问题及代码:
/*
* Copyright (c) 2016, 烟台大学计算机与控制工程学院
* All rights reserved.
* 文件名称:Cube007.cpp
* 作 者:刘小楠
* 完成日期:2016年10月9日
*
* 问题描述:试为停车场编制按上述要求进行管理的模拟程序。栈以顺序结构实现,队列以链表结构实现。
* 输入描述:无
* 输出描述:结果
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define N 10 /*停车场内最多的停车数*/
#define M 10 /*候车场内最多的停车数*/
#define Price 2 /*每单位时间停车费用*/
typedef struct
{
int CarNo[N]; /*车牌号*/
int CarTime[N]; /*进场时间*/
int top; /*栈指针*/
} SqStack; /*定义顺序栈类型,用于描述停车场*/
typedef struct
{
int CarNo[M]; /*车牌号*/
int front,rear; /*队首和队尾指针*/
} SqQueue; /*定义循环队类型,用于描述候车场*/
/*以下为顺序栈的基本运算算法*/
void InitStack(SqStack *&s)
{
s=(SqStack *)malloc(sizeof(SqStack));
s->top=-1;
}
int StackEmpty(SqStack *s)
{
return(s->top==-1);
}
int StackFull(SqStack *s)
{
return(s->top==N-1);
}
int Push(SqStack *&s,int e1,int e2)
{
if (s->top==N-1)
return 0;
s->top++;
s->CarNo[s->top]=e1;
s->CarTime[s->top]=e2;
return 1;
}
int Pop(SqStack *&s,int &e1,int &e2)
{
if (s->top==-1)
return 0;
e1=s->CarNo[s->top];
e2=s->CarTime[s->top];
s->top--;
return 1;
}
void DispStack(SqStack *s)
{
int i;
for (i=s->top; i>=0; i--)
printf("%d ",s->CarNo[i]);
printf("\n");
}
/*以下为循环队列的基本运算算法*/
void InitQueue(SqQueue *&q)
{
q=(SqQueue *)malloc (sizeof(SqQueue));
q->front=q->rear=0;
}
int QueueEmpty(SqQueue *q)
{
return(q->front==q->rear);
}
int QueueFull(SqQueue *q) /*判断队满*/
{
return ((q->rear+1)%M==q->front);
}
int enQueue(SqQueue *&q,int e) /*进队*/
{
if ((q->rear+1)%M==q->front) /*队满*/
return 0;
q->rear=(q->rear+1)%M;
q->CarNo[q->rear]=e;
return 1;
}
int deQueue(SqQueue *&q,int &e) /*出队*/
{
if (q->front==q->rear) /*队空的情况*/
return 0;
q->front=(q->front+1)%M;
e=q->CarNo[q->front];
return 1;
}
void DispQueue(SqQueue *q) /*输出队中元素*/
{
int i;
i=(q->front+1)%M;
printf("%d ",q->CarNo[i]);
while ((q->rear-i+M)%M>0)
{
i=(i+1)%M;
printf("%d ",q->CarNo[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//main函数用于模拟停车场的工作
int main()
{
int comm;
int no,e1,time,e2;
int i,j,t;
SqStack *St,*St1; //St是停车场,St1是在有车离开时,记录为该车移开位置的车辆
SqQueue *Qu; //Qu是候车场
InitStack(St);
InitStack(St1);
InitQueue(Qu);
do
{
printf("输入指令(1:到达 2:离开 3:显示停车场 4:显示候车场 0:退出):");
scanf("%d",&comm);
switch(comm)
{
case 1: /*汽车到达*/
printf("输入车号和时间(设车号和时间均为整数): ");
scanf("%d%d",&no,&time);
if (!StackFull(St)) /*停车场不满*/
{
Push(St,no,time);
printf(" >>停车场位置:%d\n",St->top+1);
}
else /*停车场满*/
{
if (!QueueFull(Qu)) /*候车场不满*/
{
enQueue(Qu,no);
printf(" >>候车场位置:%d\n",Qu->rear);
}
else
printf(" >>候车场已满,不能停车\n");
}
break;
case 2: /*汽车离开*/
printf("输入车号和时间(设车号和时间均为整数): ");
scanf("%d%d",&no,&time);
for (i=0; i<=St->top && St->CarNo[i]!=no; i++); //在栈中找
if (i>St->top)
printf(" >>未找到该编号的汽车\n");
else
{
t = St->top - i; //需要出栈的车辆数目
for (j=0; j<t; j++) //for (j=i; j<=St->top; j++)1楼评论讲的原错误写法
{
Pop(St,e1,e2);
Push(St1,e1,e2); /*倒车到临时栈St1中*/
}
Pop(St,e1,e2); /*该汽车离开*/
printf(" >>%d汽车停车费用:%d\n",no,(time-e2)*Price);
while (!StackEmpty(St1)) /*将临时栈St1重新回到St中*/
{
Pop(St1,e1,e2);
Push(St,e1,e2);
}
if (!QueueEmpty(Qu)) /*队不空时,将队头进栈St*/
{
deQueue(Qu,e1);
Push(St,e1,time); /*以当前时间开始计费*/
}
}
break;
case 3: /*显示停车场情况*/
if (!StackEmpty(St))
{
printf(" >>停车场中的车辆:"); /*输出停车场中的车辆*/
DispStack(St);
}
else
printf(" >>停车场中无车辆\n");
break;
case 4: /*显示候车场情况*/
if (!QueueEmpty(Qu))
{
printf(" >>候车场中的车辆:"); /*输出候车场中的车辆*/
DispQueue(Qu);
}
else
printf(" >>候车场中无车辆\n");
break;
case 0: /*结束*/
if (!StackEmpty(St))
{
printf(" >>停车场中的车辆:"); /*输出停车场中的车辆*/
DispStack(St);
}
if (!QueueEmpty(Qu))
{
printf(" >>候车场中的车辆:"); /*输出候车场中的车辆*/
DispQueue(Qu);
}
break;
default: /*其他情况*/
printf(" >>输入的命令错误\n");
break;
}
}
while(comm!=0);
return 0;
}
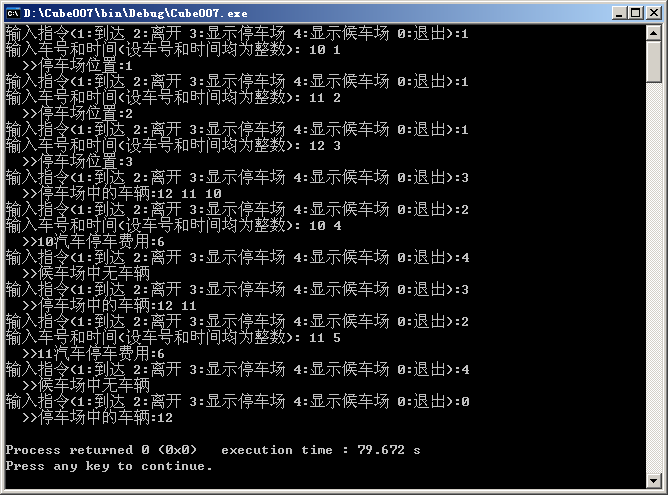
运行结果:
知识点总结:
该程序运用了顺序栈和队列两种数据结构,其中停车场是栈,汽车先进后出,候车场是队列,即先来候车的汽车先去停车,所以这就运用了队列先进先出的特点。无论是候车室还是停车场,栈满与队满同样输出不能再进入车辆。
学习心得:
在一定程度上可以将所有的数据结构算法库合并为一个算法库,最后更改主函数来完成程序。






















 314
314

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








