int count=0;
while(count<5)
{
//statement(s)
count++;
}
In the preceding code snippet, the count variable is initialized with 0. The loop will continue executing statement(s) till the value of the count variable is less than 5.
在上面的代码片段中,count变量被初始化为0。循环将继续执行语句,直到count变量的值小于5。
Chapter 4 : Arrays
第四章:数组
You can create the following types of arrays:
您可以创建以下类型的数组:
◼
One-dimensional array(一维数组)
◼
Multidimensional array(多维数组)
One-dimensional Array(一维数组)
A
one-dimensional array is a collection of elements with a single index value. A one dimensional array can have multiple columns but only one row.The creation of a one-dimensional array involves two steps:
一维数组是具有单个索引值的元素集合。一维数组可以有多列,但只有一行。 创建一维数组需要两个步骤:
1. Declare an array.(声明数组)
2. Assign values to the array.(为数组赋值)
Accessing Arrays(访问数组)
To perform various manipulations on the array, you need to access the following types of arrays:
要对数组执行各种操作,您需要访问以下类型的数组:
◼
One-dimensional array(一维数组)
◼
Two-dimensional array(二维数组)
One-dimensional Array(一维数组)
To access a one-dimensional array, the following syntax is used:
要访问一维数组,使用以下语法:
arrayname[index];
In the preceding syntax,
arrayname
specifies the name of the array and
index
specifies the
location of the array element.Consider the following code snippet:
在上述语法中,arrayname指定数组的名称,index指定数组元素的位置。 考虑以下代码片段:
String jumbledWords[] = {“alpep”,”argneo”,”rgaeps”};
System.out.println(jumbledWords[0]);
In the preceding code snippet, the
jumbledWords
array stores the various jumbled words.
The statement, System.out.println(jumbledWords[0]);, accesses the element stored in the first
index and displays it.
在上述代码片段中,jumbledWords数组存储了各种乱序的单词。语句System.out.println(jumbledWords[0]);访问存储在第一个索引中的元素并将其显示出来。
Manipulating Strings(操作字符串)
Using String Class.
To store string literals, you can use the
String
class in the
java.lang
package. The following code snippet is used to create a string object:
使用String类。要存储字符串字面值,可以使用java.lang包中的String类。以下代码片段用于创建一个字符串对象:
String s1 = new String(“Hello”);
The preceding code snippet creates a new string object in the heap memory, with a value,
Hello
, and assigns it to reference variable, s1
. In addition, it creates another string object with the value,
Hello
, in the string constant pool.
上述代码片段在堆内存中创建了一个新的字符串对象,其值为Hello,并将其赋给引用变量s1。此外,它还在字符串常量池中创建了另一个值为Hello的字符串对象。
You can also create a string object by using the following code snippet:
您还可以使用以下代码片段创建一个字符串对象:
String s1 = “Hello”;
The preceding code snippet creates a new string object with a value, Hello, in the string constant pool and assigns it to the reference variable, s1.上述代码片段在字符串常量池中创建了一个新的值为Hello的字符串对象,并将其赋给引用变量s1。
In Java,
String
class is an immutable class. This means that once a string object is created,
you cannot change its value. However, the reference variables of the String
class are mutable.
在Java中,String类是一个不可变类。这意味着一旦创建了一个字符串对象,您就无法更改其值。但是,String类的引用变量是可变的。
The following table lists the some of the most commonly used methods of the
String
class.
以下表列出了String类的一些常用方法。
See page Number: 4.15
备注:以下是string类常用方法,目测应对考试无需完全掌握,但依然给出。
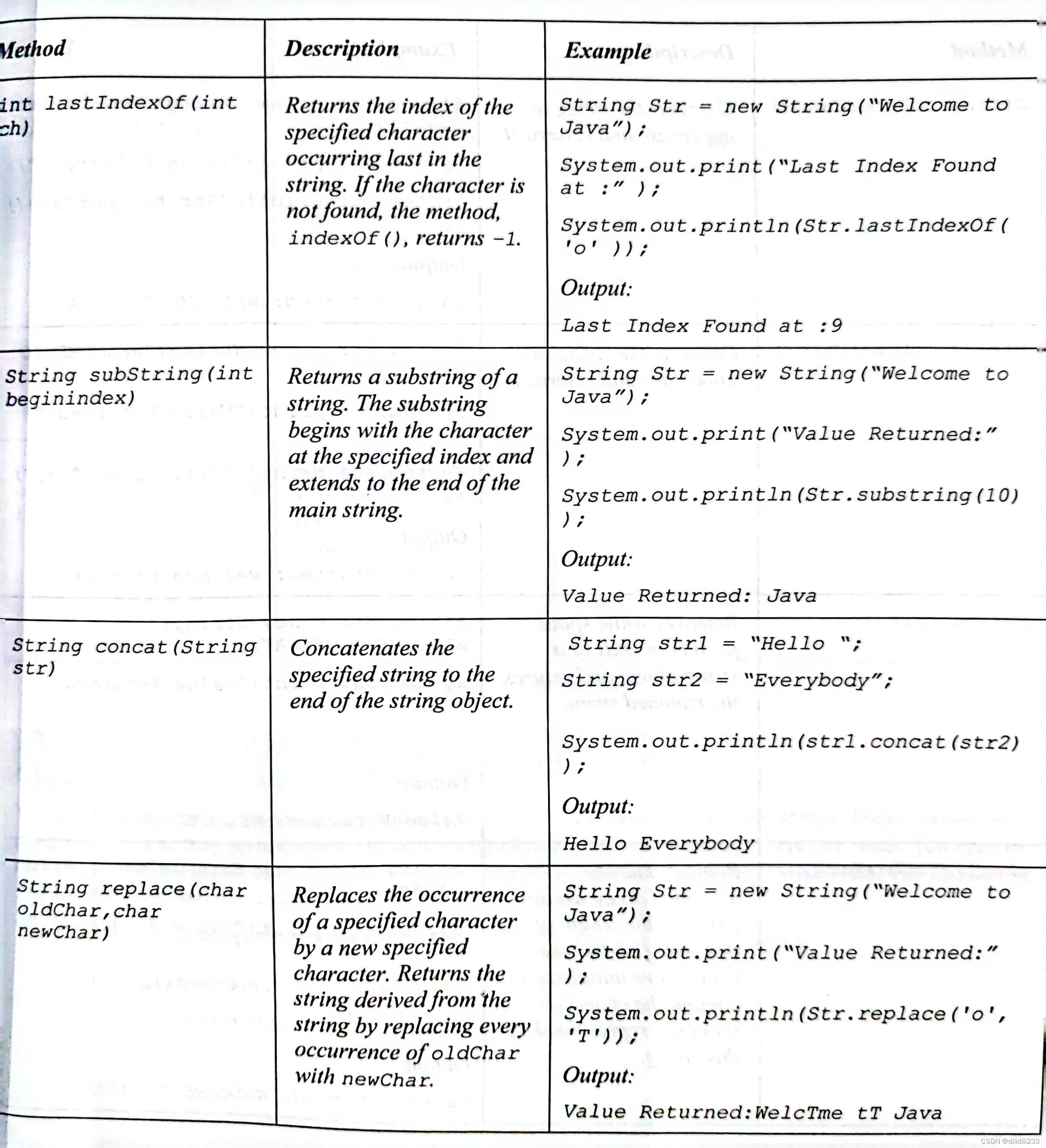
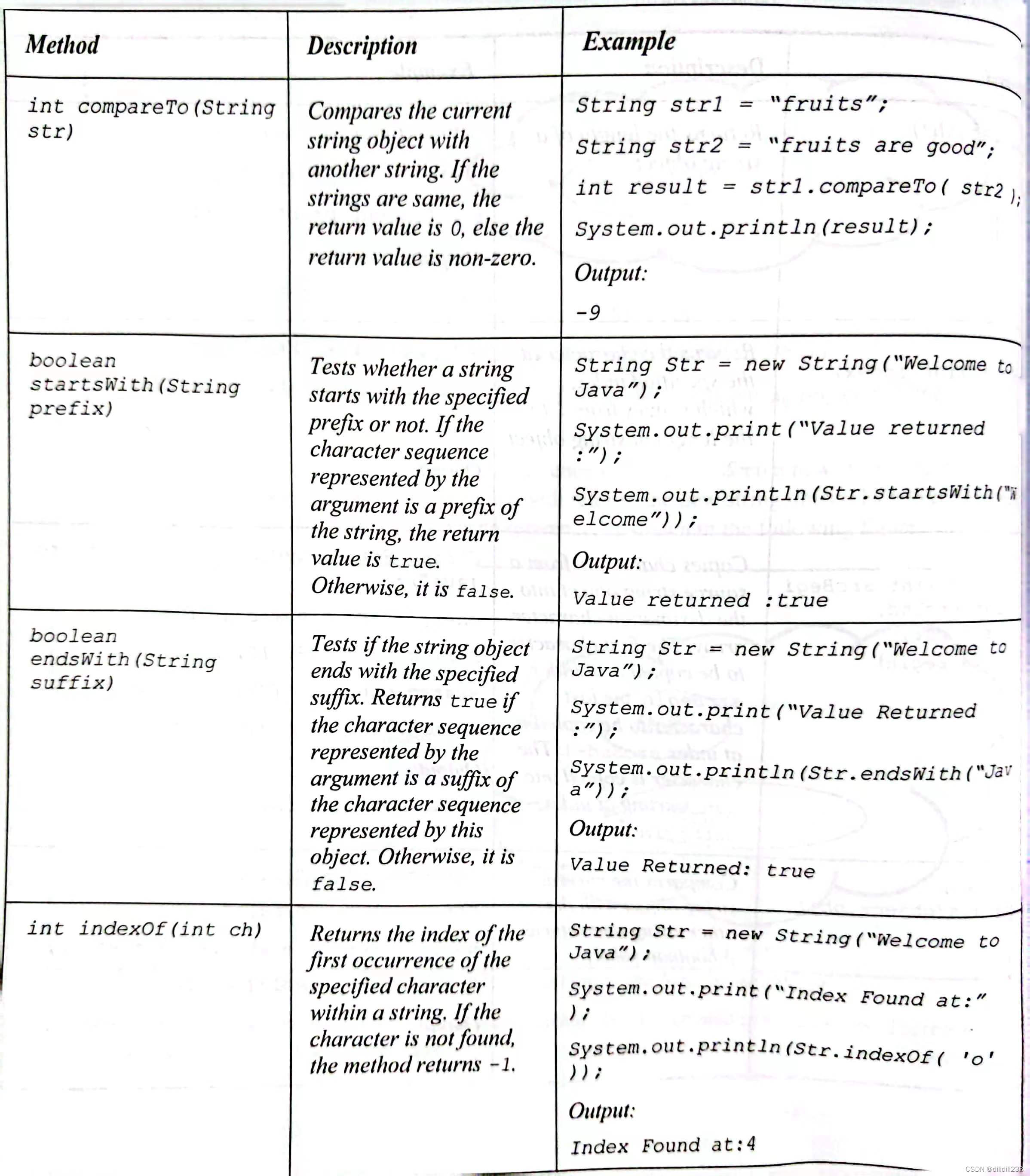
 图:常用String类方法(白皮4.15-4.19上半)
图:常用String类方法(白皮4.15-4.19上半)
Chapter 5 encapsulate reading and writing of fields
第五章:封装字段的读取和写入操作
Through agreed get/set accessors, you can encapsulate reading and writing of fields to achieve
the purpose of controlling data permissions.
通过使用约定的get/set访问器,您可以封装字段的读取和写入操作,以实现控制数据权限的目的。
◼
A class can inherit the features of a related class and add new features, as per the
requirement.(一个类可以继承相关类的特性并根据需求添加新特性。)
◼
In inheritance, the class that inherits the data members and methods from another class is
known as the subclass or derived class.(在继承中,从另一个类继承数据成员和方法的类称为子类或派生类。)
◼
The class from which the subclass inherits the features is known as the superclass or base
class.(子类继承特性的类被称为超类或基类。)
◼
In single level inheritance, a single subclass derives the functionality of an existing
superclass.(在单级继承中,单个子类派生现有超类的功能。)
◼
In multilevel inheritance, a subclass inherits the properties of another subclass.(在多级继承中,子类继承另一个子类的属性。)
◼
In hierarchical inheritance, one or more subclasses are derived from a single superclass.(在层次继承中,一个或多个子类派生自单个超类。)
◼
An abstract class is a class that contains one or more abstract methods.(抽象类是一个包含一个或多个抽象方法的类。)
◼
An abstract class cannot be instantiated but can be inherited by other classes by using the
extends keyword.(抽象类不能被实例化,但可以通过使用extends关键字被其他类继承。)
◼
Interfaces contain a set of abstract methods and static and final data members.(接口包含一组抽象方法和静态和最终数据成员。)
◼
A class that implements an interface must provide the implementation of all the methods
declared in that interface.(实现接口的类必须提供对该接口中声明的所有方法的实现。)
◼
In Java, polymorphism has the following two types
在Java中,多态性具有以下两种类型
:
⚫
Static polymorphism(静态多态性)
⚫
Dynamic polymorphism(动态多态性)
◼
In case of static polymorphism, an entity, such as a method, can exist in multiple forms.
(在静态多态性的情况下,一个实体(例如方法)可以以多种形式存在。)
◼
Dynamic polymorphism is implemented in Java by method overriding.
(动态多态性通过方法重写在Java中实现。)
◼
To override a method present in the superclass, the subclass method should have the same
name, same parameters, and same return type as the method in the superclass.
(要重写超类中存在的方法,子类方法应与超类中的方法具有相同的名称、相同的参数和相同的返回类型。)
Chapter 6:appropriate exception
第六章:异常处理
When a run-time error occurs, an exception is thrown by the JVM which can be handled by an
appropriate exception handler.
当发生运行时错误时,JVM会抛出异常,可以通过适当的异常处理程序来处理。
◼
To deal with these exceptions, Java provides various built-in exception classes.
为了处理这些异常,Java提供了各种内置的异常类。
◼
The
Throwable
class is the base class of exceptions in Java.
Throwable类是Java中异常的基类。
◼
The
Exception
class represents the conditions that a program should handle.
Exception类表示程序应该处理的条件。
◼
The
Error
class defines the exceptions related to the Java run-time environment.
Error类定义了与Java运行时环境相关的异常。
◼
Java exceptions are categorized into the following types:
Java异常分为以下几种类型:
⚫
Checked exceptions(受检异常)
⚫
Unchecked exceptions(未检查异常)
◼
You can implement exception handling in a program by using the following keywords and
blocks:
您可以使用以下关键字和块在程序中实现异常处理:
⚫
try
⚫
catch
⚫
throw
⚫
throws
⚫
finally
◼
A
try
block encloses the statements that might raise an exception and defines one or more
exception handlers associated with it.
(try块包含可能引发异常的语句,并定义与之关联的一个或多个异常处理程序。)
◼
In Java, the
catch
block is used as an exception handler.
(在Java中,catch块用作异常处理程序。)
◼
A
try
block must have at least one
catch
block that follows the
try
block,
immediately.
(try块必须有至少一个紧随其后的catch块。)
◼
You can throw an exception explicitly, by using the
throw
keyword.
(您可以使用throw关键字显式地抛出异常)
◼
The
throws
keyword is used by a method to specify the types of exceptions that the
method can throw.
(throws关键字用于方法中指定方法可能抛出的异常类型。)
◼
The statements specified in the
finally
block are executed after the control has left the
try-catch block.
(finally块中指定的语句在控制流离开try-catch块后执行。)
◼
In addition to the built-in exceptions, you can create customized exceptions, as per the
application requirements.
(除了内置异常之外,您可以根据应用程序的需求创建自定义异常。)
◼
Assertions are statements in Java that enable you to test any assumptions that you make
regarding a program during its execution.
(断言是Java中的语句,它使您能够在程序执行过程中测试对程序的任何假设。)
◼
You can implement assertions by using the
assert
keyword provided in Java.
(您可以使用Java提供的assert关键字实现断言。)
Chapter 7:
第七章:内部类&类型转换
A class defined within another class is called an inner class.
在另一个类中定义的类被称为内部类。
◼
Java provides the following four types of inner classes:
Java提供了以下四种类型的内部类:
⚫
Regular inner class(常规内部类)
⚫
Static inner class(静态内部类)
⚫
Method-local inner class(方法局部内部类
)
⚫
Anonymous inner class(匿名内部类)
◼
A regular inner class is a class whose definition appears inside the definition of another
class. The regular inner class is similar to a member of an outer class.
◼ 常规内部类是在另一个类的定义内部出现的类。常规内部类类似于外部类的成员。
◼
Static inner classes are inner classes marked with the static modifier.
◼ 静态内部类是使用static修饰符标记的内部类。
◼
A method-local inner class is defined inside the method of the enclosing class. Because the
class is defined inside a method, it needs to be instantiated within the same method.
◼ 方法局部内部类定义在封闭类的方法内部。因为该类在方法内部定义,所以需要在同一个方法内实例化。
◼
Java supports the following types of type casting:
Java支持以下类型的类型转换:
⚫
Type casting primitive data types(基本数据类型的类型转换
)
⚫
Type casting objects(对象的类型转换
)
◼
A primitive data type supports the following types of type casting:
基本数据类型支持以下类型的类型转换:
⚫
Implicit casting(隐式转换)
⚫
Explicit casting(显式转换)
◼
Implicit conversion refers to an automatic conversion of one data type into another. It occurs
if both the data types are compatible with each other.
隐式转换是指将一个数据类型自动转换为另一个数据类型。如果两个数据类型彼此兼容,就会发生隐式转换。
◼
Explicit conversion occurs when one data type cannot be implicitly converted into another
data type.
显式转换发生在一个数据类型无法隐式转换为另一个数据类型时。
◼
In case of explicit conversion, you must convert the data type into the compatible type.
在显式转换的情况下,您必须将数据类型转换为兼容的类型。
◼
The casting of object references depends on the relationship of the classes involved in the
same.
对象引用的转换取决于涉及相同继承关系的类的关系。
Chapter 8:Localization
第八章:本地化
Localization is a process of customizing the application to a specific locale and culture.
本地化是将应用程序定制为特定的区域设置和文化的过程。
◼
Localization can be implemented on different types of data, such as date, currency, and text.
本地化可以在不同类型的数据上实施,例如日期、货币和文本。
◼
To localize different types of data, it is necessary to determine the language and country.
要本地化不同类型的数据,需要确定语言和国家。
◼
To determine the language, Java provides a predefined set of language codes, such as
zh
for Chinese and
en
for English.
为了确定语言,Java提供了一组预定义的语言代码,例如中文的"zh"和英文的"en"。
◼
To work with localization, the
Locale
class of the
java.util
package is used.
为了处理本地化,使用java.util包中的Locale类。
◼
To localize the date, you need to use the various date formats. To determine the date format
according to the locale, you can use the
java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter class.
要本地化日期,需要使用各种日期格式。为了根据区域设置确定日期格式,可以使用java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter类。
Chapter 9:set interface
第九章:Set接口
The
Set
interface is used to create a collection of unique objects.
Set接口用于创建一个包含唯一对象的集合。
◼
The package,
java.util
, provides the
Iterator
interface to traverse through the set
collection.
java.util包提供了Iterator接口来遍历Set集合。
◼
The
HashSet
class provides the implementation of the
Set
interface that enables you to
create a set in which insertion is faster because it does not sort the elements.
HashSet类提供了Set接口的实现,可以创建一个插入速度较快的集合,因为它不对元素进行排序。
◼
The
TreeSet
class provides the implementation of the
Set
interface that enables you to
create a sorted set of objects.
TreeSet类提供了Set接口的实现,可以创建一个有序的对象集合。
◼
The
List
interface is used to create an ordered collection of objects, which can contain
duplicate objects.
List接口用于创建一个有序的对象集合,可以包含重复的对象。
◼
The package,
java.util
, provides the
ListIterator
interface to traverse through the
list collection.
java.util包提供了ListIterator接口来遍历List集合。
◼
The
ArrayList
class provides the implementation of the
List
interface. The ArrayList class enables you to create a resizable array.
ArrayList类提供了List接口的实现,它可以创建一个可调整大小的数组。
◼
The
Vector
class is similar to the
ArrayList
class.
Vector类与ArrayList类类似。
◼
The methods of the
Vector
class are synchronized, which means that only one thread at a
given time can access it in a multithreaded environment.
Vector类的方法是同步的,这意味着在多线程环境中只有一个线程可以访问它。
◼
The methods of the
ArrayList
class are not synchronized.
ArrayList类的方法不是同步的。
◼
The
Map
interface enables you to create a collection with key-value pair objects.
Map接口允许你创建一个带有键-值对对象的集合。
Chapter 10:Behavior parameterization
第十章:行为参数化
Behavior parameterization is the abstraction of behavior into a variable so that it can be passed.
行为参数化是将行为抽象为一个变量,以便可以传递它。
◼
The type of a behavior parameter is defined by a functional interface.
行为参数的类型由函数式接口定义。
◼
A functional interface is an interface that contains only one method.
函数式接口是只包含一个方法的接口。
◼
A Lambda expression is an anonymous function that can be used to replace an
implementation class of a functional interface.
Lambda表达式是匿名函数,可以用来替代函数式接口的实现类。
Chapter 11:Thread
第十一章:线程
A thread is defined as the path of execution of a program. It is a sequence of instructions that is
executed to define a unique flow of control.
线程被定义为程序的执行路径。它是一系列指令的执行,用于定义独特的控制流程。
◼
A program that creates two or more threads is called a multi-threaded program.
Thread priorities are the integers in the range of 1 to 10 that specify the priority of one thread
with respect to the priority of another thread.
◼ 创建两个或多个线程的程序称为多线程程序。
线程优先级是在1到10范围内的整数,用于指定一个线程相对于另一个线程的优先级。
◼
You can set the thread priority after it is created by using the
setPriority()
method
declared in the
Thread
class.
在创建线程之后,可以使用Thread类中声明的setPriority()方法设置线程的优先级。
◼
The synchronization of threads ensures that if two or more threads need to access a shared
resource, then that resource is used by only one thread at a time.
线程的同步确保如果两个或多个线程需要访问共享资源,那么该资源只会被一个线程使用。
Chapter 12
第十二章:数据流
Java handles all the input and output operations in the form of streams that act as a sequence of
bytes or characters traveling from a source to a destination.
Java以流的形式处理所有的输入和输出操作,流是一系列从源到目标的字节或字符序列。
◼
When a stream of data is being sent, it is said to be written; and when a stream of data is
being received, it is said to be read.
当数据流正在发送时,称为写入;当数据流正在接收时,称为读取。
◼
To read data in the form of characters, Java provides the
Reader
classes inside the
java.io package.
为了以字符形式读取数据,Java在java.io包中提供了Reader类。
◼
The
FileInputStream
class is used to read data and the steams of bytes from the file.
FileInputStream类用于从文件中读取数据和字节流。
◼
The
BufferedInputStream
class is used to perform the read operations by using a
temporary storage, buffer, in the memory.
BufferedInputStream类用于使用内存中的临时存储区(缓冲区)执行读操作。
◼
The
FileReader
class is used for reading characters from a file, but it does not define
any method of its own.
FileReader类用于从文件中读取字符,但它不定义任何自己的方法。
◼
The
BufferedReader
class is used to read the text from a character-input stream, such
as a file, console, and array, while buffering characters.
BufferedReader类用于从字符输入流(如文件、控制台和数组)中读取文本,并缓冲字符。
◼
To write the data in the form of bytes, Java provides the
OutputStream
classes.
为了以字节形式写入数据,Java提供了OutputStream类。
◼
To write the data in the form of characters, Java provides the
Writer
classes inside the
java.io
package.
为了以字符形式写入数据,Java在java.io包中提供了Writer类。
◼
FileOutputStream
is used for writing data, byte by byte, to a file.
FileOutputStream用于将数据逐字节写入文件。
Chapter 13:JDBC API
第十三章:通过jdbc连接java与mysql
The classes and interfaces of the JDBC API are defined in the
java.sql
and
javax.sql
packages.
JDBC API的类和接口定义在java.sql和javax.sql包中。
◼
You can load a driver and register it with the driver manager by using the
forName()
method or the
registerDriver()
method.
你可以使用forName()方法或registerDriver()方法加载并向驱动程序管理器注册驱动程序。
◼
A
Connection
object establishes a connection between a Java application and a
database.
Connection对象建立Java应用程序与数据库之间的连接。
◼
A
Statement
object sends a request and retrieves results to/ from a database.
Statement对象向数据库发送请求并检索结果。
◼
You can insert, update, and delete data from a table using the DML statements in Java
applications.
你可以使用Java应用程序中的DML语句向表中插入、更新和删除数据。
◼
You can create, alter, and drop tables from a database using the DDL statements in Java
applications.
你可以使用Java应用程序中的DDL语句创建、修改和删除数据库中的表。
◼
Once the SQL statements are executed, a
ResultSet
object stores the result retrieved
from a database.
执行SQL语句后,ResultSet对象存储从数据库检索到的结果。
Chapter A:题目整理
仅凭前文晦涩难懂的知识(面向初学者)依然难以应对考试,本文继续整理一些日常练习题,希望对你有所帮助。
1、With x = 0, which of the following are legal lines of Java code for changing the value of x to 1?
当 x = 0 时,以下哪一行是将 x 的值更改为 1 的合法 Java 代码行?
1. x++;
2. x = x + 1;
3. x += 1;
答案:1&2&3
2、What is the output of this program? 这个程序的输出是什么?
class increment
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int g = 3;
System.out.print(++g * 8);
}
}
答案:32
3、What is the output of this program? 这个程序的输出是什么?
class operators
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int var1 = 5;
int var2 = 6;
int var3;
var3 = ++ var2 * var1 / var2 + var2;
System.out.print(var3);
}
}
答案:12
4、What is the output of relational operators?关系运算符的输出是什么?
| Integer | Boolean | Characters | Double |
答案:Boolean
5、What is the output of this program?这个程序的输出是什么?
class Relational_operator
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int var1 = 5;
int var2 = 6;
System.out.print(var1 > var2);
}
}
答案:FALSE
6、Which of the following loops will execute the body of loop even when condition controlling the loop is initially false?以下哪个循环将执行循环主体,即使条件控制循环最初为 false?
| do-while | while | for | none of the mentioned |
答案:A
7.What is the output of this program?这个程序的输出是什么?
class selection_statements
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int var1 = 5;
int var2 = 6;
if ((var2 = 1) == var1)
System.out.print(var2);
else
System.out.print(++var2);
}
}
答案:2
8.What is true about a break? 关于“break”,正确的说法是?
[A]Break stops the execution of entire program 中断停止整个程序的执行
[B]Break halts the execution and forces the control out of the loop Break停止执行并强制控制退出循环
[C]Break forces the control out of the loop and starts the execution of next iteration Break强制控制退出循环并开始执行下一次迭代
[D]Break halts the execution of the loop for certain time frame Break在特定时间段内停止循环的执行
答案:B
9. What is true about do statement?以下陈述正确的是?
[A] do statement executes the code of a loop at least once do语句至少执行一次循环的代码
[B] do statement does not get execute if condition is not matched in the first iteration 如果条件在第一次迭代中不匹配,do语句将不会执行
[C] do statement checks the condition at the beginning of the loop do语句检查循环开始时的条件
[D] do statement executes the code more than once always do语句总是多次执行代码
答案:A
10、Which of these values can a boolean variable contain?布尔变量可以包含哪些值?
答案:True & False
11、Which one not is a valid keyword?哪一个不是有效的关键字?
[a] for [b] loop [c] int [d] while
答案:b
12.which of the following is not a operator?以下哪项不是运算符?
答案: ;
13、What is the output of this program?这个程序的输出是什么?
class Relational_operator
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
int a = 20;
int b = 6;
System.out.print(++a + ++a);
}
}
答案:43
14、which of the following is a unary opeartors in java?以下哪项是Java中的一元运算符?
答案:++
15、John wants to create a class in which he wants to hide its member variables from all the other classes inluding the Child Classes . Which one of the following access specifies should be use? John 想要创建一个类,他想在其中对包含子类的所有其他类隐藏其成员变量。应使用以下哪一个访问权限指定?
| private | protected | public | default |
答案:private
16、Predict the output of the following program.预测以下程序的输出。
public class Test
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
boolean var1 = true;
boolean var2 = false;
if (var1)
System.out.println(var1);
else
System.out.println(var2);
}
}
答案:true
17、Jim wants to define a variable to store numbers, which of the following is not a variable name?Jim 想定义一个变量来存储数字,以下哪项不是变量名?
答案:3count
18、Which of the following component is not a part of the Java architecture?以下哪个组件不是 Java 体系结构的一部分?
| Source File(.java) | class file (.class) | Java virtual machine (JVM) | CPU |
答案:CPU
19、Which of the following class name is not correct?以下哪个类名不正确?
| class | guess | GuessNumber | _guess |
答案:class
20、Tom wants to develop a student management program, but the program cannot run. Please determine which line of code is wrong? 汤姆想开发一个学生管理程序,但该程序无法运行。请确定哪一行代码是错误的?
class $_Manager{
1 int age;
2 } class 2Manager{
3 private String name;
4 }
答案:2
21、Which of the following represents the correct output of 20-3*4+10/2?以下哪项代表 20-3*4+10/2 的正确输出?
答案:13
22、Identify the output of the following code?辨认以下代码的输出?
boolean result = (4 > 5) && (3 < 6) || (9>7);
System.out.println(result);
答案:true
23、Which of the following operators is used to find the remainder after dividing two numbers?以下哪个运算符用于查找除以两个数字后的余数?
答案:%
24、Predict the output of the following code: 预测以下代码的输出:
int m = 5, n = 5;
if(m > n){
System.out.println("True");
}else if(m < n}{
System.out.println("False");
}else{
System.out.println("Equals");
}
答案:report an error(将会报错)
25、Which of the correct syntax of creating class?创建类的正确语法是什么?
A B C D
Class Abc{
//statements
} | class 3Abc{
//statements
} | class Abc{
//statements
} | class Abc(){
//statements
} |
答案:C(左数第三个)








 图:常用String类方法(白皮4.15-4.19上半)
图:常用String类方法(白皮4.15-4.19上半)




















 152
152

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








