1,我们都知道 laravel 框架的入口是 public/index.php 文件,我们看一下源码:
/*
|--------------------------------------------------------------------------
| Run The Application
|--------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
| Once we have the application, we can handle the incoming request
| through the kernel, and send the associated response back to
| the client's browser allowing them to enjoy the creative
| and wonderful application we have prepared for them.
|
*/
$kernel = $app->make(Illuminate\Contracts\Http\Kernel::class);
$response = $kernel->handle(
$request = Illuminate\Http\Request::capture()
);
从源码我们看到,是先从服务容器中解析出 Illuminate\Contracts\Http\Kernel::class 的服务实例,再执行服务的 handle 方法处理 HTTP 请求。
我们找到了 Illuminate\Foundation\Http\kernel::class 服务实例
<?php
namespace Illuminate\Foundation\Http;
use Exception;
use Throwable;
use Illuminate\Routing\Router;
use Illuminate\Routing\Pipeline;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Facade;
use Illuminate\Contracts\Debug\ExceptionHandler;
use Illuminate\Contracts\Foundation\Application;
use Illuminate\Contracts\Http\Kernel as KernelContract;
use Symfony\Component\Debug\Exception\FatalThrowableError;
class Kernel implements KernelContract
{
/**
* Handle an incoming HTTP request. 处理 HTTP 请求
* @see https://github.com/laravel/framework/blob/5.6/src/Illuminate/Foundation/Http/Kernel.php#L111
*
* @param \Illuminate\Http\Request $request
* @return \Illuminate\Http\Response
*/
public function handle($request)
{
try {
$request->enableHttpMethodParameterOverride();
$response = $this->sendRequestThroughRouter($request);
} catch (Exception $e) {
...
} catch (Throwable $e) {
...
}
$this->app['events']->dispatch(
new Events\RequestHandled($request, $response)
);
return $response;
}
/**
* Send the given request through the middleware / router. 将用户请求发送到中间件和路由
*
* @param \Illuminate\Http\Request $request
* @return \Illuminate\Http\Response
*/
protected function sendRequestThroughRouter($request)
{
$this->app->instance('request', $request);
Facade::clearResolvedInstance('request');
$this->bootstrap();
return (new Pipeline($this->app))
->send($request)
->through($this->app->shouldSkipMiddleware() ? [] : $this->middleware)
->then($this->dispatchToRouter());
}
/**
* Get the route dispatcher callback. 获取分发路由回调(或者控制器)
* @see https://github.com/laravel/framework/blob/5.6/src/Illuminate/Foundation/Http/Kernel.php#L171
* @return \Closure
*/
protected function dispatchToRouter()
{
return function ($request) {
$this->app->instance('request', $request);
return $this->router->dispatch($request);
};
}
}
在 Kernel 的类中看到 handle 方法调用 sendRequestThroughRouter 方法

在这个方法中有全局中间件和路由分发,在全局中间件运行完之后,会调用 dispatchToRouter 方法返回的回调方法,我们看一下这个方法:

当前类 Illuminate\Foundation\Http\Kernel 的 $router 属性是 Illuminate\Routing\Router 类的对象,下面我们看
Illuminate\Routing\Router 类的 dispatch 方法,如下:
<?php
namespace Illuminate\Routing;
...
class Router implements RegistrarContract, BindingRegistrar
{
...
/**
* Dispatch the request to the application. 将 HTTP 请求分发到应用程序。
*
* @param \Illuminate\Http\Request $request
* @return \Illuminate\Http\Response|\Illuminate\Http\JsonResponse
*/
public function dispatch(Request $request)
{
$this->currentRequest = $request;
return $this->dispatchToRoute($request);
}
/**
* Dispatch the request to a route and return the response. 将请求分发到路由,并返回响应。
*
* @param \Illuminate\Http\Request $request
* @return mixed
*/
public function dispatchToRoute(Request $request)
{
return $this->runRoute($request, $this->findRoute($request));
}
/**
* Find the route matching a given request. 查找与请求 request 匹配的路由。
*
* @param \Illuminate\Http\Request $request
* @return \Illuminate\Routing\Route
*/
protected function findRoute($request)
{
// 从 RouteCollection(由 Router::get('/', callback) 等设置的路由) 集合中查找与 $request uri 相匹配的路由配置。
$this->current = $route = $this->routes->match($request);
$this->container->instance(Route::class, $route);
return $route;
}
/**
* Return the response for the given route. 执行路由配置的闭包(或控制器)返回响应 $response。
*
* @param Route $route
* @param Request $request
* @return mixed
*/
protected function runRoute(Request $request, Route $route)
{
$request->setRouteResolver(function () use ($route) {
return $route;
});
$this->events->dispatch(new Events\RouteMatched($route, $request));
return $this->prepareResponse($request,
$this->runRouteWithinStack($route, $request)
);
}
/**
* Run the given route within a Stack "onion" instance. 运行给定路由,会处理中间件等处理(这里的中间件不同于 Kernel handle 中的路由,是仅适用当前路由或路由组的局部路由)。
*
* @param \Illuminate\Routing\Route $route
* @param \Illuminate\Http\Request $request
* @return mixed
*/
protected function runRouteWithinStack(Route $route, Request $request)
{
$shouldSkipMiddleware = $this->container->bound('middleware.disable') &&
$this->container->make('middleware.disable') === true;
$middleware = $shouldSkipMiddleware ? [] : $this->gatherRouteMiddleware($route);
return (new Pipeline($this->container))
->send($request)
->through($middleware)
->then(function ($request) use ($route) {
return $this->prepareResponse(
// $route->run() 将运行当前路由闭包(或控制器)生成结果执行结果。
$request, $route->run()
);
});
}
/**
* Create a response instance from the given value.
*
* @param \Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Request $request
* @param mixed $response
* @return \Illuminate\Http\Response|\Illuminate\Http\JsonResponse
*/
public function prepareResponse($request, $response)
{
return static::toResponse($request, $response);
}
...
}
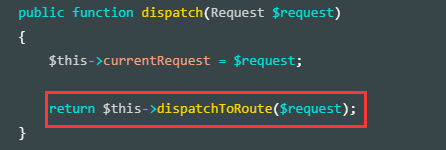
继续调用 dispatchToRoute 方法,如下:
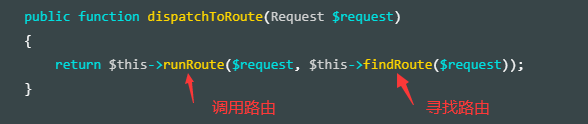
我们今天的重点是 findRoute 方法,也就是寻找路由。

这里的核心逻辑是调用 Illuminate\Routing\RouteCollection 的 match 方法匹配路由:
public function match(Request $request)
{
$routes = $this->get($request->getMethod());
// First, we will see if we can find a matching route for this current request
// method. If we can, great, we can just return it so that it can be called
// by the consumer. Otherwise we will check for routes with another verb.
$route = $this->matchAgainstRoutes($routes, $request);
if (! is_null($route)) {
return $route->bind($request);
}
// If no route was found we will now check if a matching route is specified by
// another HTTP verb. If it is we will need to throw a MethodNotAllowed and
// inform the user agent of which HTTP verb it should use for this route.
$others = $this->checkForAlternateVerbs($request);
if (count($others) > 0) {
return $this->getRouteForMethods($request, $others);
}
throw new NotFoundHttpException;
}在上述方法定义中,首先通过 $this->get($request->getMethod()) 获取当前请求方法(GET、POST等)下的所有路由定义,该方法返回结果是 Illuminate\Routing\Route 实例数组
接下来调用 $this->matchAgainstRoutes($routes, $request) 通过当前请求实例 $request 从返回的路由数组 $routes 中匹配路由:
protected function matchAgainstRoutes(array $routes, $request, $includingMethod = true)
{
[$fallbacks, $routes] = collect($routes)->partition(function ($route) {
return $route->isFallback;
});
return $routes->merge($fallbacks)->first(function ($value) use ($request, $includingMethod) {
return $value->matches($request, $includingMethod);
});
}这个方法分为 2 部分,第一部分把所有的 get 路由分为 2 个容器,第一个容器只包含回退路由,第二个容器包含除去回退路由的所有 get 路由。第二部分把上面的 2 个容器合并,注意了此时的回退路由在所有 get 路由的的最后面。合并完之后遍历容器中的每一个路由,找到第一个符合规则的路由,上面的 first 方法的每一个参数都是我们注册的路由对象,Laravel 中的每一个路由对象都是 Illuminate\Routing\Route 类的实例
对应的路由匹配逻辑源码则是 Illuminate\Routing\Route 的 matches 方法:
public function matches(Request $request, $includingMethod = true)
{
$this->compileRoute();
foreach ($this->getValidators() as $validator) {
if (! $includingMethod && $validator instanceof MethodValidator) {
continue;
}
if (! $validator->matches($this, $request)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}在该方法中,会通过 $this->getValidators() 返回的四个维度的数据对当前请求进行匹配,分别是请求路径URI、请求方法(GET、POST等)、Scheme(HTTP、HTTPS等) 和域名。这里面应用了责任链模式,只要一个匹配校验不通过,则退出校验,只有所有四个维度数据校验都通过了,才算通过,具体每个维度数据校验都是一个独立的类来完成,感兴趣的可以自己去看下,这里就不深入展开了。
接下来,代码控制流程回到 Illuminate\Routing\RouteCollection 的 match 方法,如果匹配到定义的路由,则返回路由信息:
if (! is_null($route)) {
return $route->bind($request);
}否则检查下其它请求方式有没有与当前请求匹配的路由,如果有的话抛出 MethodNotAllowed 异常:
$others = $this->checkForAlternateVerbs($request);
if (count($others) > 0) {
return $this->getRouteForMethods($request, $others);
}如果也没有的话才抛出 NotFoundHttpException 异常,返回 404 响应。
处理路由业务逻辑
如果在路由匹配中找到了匹配路由,没有抛出异常,则代码控制流程进入执行路由阶段,对应的方法是 Illuminate\Routing\Router 的 runRoute 方法:
protected function runRoute(Request $request, Route $route)
{
$request->setRouteResolver(function () use ($route) {
return $route;
});
$this->events->dispatch(new Events\RouteMatched($route, $request));
return $this->prepareResponse($request,
$this->runRouteWithinStack($route, $request)
);
}该方法中第一段代码将匹配到的路由设置到当前请求的路由解析器属性中,然后触发一个路由匹配事件RouteMatched,最后通过 runRouteWithinStack 方法执行路由业务逻辑:
protected function runRouteWithinStack(Route $route, Request $request)
{
$shouldSkipMiddleware = $this->container->bound('middleware.disable') &&
$this->container->make('middleware.disable') === true;
$middleware = $shouldSkipMiddleware ? [] : $this->gatherRouteMiddleware($route);
return (new Pipeline($this->container))
->send($request)
->through($middleware)
->then(function ($request) use ($route) {
return $this->prepareResponse(
$request, $route->run()
);
});
}首先还是判断系统是否禁用中间件,如果没有的话从匹配路由实例 $route 中通过 gatherRouteMiddleware 方法解析出当前路由上应用的路由中间件,并通过管道方式执行,中间件校验逻辑都通过之后,调用 prepareResponse 方法处理请求,准备返回响应,响应内容由 Illuminate\Routing\Route 的 run 方法返回:
public function run()
{
$this->container = $this->container ?: new Container;
try {
if ($this->isControllerAction()) {
return $this->runController();
}
return $this->runCallable();
} catch (HttpResponseException $e) {
return $e->getResponse();
}
}在该方法中,会判断如果路由是由控制方法定义,则执行对应的控制器方法并返回结果:
return $this->runController();如果路由是通过闭包函数定义的话,则执行对应的闭包函数并返回处理结果:
return $this->runCallable();不管采用那种方式定义,返回的响应内容都会经由前面提到的 prepareResponse 进行处理,最终通过 toResponse 方法进行处理后准备发送给客户端浏览器
public static function toResponse($request, $response)
{
if ($response instanceof Responsable) {
$response = $response->toResponse($request);
}
if ($response instanceof PsrResponseInterface) {
$response = (new HttpFoundationFactory)->createResponse($response);
} elseif ($response instanceof Model && $response->wasRecentlyCreated) {
$response = new JsonResponse($response, 201);
} elseif (! $response instanceof SymfonyResponse &&
($response instanceof Arrayable ||
$response instanceof Jsonable ||
$response instanceof ArrayObject ||
$response instanceof JsonSerializable ||
is_array($response))) {
$response = new JsonResponse($response);
} elseif (! $response instanceof SymfonyResponse) {
$response = new Response($response);
}
if ($response->getStatusCode() === Response::HTTP_NOT_MODIFIED) {
$response->setNotModified();
}
return $response->prepare($request);
}以上就是整个路由的处理过程
下面我用大白话来叙述一下:
1.当用户发起一个请求时,首先进入的是public/index.php文件中,这个文件解析了一个Kernel类,再执行了一个handle方法
2.在这个方法中调用了一个 sendRequestThroughRouter 方法,这个方法将请求发送到中间件和路由分发 dispatchToRouter 中,这个由管道组件完成,
3.在 dispatchToRouter 方法中又调用了 一个 dispatch 方法,
4.在 dispatch 中又调用了 dispatchToRoute 方法,这个方法中的主体逻辑分为两部分,首先是通过 findRoute 方法进行路由匹配,然后通过 runRoute 执行对应的路由逻辑,
4.1 findRoute 方法是获取到匹配路由之后将其绑定到容器,然后返回,在findRoute方法中调用了一个重要的方法是match方法,在match方法中首先通过 $this->get($request->getMethod()) 获取当前请求方法(GET、POST等)下的所有路由定义,该方法返回结果是 Illuminate\Routing\Route 实例数组,接下来调用 matchAgainstRoutes,在该方法中,这个方法分为 2 部分
4.1.1 第一部分把所有的 get 路由分为 2 个容器,第一个容器只包含回退路由,第二个容器包含除去回退路由的所有 get 路由。
4.1.2 第二部分把上面的 2 个容器合并,注意了此时的回退路由在所有 get 路由的的最后面。合并完之后遍历容器中的每一个路由,找到第一个符合规则的路由,
4.2.1 在这个过程中会调用matchs方法,在该方法中,会通过 $this->getValidators() 返回的四个维度的数据对当前请求进行匹配,分别是请求路径URI、请求方法(GET、POST等)、Scheme(HTTP、HTTPS等) 和域名,只要一个匹配校验不通过,则退出校验,只有所有四个维度数据校验都通过了,才算通过,如果没有匹配到路由的话,就会去匹配其他的请求方式有没有有没有与当前请求匹配的路由,如果有的话抛出 MethodNotAllowed 异常,如果也没有的话才抛出 NotFoundHttpException 异常,返回 404 响应。
5.如果在路由匹配中找到了匹配路由,就进入到了执行路由阶段runRoute,在方法中触发一个路由匹配事件RouteMatched,最后通过 runRouteWithinStack 方法执行路由业务逻辑,首先判断系统是否禁用中间件,如果没有的话从匹配路由实例 $route 中通过 gatherRouteMiddleware 方法解析出当前路由上应用的路由中间件,并通过管道方式执行,中间件校验都通过之后,调用 prepareResponse 方法处理请求,准备返回响应,响应内容由 Illuminate\Routing\Route 的 run 方法返回,在该方法中,会判断路由是由控制器方法定义还是闭包函数定义,不管采用那种方式定义,返回的响应内容都会经由前面提到的 prepareResponse 进行处理,最终通过 toResponse 方法进行处理后准备发送给客户端浏览器
参考1:https://learnku.com/articles/13622/the-principle-of-laravel-routing-execution






















 534
534











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








