基本概念:
条件变量是线程可用的另一种同步机制。条件变量给多个线程提供了一个会合的场所。条件变量与互斥量一起使用时,允许线程以无竞争的方式等待特定条件发生。
条件变量本身是互斥量保护的。线程在改变条件状态之前必须首先锁住互斥量。
在使用条件变量之前,必须先对它进行初始化。由pthread_cond_t数据类型表示的条件变量可以用两种方式初始化,可以把常量PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER赋给静态分配的条件变量,但是如果条件变量是动态分配的,则需要使用pthread_cond_init函数对它初始化。
一、初始化锁与销毁锁
PTHREAD_COND_DESTROY(P) POSIX Programmer's Manual PTHREAD_COND_DESTROY(P)
NAME
pthread_cond_destroy, pthread_cond_init - destroy and initialize condi‐
tion variables
SYNOPSIS
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond);
int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,
const pthread_condattr_t *restrict attr);
pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
二、等待条件变真
PTHREAD_COND_TIMEDWAIT(P) POSIX Programmer's Manual PTHREAD_COND_TIMEDWAIT(P)
NAME
pthread_cond_timedwait, pthread_cond_wait - wait on a condition
SYNOPSIS
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_cond_timedwait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,
pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex,
const struct timespec *restrict abstime);
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond,
pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex);
调用者把锁住的互斥量传给函数,函数然后自动把调用线程放到等待条件的线程列表上,对互斥量解锁,pthread_cond_wait返回时,互斥量再次被锁住。pthread_cond_timedwait多了一个超时参数,需要注意的是这个时间值是一个绝对数而不是相对数。
三、唤醒等待线程
PTHREAD_COND_BROADCAST(P) POSIX Programmer's Manual PTHREAD_COND_BROADCAST(P)
NAME
pthread_cond_broadcast, pthread_cond_signal - broadcast or signal a
condition
SYNOPSIS
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond);
int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond);pthread_cond_signal函数至少能唤醒一个等待该条件的线程,而pthread_cond_broadcast函数则能唤醒等待该条件的所有线程,必须注意,一定要在改变条件状态以后再给线程发信号。
如果某个线程调用了pthread_cond_signal,不过当时没有任何线程阻塞在pthread_cond_wait调用中,那么发往相应条件变量的信号将丢失。
四、条件变量属性
目前条件变量支持两个属性:进程共享属性和时钟属性,这里不展开讨论。
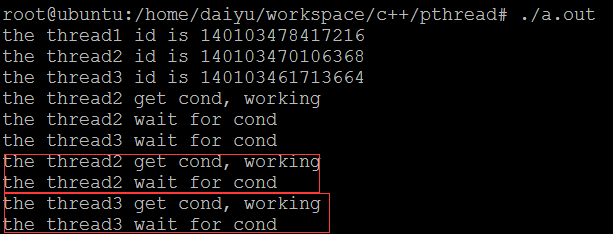
例子1,单个唤醒 ,gcc pthread_cond_signal.c -pthread
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
static int num = 0;
static int count = 100000;
static pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
static pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
void Perror(const char *s)
{
perror(s);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
void* fun2(void *arg)
{
pthread_t thread_id = pthread_self();
printf("the thread2 id is %ld\n", (long)thread_id);
sleep(1);
// get num
for ( ; ; ) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
while (num == 0) {
printf("the thread2 wait for cond\n");
pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex);
}
printf("the thread2 get cond, working\n");
num -= 1;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
}
void* fun3(void *arg)
{
pthread_t thread_id = pthread_self();
printf("the thread3 id is %ld\n", (long)thread_id);
sleep(1);
// get num
for ( ; ; ) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
while (num == 0) {
printf("the thread3 wait for cond\n");
pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex);
}
printf("the thread3 get cond, working\n");
num -= 1;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
}
int main()
{
int err;
pthread_t thread1;
pthread_t thread2;
pthread_t thread3;
thread1 = pthread_self();
printf("the thread1 id is %ld\n", (long)thread1);
// Create thread
err = pthread_create(&thread2, NULL, fun2, NULL);
if (err != 0) {
Perror("can't create thread2\n");
}
err = pthread_create(&thread3, NULL, fun3, NULL);
if (err != 0) {
Perror("can't create thread3\n");
}
// detach thread3
err = pthread_detach(thread2);
if (err != 0) {
Perror("can't detach thread2\n");
}
err = pthread_detach(thread3);
if (err != 0) {
Perror("can't detach thread3\n");
}
// set num
for ( ; ; ) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
num += 1;
pthread_cond_signal(&cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
sleep(10);
}
return 0;
}
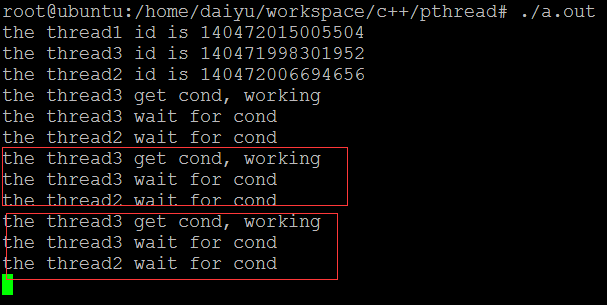
例子2,多个唤醒,gcc pthread_cond_broadcast.c -pthread
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
static int num = 0;
static int count = 100000;
static pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
static pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
void Perror(const char *s)
{
perror(s);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
void* fun2(void *arg)
{
pthread_t thread_id = pthread_self();
printf("the thread2 id is %ld\n", (long)thread_id);
sleep(1);
// get num
for ( ; ; ) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
while (num == 0) {
printf("the thread2 wait for cond\n");
pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex);
}
printf("the thread2 get cond, working\n");
num -= 1;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
}
void* fun3(void *arg)
{
pthread_t thread_id = pthread_self();
printf("the thread3 id is %ld\n", (long)thread_id);
sleep(1);
// get num
for ( ; ; ) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
while (num == 0) {
printf("the thread3 wait for cond\n");
pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex);
}
printf("the thread3 get cond, working\n");
num -= 1;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
}
int main()
{
int err;
pthread_t thread1;
pthread_t thread2;
pthread_t thread3;
thread1 = pthread_self();
printf("the thread1 id is %ld\n", (long)thread1);
// Create thread
err = pthread_create(&thread2, NULL, fun2, NULL);
if (err != 0) {
Perror("can't create thread2\n");
}
err = pthread_create(&thread3, NULL, fun3, NULL);
if (err != 0) {
Perror("can't create thread3\n");
}
// detach thread3
err = pthread_detach(thread2);
if (err != 0) {
Perror("can't detach thread2\n");
}
err = pthread_detach(thread3);
if (err != 0) {
Perror("can't detach thread3\n");
}
// set num
for ( ; ; ) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
num += 1;
pthread_cond_broadcast(&cond);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
sleep(10);
}
return 0;
}
例子2的运行结果,每次有多个线程被唤醒,但是获取到锁的时候,可能条件已经被其他唤醒的线程处理了,所以必须套在while中检查条件是否成熟:
参考:《unix环境高级编程》·第三版
End;










 条件变量是Linux多线程同步的一种机制,常与互斥量配合使用。线程在等待特定条件时会释放互斥锁,条件变化后通过signal或broadcast唤醒等待线程。本文介绍了条件变量的初始化、等待、唤醒以及相关属性,并提供了示例代码。
条件变量是Linux多线程同步的一种机制,常与互斥量配合使用。线程在等待特定条件时会释放互斥锁,条件变化后通过signal或broadcast唤醒等待线程。本文介绍了条件变量的初始化、等待、唤醒以及相关属性,并提供了示例代码。














 1725
1725

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








