题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1560
DNA sequence
Time Limit: 15000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 2999 Accepted Submission(s): 1462
Problem Description
The twenty-first century is a biology-technology developing century. We know that a gene is made of DNA. The nucleotide bases from which DNA is built are A(adenine), C(cytosine), G(guanine), and T(thymine). Finding the longest common subsequence between DNA/Protein sequences is one of the basic problems in modern computational molecular biology. But this problem is a little different. Given several DNA sequences, you are asked to make a shortest sequence from them so that each of the given sequence is the subsequence of it.
For example, given "ACGT","ATGC","CGTT" and "CAGT", you can make a sequence in the following way. It is the shortest but may be not the only one.
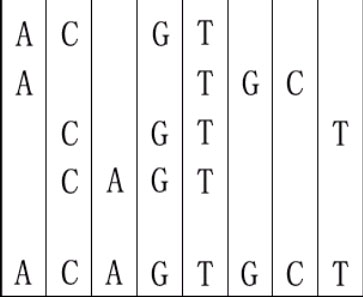
For example, given "ACGT","ATGC","CGTT" and "CAGT", you can make a sequence in the following way. It is the shortest but may be not the only one.

Input
The first line is the test case number t. Then t test cases follow. In each case, the first line is an integer n ( 1<=n<=8 ) represents number of the DNA sequences. The following k lines contain the k sequences, one per line. Assuming that the length of any sequence is between 1 and 5.
Output
For each test case, print a line containing the length of the shortest sequence that can be made from these sequences.
Sample Input
1 4 ACGT ATGC CGTT CAGT
Sample Output
8
Author
LL
Source
题解:
一开始以为是直接用回溯的方法,结果TLE。看了题解是用IDA*(迭代加深搜),其实自己不太了解迭代加深搜为什么比较快,而且什么时候用合适?下面是自己对迭代加深搜的一些浅薄的了解:
1.首先迭代加深搜适合用在:求最少步数(带有BFS的特点)并且不太容易估计搜索深度的问题上,同时兼有了BFS求最少步数和DFS易写、无需多开数组的特点。
2.相对于赤裸裸的回溯,迭代加深搜由于限制了搜索深度,所以也能适当地剪枝。
3.我编不下去了……
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#define ms(a,b) memset((a),(b),sizeof((a)))
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int INF = 2e9;
const LL LNF = 9e18;
const int MOD = 1e9+7;
const int MAXN = 10+10;
int n;
char dna[MAXN][MAXN];
int len[MAXN], pos[MAXN];
char s[4] = {'A', 'G', 'C', 'T'};
bool dfs(int k, int limit) //k为放了几个, k+1才为当前要放的
{
int maxx = 0, cnt = 0; //maxx为最长剩余的dna片段, cnt为剩余的片段之和(核苷酸链?好怀念啊)
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++)
{
cnt += len[i]-pos[i];
maxx = max(maxx, len[i]-pos[i]);
}
if(cnt==0) return true; //如果片段都放完,则已得到答案
if(cnt<=limit-k) return true; //剪枝:片段之和小于等于剩余能放数量,肯定能够得到答案
if(maxx>limit-k) return false; //剪枝:最小的估计值都大于剩余能放数量,肯定不能得到答案
int tmp[MAXN];
for(int i = 0; i<4; i++)
{
memcpy(tmp, pos, sizeof(tmp));
bool flag = false;
for(int j = 0; j<n; j++)
if(dna[j][pos[j]]==s[i])
pos[j]++, flag = true;
//k+1<=limit:在限制范围内
if(k+1<=limit && flag && dfs(k+1, limit) )
return true;
memcpy(pos, tmp, sizeof(pos));
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
int limit = 0;
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++)
{
scanf("%s",dna[i]);
len[i] = strlen(dna[i]);
limit = max(limit, len[i]);
}
ms(pos, 0);
while(!dfs(0, limit))
limit++;
printf("%d\n", limit);
}
}
代码二:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#define ms(a,b) memset((a),(b),sizeof((a)))
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int INF = 2e9;
const LL LNF = 9e18;
const int MOD = 1e9+7;
const int MAXN = 10+10;
int n;
char dna[MAXN][MAXN];
int len[MAXN], pos[MAXN];
char s[4] = {'A', 'G', 'C', 'T'};
bool dfs(int k, int limit) //k为放了几个, k+1才为当前要放的
{
if(k>limit) return false;
int maxx = 0, cnt = 0; //maxx为最长剩余的dna片段, cnt为剩余的片段之和(核苷酸链?好怀念啊)
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++)
{
cnt += len[i]-pos[i];
maxx = max(maxx, len[i]-pos[i]);
}
if(cnt==0) return true; //如果片段都放完,则已得到答案
if(cnt<=limit-k) return true; //剪枝:片段之和小于等于剩余能放数量,肯定能够得到答案
if(maxx>limit-k) return false; //剪枝:最小的估计值都大于剩余能放数量,肯定不能得到答案
int tmp[MAXN];
for(int i = 0; i<4; i++)
{
memcpy(tmp, pos, sizeof(tmp));
bool flag = false;
for(int j = 0; j<n; j++)
if(dna[j][pos[j]]==s[i])
pos[j]++, flag = true;
if(flag && dfs(k+1, limit) )
return true;
memcpy(pos, tmp, sizeof(pos));
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
int limit = 0;
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++)
{
scanf("%s",dna[i]);
len[i] = strlen(dna[i]);
limit = max(limit, len[i]);
}
ms(pos, 0);
while(!dfs(0, limit))
limit++;
printf("%d\n", limit);
}
}























 384
384











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








