一点,mybatis-spring包中提供了MapperScannerConfigurer来解决这个问题。
MapperScannerConfigurer可以指定扫描某个包,为这个包下的所有Mapper接口,在Spring上下文中都创建代理对象,在使用这些Mapper接口时直接通过@Autowired注入即可。
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.learn.spring.mybatis.mapper"/>
<!--<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactory"/>-->
<!--<property name="sqlSessionTemplateBeanName" value="sqlSessionTemplate"/>-->
</bean>
basePackage 属性是用于指定Mapper接口的包路径。如果的Mapper接口位于不同的包下,可以使用分号”;”或者逗号”,”进行分割。如果某个路径还包含子包,子包中的Mapper接口也能递归地被搜索到。
至此,在applicationContext.xml中有四种方式可以创建Mapper接口的代理对象,或者创建SqlSession,通过SqlSession获取Mapper对象。如下所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<!--创建bean-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.learn.spring.mybatis.service.UserService"/>
<!--扫描properties外部属性文件-->
<context:property-placeholder location="properties/db.properties"/>
<!-- 1.配置数据源,使用 druid 配置数据库连接池 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"
destroy-method="close" lazy-init="false">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
<property name="initialSize" value="1"/>
<property name="maxActive" value="50"/>
<property name="maxWait" value="30000"/>
<!-- 配置扩展插件,监控统计用的filter:stat,日志用的filter:log4j,防御sql注入的filter:wall -->
<property name="filters" value="stat,wall"/>
</bean>
<!--2.创建SqlSessionFactory-->
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<!--引用数据源-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<!--设置实体类别名-->
<property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="com.learn.spring.mybatis.entity"/>
<!--设置mybatis映射文件-->
<property name="mapperLocations" value="mapper/*.xml"/>
<!--设置mybatis全局配置文件路径-->
<!--<property name="configLocation" value="mybatis-config.xml"/>-->
</bean>
<!-- 方式一:使用sqlSessionTemplate -->
<bean id="sqlSessionTemplate" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate">
<constructor-arg ref="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>
<!-- 方式二:使用SqlSessionDaoSupport -->
<bean id="userDao" class="com.learn.spring.mybatis.dao.UserDao">
<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>
<!-- 方式三:使用MapperFactoryBean -->
<!--3.利用MapperFactoryBean类扫描mapper接口,MapperFactoryBean继承SqlSessionDaoSupport-->
<!--<bean id="factoryBean" class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperFactoryBean">
<property name="mapperInterface" value="com.learn.spring.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper"/>
<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>-->
<!-- 方式四:使用MapperScannerConfigurer -->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.learn.spring.mybatis.mapper"/>
<!--<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactory"/>-->
<!--<property name="sqlSessionTemplateBeanName" value="sqlSessionTemplate"/>-->
</bean>
<!--4.设置事务管理器-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<!--默认事务超时时间-->
<property name="defaultTimeout" value="30000"/>
<!--数据源-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<!--提交失败的话,也进行回滚-->
<property name="rollbackOnCommitFailure" value="true"/>
</bean>
<!--开启声明式事务-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
</beans>
2.6、@MapperScan
mybatis-spring提供了@MapperScan注解,可以取代xml配置中的MapperScannerConfigurer。在springboot中也会使用@MapperScan注解,需要注意的是,@MapperScan注解是mybatis-spring中提供的,并不是mybatis-springboot-starter中提供的。
下面是通过@MapperScan注解的方式来配置mybatis与spring整合。
@MapperScan(
//等价于MapperScannerConfigurer的basePackage属性
basePackages = "com.learn.spring.mybatis.mapper",
//等价于MapperScannerConfigurer的markerInterface属性
markerInterface = Mapper.class,
//等价于MapperScannerConfigurer的annotationClass属性
annotationClass = Mapper.class,
//等价于MapperScannerConfigurer的sqlSessionFactoryBeanName属性
sqlSessionFactoryRef = "sqlSessionFactory")
创建一个配置类DatasourceConfig,代替spring的配置文件applicationContext.xml。
package com.learn.spring.mybatis.config;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.SimpleDriverDataSource;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
/**
* @author 倚天照海
*/
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:properties/db.properties")
@ComponentScan("com.learn.spring.mybatis")
@MapperScan(value = "com.learn.spring.mybatis.mapper")
@EnableTransactionManagement //开启事务
public class DatasourceConfig {
@Value("${jdbc.driver}")
private String driver;
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String password;
private String mapperLocations = "classpath:mapper/*.xml";
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
// SimpleDriverDataSource dataSource = new SimpleDriverDataSource();
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(driver);
dataSource.setUrl(url);
dataSource.setUsername(username);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
return dataSource;
}
@Bean("sqlSessionFactory")
public SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
sqlSessionFactory.setDataSource(dataSource);
// 通过setMapperLocations解决mapper.java与mapper.xml不在同一个目录下的问题
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver resolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
// 使用 getResource 方法报错:Failed to parse mapping resource: 'class path resource [mapper/*.xml]',
// getResource:从类的根路径下获取文件, getResources:获取所有类路径下的指定文件
sqlSessionFactory.setMapperLocations(resolver.getResources(mapperLocations));
return sqlSessionFactory;
}
@Bean("datasourceManager")
public DataSourceTransactionManager getDatasourceManager(DataSource dataSource) {
/*DataSourceTransactionManager datasourceManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
datasourceManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
return datasourceManager;*/
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
}
UserService类:
package com.learn.spring.mybatis.service;
import com.learn.spring.mybatis.entity.User;
import com.learn.spring.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/**
* @Author: 倚天照海
*/
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
public void saveUser(User user) {
userMapper.createUser(user);
}
public void deleteUser(Integer id) {
userMapper.deleteUserById(id);
}
public void updateUser(User user) {
userMapper.updateUserById(user);
}
public User queryUserById(Integer id) {
return userMapper.queryUserById(id);
}
}
在测试类上使用上述配置类:
import com.learn.spring.mybatis.config.DatasourceConfig;
import com.learn.spring.mybatis.entity.User;
import com.learn.spring.mybatis.service.UserService;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
/**
* @Author: 倚天照海
*/
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
//@ContextConfiguration(locations = { "classpath:spring/applicationContext.xml" })
@ContextConfiguration(classes = {DatasourceConfig.class})
public class SpringMybatisTest {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Test
public void saveUser() {
User user = buildUser(1, "张三");
userService.saveUser(user);
User queryUser = userService.queryUserById(1);
Assert.assertEquals(user.getUsername(), queryUser.getUsername());
}
@Test
public void updateUser() {
User user = buildUser(1, "李四");
userService.updateUser(user);
User queryUser = userService.queryUserById(1);
Assert.assertEquals("李四", queryUser.getUsername());
}
@Test
public void deleteUser() {
userService.deleteUser(1);
User queryUser = userService.queryUserById(1);
Assert.assertNull(queryUser);
}
private User buildUser(Integer id, String name) {
User user = new User();
user.setUserId(id);
user.setUsername(name);
return user;
}
}
2.7、spring整合mybatis的事务管理
mybatis与spring进行整合另一个核心要点是事务。整合后,将事务委派给spring来管理。spring提供了声明式事务管理的功能,可以让事务代码变得非常简单。
可以通过spring配置文件和注解两种方式使用声明式事务。
1、通过spring配置文件开启事务
<!--spring 事务管理器-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<!--默认事务超时时间-->
<property name="defaultTimeout" value="30000"/>
<!--数据源-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
<!--提交失败的话,也进行回滚-->
<property name="rollbackOnCommitFailure" value="true"/>
</bean>
<!--开启声明式事务-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
2、通过注解开启事务
在配置类或启动类上加上@EnableTransactionManagement注解开启事务,并创建DataSourceTransactionManager实例bean。
package com.learn.spring.mybatis.config;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
/**
* @author 倚天照海
*/
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:properties/db.properties")
@ComponentScan("com.learn.spring.mybatis")
@MapperScan(value = "com.learn.spring.mybatis.mapper")
@EnableTransactionManagement //开启事务
public class DatasourceConfig {
@Value("${jdbc.driver}")
private String driver;
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String password;
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
// SimpleDriverDataSource dataSource = new SimpleDriverDataSource();
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(driver);
dataSource.setUrl(url);
dataSource.setUsername(username);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
return dataSource;
}
@Bean("datasourceManager")
public DataSourceTransactionManager getDatasourceManager(DataSource dataSource) {
/*DataSourceTransactionManager datasourceManager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
datasourceManager.setDataSource(dataSource);
return datasourceManager;*/
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
}
然后在业务bean的方法上添加@Transactional注解,此时这个方法就自动具备了事务的功能,如果出现异常,会自动回滚,没有出现异常则自动交。
package com.learn.spring.mybatis.service;
import com.learn.spring.mybatis.entity.User;
import com.learn.spring.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
/**
* @Author: 倚天照海
*/
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void saveUser(User user) {
// todo
}
}
mybatis自身提供了一个TransactionFactory接口,当通过mybatis-spring与spring进行整合后,引入了另外一个TransactionFactory接口实现SpringManagedTransactionFactory,如下图:
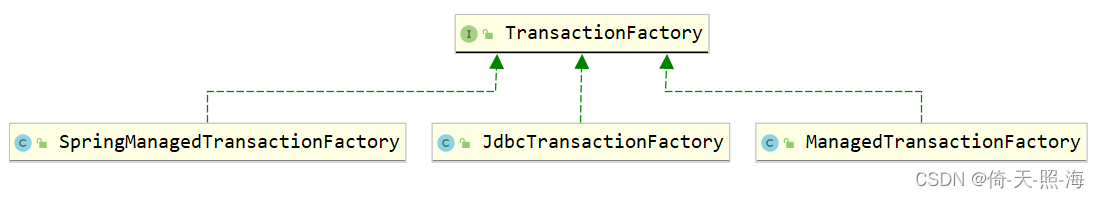
SpringManagedTransactionFactory作用就是将事务委托给spring进行管理。前面提到的SqlSessionFacoryBean有一个transactionFactory属性,如果没有指定的情况下,默认就是使用SpringManagedTransactionFactory。






















 1431
1431











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








