目前,大多数的Android应用程序都会使用HTTP协议来发送和接收网络数据,而Android中主要提供了两种方式来进行HTTP操作,HttpURLConnection和HttpClient。
GET和POST的对比
举个例子:get方式类似于明信片,只有请求头,没有请求体。而post方式类似于一封信,信封上的内容为请求头;信里面的内容为请求体(请求头和请求体是分开的)。
含义
- GET:通过请求URI得到资源。一般用于获取/查询资源信息
- POST:用于向服务器提交新的内容。一般用于更新资源信息
主要区别
- get方式主要用于从服务器取回数据,post方式主要用于向服务器提交数据
- get类似于明信片,只有请求头,没有请求体;post类似于一封信,信封上的内容为请求头;信里面的内容为请求体
- 使用get方式向服务器提交的数据量较小,通常不超过2K,使用post方式向服务器提交的数据量通常没有限制(明信片不能多写,而写信可以写很多内容)
- get请求是将所要提交的数据附在URL之后,而post请求是将提交的数据放置在请求体当中
HttpURLConnection
概念
HttpURLConnection是一种多用途、轻量极的HTTP客户端,使用它来进行HTTP操作可以适用于大多数的应用程序。虽然HttpURLConnection的API提供的比较简单,但是同时这也使得我们可以更加容易地去使用和扩展它。
更新历史
- Android 2.2之前,HttpURLConnection一直存在着一些令人厌烦的bug。比如说对一个可读的InputStream调用close()方法时,就有可能会导致连接池失效了。
- Android 2.3,加入了更加透明化的响应压缩。HttpURLConnection会自动在每个发出的请求中加入如下消息头,并处理相应的返回结果:Accept-Encoding: gzip。还增加了一些HTTPS方面的改进,现在HttpsURLConnection会使用SNI(Server Name Indication)的方式进行连接,使得多个HTTPS主机可以共享同一个IP地址。除此之外,还增加了一些压缩和会话的机制。如果连接失败,它会自动去尝试重新进行连接。这使得HttpsURLConnection可以在不破坏老版本兼容性的前提下,更加高效地连接最新的服务器。
- Android 4.0,添加了一些响应的缓存机制。通常我们就可以使用反射的方式来启动响应缓存功能,下面示例代码展示了如何在Android 4.0及以后的版本中去启用响应缓存的功能,同时还不会影响到之前的版本:
private void enableHttpResponseCache() {
try {
long httpCacheSize = 10 * 1024 * 1024; // 10 MiB
File httpCacheDir = new File(getCacheDir(), "http");
Class.forName("android.net.http.HttpResponseCache")
.getMethod("install", File.class, long.class)
.invoke(null, httpCacheDir, httpCacheSize);
} catch (Exception httpResponseCacheNotAvailable) {
}
}如何使用
- 获取HttpURLConnection的实例(一般只需new出一个URL对象)并传入目标的网络地址,然后调用一下openConnection()方法即可,如下代码:
URL url = new URL("http://www.baidu.com");
HttpURLConnection connection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();- 设置HTTP请求方式,常用的方式主要有两个,GET和POST。GET表示希望从服务器那里获取数据,而POST则表示希望提交数据给服务器。写法如下:
connection.setRequestMethod("GET");- 进行一些自由的定制,比如设置连接超时、读取超时的毫秒数,以及服务器希望得到的一些消息头等,这部分内容根据自己的实际情况进行编写,写法如下:
connection.setConnectTimeout(8000);
connection.setReadTimeout(8000);- 调用getInputStream()方法获取到服务器返回的输入流,然后就是对输入流进行读取,如下所示:
InputStream in = connection.getInputStream();- 最后调用disconnect()方法将HTTP连接关闭掉,如下所示:
connection.disconnect();实例操作
新建activity_httpurlconnection_httpclient.xml,如下代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/send_request_button"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="发送请求" />
</LinearLayout>新建HttpURLConnectionOrHttpClientActivity,代码如下:
public class HttpURLConnectionOrHttpClientActivity extends Activity {
private static final String TAG = "HttpURLConnectionOrHttpClientActivity";
private Button mSendRequestButton;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_httpurlconnection_httpclient);
mSendRequestButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.send_request_button);
mSendRequestButton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
sendRequestWithHttpURLConnection();
}
});
}
private void sendRequestWithHttpURLConnection() {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
HttpURLConnection connection = null; // 获取HttpURLConnection的实例
try {
URL url = new URL("http://www.baidu.com");
connection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
connection.setRequestMethod("GET"); // 设置HTTP请求方式
connection.setConnectTimeout(8000); // 自由的定制,设置连接超时、读取超时的毫秒数
connection.setReadTimeout(8000);
InputStream in = connection.getInputStream(); // 获取到服务器返回的输入流
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in)); // 对输入流进行读取
StringBuilder response = new StringBuilder();
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
response.append(line);
}
Log.d(TAG, response.toString());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (connection != null) { // 将HTTP连接关闭掉
connection.disconnect();
}
}
}
}).start();
}
}可以看到,我们在按钮点击事件里调用了sendRequestWithHttpURLConnection()方法,在这个方法中先是开启了一个子线程,然后在子线程里使用HttpURLConnection发出一条HTTP请求,请求的目标地址就是百度的首页。接着利用BufferedReader对服务器返回的流进行读取,最终取出结果并以Log方式显示。运行程序,如下图:
如果想要提交数据给服务器,只需要将HTTP请求的方法改成POST,并在获取输入流之前把要提交的数据写出即可。注意每条数据都要以键值对的形式存在,数据与数据之间用&符号隔开,比如说我们想要向服务器提交用户名和密码,就可以这样写:
connection.setRequestMethod("POST");
DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(connection.getOutputStream());
out.writeBytes("username=admin&password=123456");HttpClient
概念
HttpClient是Apache提供的HTTP网络访问接口,从一开始的时候就被引入到了Android API中。DefaultHttpClient和AndroidHttpClient都是HttpClient具体的实现类,它们都拥有众多的API,而且实现比较稳定,bug数量也很少。但同时也由于HttpClient的API数量过多,使得我们很难在不破坏兼容性的情况下对它进行升级和扩展,所以目前Android团队在提升和优化HttpClient方面的工作态度并不积极。
如何使用
- 创建一个DefaultHttpClient的实例
HttpClient是一个接口,因此无法创建它的实例,通常情况下都会创建一个DefaultHttpClient的实例,如下所示:
HttpClient httpClient = new DefaultHttpClient();- 发起请求,并传入目标的网络地址
发起一条GET请求,就可以创建一个HttpGet对象,并传入目标的网络地址,然后调用HttpClient的execute()方法即可:
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet("http://www.baidu.com");
httpClient.execute(httpGet);
如果是发起一条POST请求,需要创建一个HttpPost对象,并传入目标的网络地址,如下所示:
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost("http://www.baidu.com");然后通过一个NameValuePair集合来存放待提交的参数,并将这个参数集合传入到一个UrlEncodedFormEntity中,然后调用HttpPost的setEntity()方法将构建好的UrlEncodedFormEntity传入,如下所示:
List<NameValuePair> params = new ArrayList<NameValuePair>();
params.add(new BasicNameValuePair("username", "admin"));
params.add(new BasicNameValuePair("password", "123456"));
UrlEncodedFormEntity entity = new UrlEncodedFormEntity(params, "utf-8");
httpPost.setEntity(entity);
- 调用HttpClient的execute()方法
HttpPost和HttpGet一样,调用HttpClient的execute()方法,并将HttpPost对象传入即可:
httpClient.execute(httpPost);执行execute()方法之后会返回一个HttpResponse对象,服务器所返回的所有信息就会包含在这里面。通常情况下我们都会先取出服务器返回的状态码,如果等于200就说明请求和响应都成功了,如下所示:
if (httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200) {
// 请求和响应都成功了
}
接下来在这个if判断的内部取出服务返回的具体内容,可以调用getEntity()方法获取到一个HttpEntity实例,然后再用EntityUtils.toString()这个静态方法将HttpEntity转换成字符串即可,如下所示:
HttpEntity entity = httpResponse.getEntity();
String response = EntityUtils.toString(entity);
注意:如果服务器返回的数据是带有中文的,直接调用EntityUtils.toString()方法进行转换会有乱码的情况出现,这个时候只需要在转换的时候将字符集指定成utf-8就可以了,如下所示:
String response = EntityUtils.toString(entity, "utf-8");选择HttpURLConnection还是HttpClient
在Android 2.2之前,HttpClient拥有较少的bug,因此建议使用它。
在Android 2.3及以后,HttpURLConnection则是最佳的选择。它的API简单,体积较小,非常适用于Android项目。压缩和缓存机制可以有效地减少网络访问的流量,在提升速度和省电方面也起到了较大的作用。对于新的应用程序应该更加偏向于使用HttpURLConnection,因为在以后的工作当中我们也会将更多的时间放在优化HttpURLConnection上面。
自定义HTTP通用类
新建Http通用类
新建HttpUtils ,包括HttpURLConnection和HttpClient分别以get、post方式提交数据,具体代码如下:
public class HttpUtils {
private static final String TAG = "HttpUtils";
public HttpUtils() {
}
/**
* 以HttpURLConnection POST提交表单
*
* @param path URL
* @param params 填写的url的参数
* @param encode 字节编码
* @return
*/
public static String sendPostRequest(String path, Map<String, String> params, String encode) {
String result = "";
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer(); // 作为StringBuffer初始化的字符串
HttpURLConnection urlConnection = null;
try {
if (params != null && !params.isEmpty()) {
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : params.entrySet()) {
buffer.append(entry.getKey()).append("=").append(URLEncoder.encode(entry.getValue(), encode)).append("&");
}
buffer.deleteCharAt(buffer.length() - 1); // 删除掉最有一个&
}
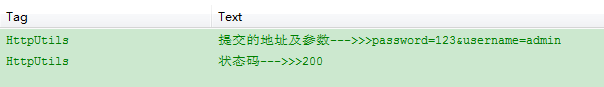
Log.i(TAG, "提交的地址及参数--->>>" + String.valueOf(buffer.toString()));
URL url = new URL(path);
urlConnection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
urlConnection.setConnectTimeout(3000);
urlConnection.setRequestMethod("POST"); // 设置HTTP请求方式
urlConnection.setDoInput(true);
urlConnection.setDoOutput(true);
// 获得上传信息的字节大小以及长度
byte[] mydata = buffer.toString().getBytes();
// 表示设置请求体的类型是文本类型
urlConnection.setRequestProperty("Content-Type", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded");
urlConnection.setRequestProperty("Content-Length", String.valueOf(mydata.length));
// 获得输出流,向服务器输出数据
OutputStream outputStream = urlConnection.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write(mydata, 0, mydata.length);
outputStream.close();
// 获得服务器响应的结果和状态码
int responseCode = urlConnection.getResponseCode();
Log.i(TAG, "状态码--->>>" + String.valueOf(responseCode));
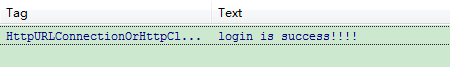
if (responseCode == 200) {
result = changeInputStream(urlConnection.getInputStream(), encode);
}
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (urlConnection != null) {
urlConnection.disconnect();
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* 以HttpURLConnection GET方式请求
*
* @param path URL
* @param params 填写的url的参数
* @param encode 字节编码
* @return
*/
public static String sendGetRequest(String path, Map<String, String> params, String encode) {
String result = "";
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer(path);
HttpURLConnection conn = null;
if (params != null && !params.isEmpty()) {
buffer.append('?');
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : params.entrySet()) {
try {
buffer.append(entry.getKey()).append('=').append(URLEncoder.encode(entry.getValue(), encode)).append('&');
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
buffer.deleteCharAt(buffer.length() - 1);
}
Log.i(TAG, "提交的地址及参数--->>>" + String.valueOf(buffer.toString()));
try {
URL url = new URL(buffer.toString());
conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setRequestMethod("GET");
conn.setReadTimeout(5000);
conn.setConnectTimeout(5000);
int responseCode = conn.getResponseCode();
Log.i(TAG, "状态码--->>>" + String.valueOf(responseCode));
if (responseCode == 200) {
result = changeInputStream(conn.getInputStream(), encode);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (conn != null) {
conn.disconnect();
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* 以HttpClient POST方式提交表单
*
* @param path URL
* @param map 填写的url的参数
* @param encode 字节编码
* @return
*/
public static String sendHttpClientPost(String path, Map<String, String> map, String encode) {
String result = "";
try {
List<NameValuePair> list = new ArrayList<NameValuePair>();
if (map != null && !map.isEmpty()) {
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
list.add(new BasicNameValuePair(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()));
}
}
UrlEncodedFormEntity entity = new UrlEncodedFormEntity(list, encode); // 创建代表请求体的对象
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(path); // 生成使用POST方法的请求对象
httpPost.setEntity(entity); // 将请求体放置在请求对象当中
DefaultHttpClient client = new DefaultHttpClient();
HttpResponse httpResponse = client.execute(httpPost); // 执行请求对象,获取服务器返还的相应对象
int responseCode = httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode();
Log.i(TAG, "状态码--->>>" + String.valueOf(responseCode));
if (responseCode == 200) {
result = changeInputStream(httpResponse.getEntity().getContent(), encode);
}
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClientProtocolException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
/**
* 以HttpClient Get方式请求
*
* @param path URL
* @param map 填写的url的参数
* @param encode 字节编码
* @return
*/
public static String sendHttpClientGet(String path, Map<String, String> map, String encode) {
String result = "";
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer(path);
if (map != null && !map.isEmpty()) {
buffer.append('?');
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) {
try {
buffer.append(entry.getKey()).append('=').append(URLEncoder.encode(entry.getValue(), encode)).append('&');
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
buffer.deleteCharAt(buffer.length() - 1);
}
HttpClient httpClient = new DefaultHttpClient(); // 创建HttpClient对象
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(buffer.toString()); // 创建代表请求的对象,参数是访问的服务器地址
try {
HttpResponse httpResponse = httpClient.execute(httpGet); // 执行请求,获取服务器发还的相应对象
int responseCode = httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode();
Log.i(TAG, "状态码--->>>" + String.valueOf(responseCode));
if (responseCode == 200) {
result = changeInputStream(httpResponse.getEntity().getContent(), encode);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
/**
* 将一个输入流转换成指定编码的字符串
*
* @param inputStream
* @param encode
* @return
*/
private static String changeInputStream(InputStream inputStream, String encode) {
ByteArrayOutputStream outputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] data = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
String result = "";
if (inputStream != null) {
try {
while ((len = inputStream.read(data)) != -1) {
outputStream.write(data, 0, len);
}
result = new String(outputStream.toByteArray(), encode);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return result;
}
}新建Activity
我们直接修改HttpURLConnectionOrHttpClientActivity中的代码,如下:
public class HttpURLConnectionOrHttpClientActivity extends Activity {
private static final String TAG = "HttpURLConnectionOrHttpClientActivity";
private Button mSendRequestButton;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_httpurlconnection_httpclient);
mSendRequestButton = (Button) findViewById(R.id.send_request_button);
mSendRequestButton.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
String path = "http://192.168.111.118:8080/myhttp/servlet/LoginAction";
Map<String, String> params = new HashMap<String, String>();
params.put("username", "admin");
params.put("password", "123");
String result = HttpUtils.sendPostRequest(path, params, "UTF-8");
Log.d(TAG, result);
}
}).start();
}
});
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
}
}部署服务端程序
下载服务端程序:http://download.csdn.net/detail/dengchenhe/8525281
将下载的myhttp.war文件,部署在Apache Tomcat目录下。
运行APP程序
修改HttpURLConnectionOrHttpClientActivity如下部分:
String result = HttpUtils.sendPostRequest(path, params, "UTF-8");- HttpUtils.sendPostRequest:以HttpURLConnection POST提交
- HttpUtils.sendGetRequest:以HttpURLConnection GET方式请求
- HttpUtils.sendHttpClientPost:以HttpClient POST方式提交
- HttpUtils.sendHttpClientGet:以HttpClient GET方式请求























 2153
2153

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








