广度优先算法适用于计算有向无权图计算最短路径。狄克斯特拉算法是有向加权图计算最小开销的算法,不适用于负权边的情况。
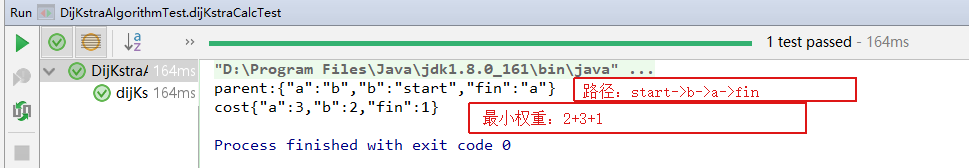
下面是代码示例,起点是start,经过a点权重是6,b点的权重是2,a点到终点fin的权重是1。b点到a点的权重是3,到fin点的权重是5,现在计算从start到fin的最小权重路径。

package com.teriste.algorithm;
import org.apache.commons.collections.MapUtils;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class DijKstraAlgorithm {
//节点关系及权重
public static Map<String,Map<String,Integer>> graph = new HashMap<>();
//每个节点的开销,从起点到该节点的开销
public static Map<String,Integer> cost = new HashMap<>();
//每个节点的父节点
public static Map<String,String> parent = new HashMap<>();
//记录处理过的节点避免重复处理
//public static List<String> processed = new ArrayList<>();
static {
//起点
Map<String,Integer> start = new HashMap<>();
//起点到a点的权重
start.put("a",6);
//起点到b点的权重
start.put("b",2);
graph.put("start",start);
//a点
Map<String,Integer> a = new HashMap<>();
//a到fin点的权重
a.put("fin",1);
graph.put("a",a);
//b点
Map<String,Integer> b = new HashMap<>();
//b到a点的权重
b.put("a",3);
//b到fin点的权重
b.put("fin",5);
graph.put("b",b);
//fin点是终点
graph.put("fin",null);
//-------------------------------
cost.put("a",6);
cost.put("b",2);
//------------------------
parent.put("a","start");
parent.put("b","start");
parent.put("fin",null);
}
//遍历输入节点的所有临近节点,
public void dijKstraCalc(String key){
Map<String,Integer> start = graph.get(key);
if (MapUtils.isEmpty(start)){
return;
}
if (MapUtils.isNotEmpty(start)){
//遍历临近节点
for(Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry:start.entrySet()){
if (entry.getValue()==null){
return;
}
/**
* 取出到该临近节点的权重和cost记录的到该临近节点的权重比较,
* 取最小权重存入cost,
* 并记录到该临近节点的最小权重的节点记录到parent散列表
*/
if (null==cost.get(entry.getKey())||entry.getValue()<cost.get(entry.getKey())){
cost.put(entry.getKey(),entry.getValue());
parent.put(entry.getKey(),key);
}
//递归遍历该该节点的临近节点的临近节点直到最后一个节点结束
dijKstraCalc(entry.getKey());
}
}
}
}
测试:
package com.teriste.algorithm;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import org.junit.Test;
public class DijKstraAlgorithmTest {
@Test
public void dijKstraCalcTest(){
DijKstraAlgorithm algorithm = new DijKstraAlgorithm();
//输入起点,开始计算
algorithm.dijKstraCalc("start");
//节点的父子关系
System.out.println("parent:"+JSON.toJSONString(DijKstraAlgorithm.parent));
//到该节点的权重
System.out.println("cost"+JSON.toJSONString(DijKstraAlgorithm.cost));
}
}
参考文献:《算法图解》






















 5249
5249











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








