学习插头dp差不多也有段时间了, 最开始水的一道题是Eat the tree, 多回路类型的插头dp。那时候看了cdq的《基于连通性状态压缩的动态规划问题》以及各路大神的blog, 然而对于插头dp仍是一头雾水, 虽然对于大神们来说插头dp还是挺水的, 但是我还是花了很长时间才最终看懂了那些位运算代表的含义。
这道题正好是cdq论文中的例题, 方法在论文中也说得比较明确了, 这里我来说说我对于括号表示法的理解。首先, 我们的动态规划是一行一行来的, dp[i][j] 的下一个格子为 dp[i][j + 1], 而dp[i][m] 的下一个格子为 dp[i + 1][1] 每个格子的每个状态都记录着与轮廓线有共线的格子的边的插头状态 (我自己也觉得这句话有点绕, 语文不太好 = =) 差不多是下面这种样子 :
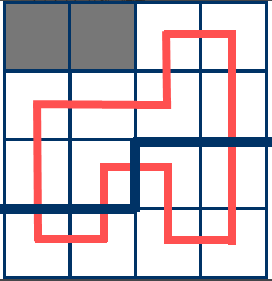
这里当前格子为(3, 2),而插头状态为 11101(用1表示有插头, 0表示没插头)
而对于(3,2)这一个格子,我们另外用两个值left 和 up表示这个格子左边和上边是否有通向它的插头。这里left = 1, up = 0。
剩下要做的就是状态转移了。这里中要注意的是因为只能有一个回路,而在括号法中当left=1, up=2的插头连接时会形成回路, 所以这种情况只能出现在最后一个无障碍的格子中。
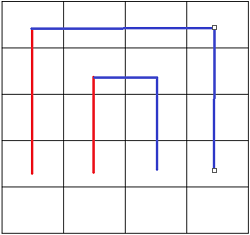
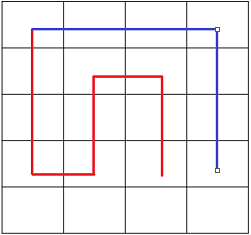
还有一个要注意的地方是当相同方向的括号连接时, 要注意改变附近的某个插头的括号方向, 具体见下图:
其中红色为论文中的左括号, 而蓝色为右括号, 很显然当有相同颜色的插头连接时, 我们要改变附近某个插头的颜色。
下面是我的代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define update(a, b) (a) += (b)
using namespace std;
const int HASH = 10007;
const int STATE = 1000010;
struct HASHMAP {
int head[HASH], state[STATE], nxt[STATE], num;
long long f[STATE];
void init() {
num = 0;
memset(head, -1, sizeof head);
}
void push(int st, long long ans) {
int h = st % HASH;
for (int i = head[h]; ~ i; i = nxt[i]) {
if (st == state[i]) {
f[i] += ans;
return;
}
}
state[num] = st;
nxt[num] = head[h];
f[num] = ans;
head[h] = num++;
}
} dp[2];
int n, m;
int a[15][15];
int ex, ey;
void init() {
char s[20];
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%s", s);
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
a[i][j] = s[j - 1] == '.';
if (a[i][j]) ex = i, ey = j;
}
}
}
int get(int st, int pos) {
return st >> (pos << 1) & 3;
}
int change(int st, int pos, int w) {
st ^= get(st, pos) << (pos << 1);
st ^= w << (pos << 1);
return st;
}
long long plugdp() {
HASHMAP *now = dp, *pre = dp + 1;
now->init();
now->push(0, 1);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int k = 0; k < now->num; k++) now->state[k] <<= 2;
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
swap(now, pre);
now->init();
for (int k = 0; k < pre->num; k++) {
int st = pre->state[k];
long long add = pre->f[k];
int left = get(st, j - 1);
int up = get(st, j);
if (!a[i][j]) {
now->push(change(change(st, j - 1, 0), j, 0), add);
continue;
}
if (left && up) {
int nst = change(change(st, j - 1, 0), j, 0);
if (left == 1 && up == 2) {
if (i == ex && j == ey) now->push(nst, add);
} else {
if (left == up) {
int cnt = 0;
for (int idx = left == 1 ? j : j - 1; idx <= m && idx >= 0; left == 1 ? idx++ : idx--) {
int t = get(st, idx);
if (t == 1) cnt++;
if (t == 2) cnt--;
if (!cnt) {
nst = change(nst, idx, left);
break;
}
}
}
now->push(nst, add);
}
} else if (left || up) {
int w = left | up;
if (a[i][j + 1]) now->push(change(change(st, j - 1, 0), j, w), add);
if (a[i + 1][j]) now->push(change(change(st, j - 1, w), j, 0), add);
} else {
if (a[i][j + 1] && a[i + 1][j]) now->push(change(change(st, j - 1, 1), j, 2), add);
}
}
}
}
long long ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < now->num; i++) ans += now->f[i];
return ans;
}
int main() {
init();
printf("%lld\n", plugdp());
}





















 92
92

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








