ray tracing in one weekend 个人记录
1. ppm图片格式
图片格式的一种
- PBM是位图(bitmap)仅有黑与白,没有灰
- PGM是灰度图(grayscale)
- PPM是通过RGB三种颜色显现的图像(pixmaps)
示例:
P3
200 100
255
0 253 51
1 253 51
…………
100 253 31
写ppm文件:
// main()
//像素的颜色基于图像坐标
int nx = 200, ny = 100;
std::ofstream fout("test1.ppm");
fout << "P3" << endl << nx << " " << ny << endl << 255 << endl; //P is capital
for (int j = ny - 1; j >= 0; j--)
{
for (int i = 0; i < nx; i++)
{
vec3 rgb(float(i) / float(nx), float(j) / float(ny), 0.2);
fout << int(255.99*rgb[0]) << " " << int(255.99*rgb[1]) << " " << int(255.99*rgb[2]) << endl;
}
}
fout.close();

2. 光线 ray
光线追踪的基础就是光线 ray = origin+t*direction
class Ray
{
public:
Ray(){}
Ray(const vec3& o, const vec3& d):o(o), d(d){}
vec3 origin() const { return o; }
vec3 direction() const { return d; }
vec3 point_at_t(float t) { return o + t * d; }
private:
vec3 o, d;
};
应用:
建立坐标系:z=-1是图像平面

// main()
//像素的颜色基于ray
int nx = 200, ny = 100;
vec3 left_lower_corner(-2, -1, -1), up(0, 2, 0), right(4, 0, 0), origin(0, 0, 0);
std::ofstream fout("test2.ppm");
fout << "P3" << endl << nx << " " << ny << endl << 255 << endl; //P is capital
for (int j = ny - 1; j >= 0; j--)
{
for (int i = 0; i < nx; i++)
{
float u = float(i) / float(nx), v = float(j) / float(ny);
Ray r(origin, left_lower_corner + u * right + v * up);
vec3 rgb = color(r);
fout << int(255.99*rgb[0]) << " " << int(255.99*rgb[1]) << " " << int(255.99*rgb[2]) << endl;
}
}
fout.close();
设置颜色(背景),此处随意设置t为[0,1]区间范围内的值,然后从两个颜色中插值得到最后的颜色,blended_value = (1-t)start_value + tend_value:
vec3 color(const Ray& r)
{
vec3 unit_direction = normalize(r.direction());
float t = 0.5*(unit_direction[1] + 1.0);
return vec3(1.0 - t, 1.0 - t, 1.0 - t) + vec3(t*0.5, t*0.7, t*1.0);
}

3. 一个球
是否与球相交,即为下式(一元二次方程)是否存在解:
(
x
−
c
x
)
∗
(
x
−
c
x
)
+
(
y
−
c
y
)
∗
(
y
−
c
y
)
+
(
z
−
c
z
)
∗
(
z
−
c
z
)
=
R
∗
R
(x-cx)*(x-cx) + (y-cy)*(y-cy) + (z-cz)*(z-cz) = R*R
(x−cx)∗(x−cx)+(y−cy)∗(y−cy)+(z−cz)∗(z−cz)=R∗R
= > d o t ( ( p − C ) ( p − C ) ) = ( x − c x ) ∗ ( x − c x ) + ( y − c y ) ∗ ( y − c y ) + ( z − c z ) ∗ ( z − c z ) =>dot((p-C)(p-C)) = (x-cx)*(x-cx) + (y-cy)*(y-cy) + (z-cz)*(z-cz) =>dot((p−C)(p−C))=(x−cx)∗(x−cx)+(y−cy)∗(y−cy)+(z−cz)∗(z−cz)
< = = > d o t ( ( A + t ∗ B − C ) , ( A + t ∗ B − C ) ) = R ∗ R <==>dot((A + t*B - C),(A + t*B - C)) = R*R <==>dot((A+t∗B−C),(A+t∗B−C))=R∗R
=
>
t
∗
t
∗
d
o
t
(
B
,
B
)
+
2
∗
t
∗
d
o
t
(
A
−
C
,
A
−
C
)
+
d
o
t
(
C
,
C
)
−
R
∗
R
=
0
=>t*t*dot(B,B) + 2*t*dot(A-C,A-C) + dot(C,C) - R*R = 0
=>t∗t∗dot(B,B)+2∗t∗dot(A−C,A−C)+dot(C,C)−R∗R=0
t为ray的参数,A为ray的origin点,B为ray的direction,C为球心坐标,R为半径
bool hit_sphere(const vec3& center, float radius, const Ray& r)
{
/// A:r.origin() B:r.direction() C:center
/// t*t*dot(B, B) + 2 * t*dot(B, A - C) + dot(A - C, A - C) - R * R = 0;
vec3 CA = r.origin() - center;
float a = dot(r.direction(), r.direction()),
b = 2 * dot(r.direction(), CA),
c = dot(CA, CA) - radius * radius;
return b * b - 4 * a*c > 0;
}
vec3 color(const Ray& r)
{
// the color for hit
if (hit_sphere(vec3(0, 0, 1), 0.5, r))
return vec3(1, 0, 0);
// background
vec3 unit_direction = normalize(r.direction());
float t = 0.5*(unit_direction[1] + 1.0);
return vec3(1.0 - t, 1.0 - t, 1.0 - t) + vec3(t*0.5, t*0.7, t*1.0);
}

4. 法向量
法向量是从圆心指向切点

float hit_sphere(const vec3& center, float radius, const Ray& r)
{
/// A:r.origin() B:r.direction() C:center
/// t*t*dot(B, B) + 2 * t*dot(B, A - C) + dot(A - C, A - C) - R * R = 0;
vec3 CA = r.origin() - center;
float a = dot(r.direction(), r.direction()),
b = 2 * dot(r.direction(), CA),
c = dot(CA, CA) - radius * radius,
discriminant = b * b - 4 * a*c;
if (discriminant < 0)
return -1;
else
return (-b - sqrt(discriminant)) / (2.0*a);
}
vec3 color(const Ray& r)
{
vec3 center(0, 0, -1);
// the color for hit
float t = hit_sphere(center, 0.5, r);
if (t > 0)
{
vec3 N = normalize(r.point_at_t(t) - center); //[-1,1]
return vec3(0.5)*(N + vec3(1));
}
// background
vec3 unit_direction = normalize(r.direction());
t = 0.5*(unit_direction[1] + 1.0);
return vec3(1.0 - t, 1.0 - t, 1.0 - t) + vec3(t*0.5, t*0.7, t*1.0);
}

5. 多个球
Hitable.h
#pragma once
#include <list>
#include "Ray.h"
using std::list;
struct hit_record
{
float t;
vec3 p, normal;
};
// object
class Hitable
{
public:
virtual bool hit(const Ray& r, float t_min, float t_max, hit_record& rec) const = 0;
};
class Sphere : public Hitable
{
public:
Sphere() {}
Sphere(vec3 center, float radius):center(center), radius(radius){}
virtual bool hit(const Ray& r, float t_min, float t_max, hit_record& rec) const;
private:
vec3 center;
float radius;
};
//object list
class Hitable_list : public Hitable
{
public:
Hitable_list() {}
Hitable_list(list<Hitable*>& l) :l(l) {}
virtual bool hit(const Ray& r, float t_min, float t_max, hit_record& rec) const;
private:
list<Hitable*> l;
};
Hitable.cpp
- 球的相交求根判断(-b - sqrt(discriminant)) / (2.0*a) 约去2
- 多个球计算最近相交点的法向量,作为当前像素颜色
#include "Hitable.h"
bool Sphere::hit(const Ray& r, float t_min, float t_max, hit_record& rec) const
{
/// A:r.origin() B:r.direction() C:center
/// t*t*dot(B, B) + 2 * t*dot(B, A - C) + dot(A - C, A - C) - R * R = 0;
vec3 CA = r.origin() - center;
float a = dot(r.direction(), r.direction()),
b = dot(r.direction(), CA),
c = dot(CA, CA) - radius * radius,
discriminant = b * b - a*c;
if (discriminant < 0)
{
return false;
}
else
{
float solution = (-b - sqrt(discriminant)) / a;
if (solution > t_min && solution < t_max)
{
rec.t = solution;
rec.p = r.point_at_t(solution);
rec.normal = (rec.p - center) / radius;
return true;
}
solution = (-b + sqrt(discriminant)) / a;
if (solution > t_min && solution < t_max)
{
rec.t = solution;
rec.p = r.point_at_t(solution);
rec.normal = (rec.p - center) / radius;
return true;
}
}
}
bool Hitable_list::hit(const Ray& r, float t_min, float t_max, hit_record& rec) const
{
hit_record tmp_record;
bool hit_anything = false;
double closet_t_so_far = t_max;
for (auto object : l)
{
if (object->hit(r, t_min, closet_t_so_far, tmp_record))
{
hit_anything = true;
closet_t_so_far = tmp_record.t;
rec = tmp_record;
}
}
return hit_anything;
}
color()函数
vec3 color(const Ray& r, Hitable_list& object_list)
{
// the color for hit
hit_record rec;
if (object_list.hit(r, 0, INT_MAX, rec))
{
return vec3(0.5)*(rec.normal + vec3(1));
}
// background
vec3 unit_direction = normalize(r.direction());
float t = 0.5*(unit_direction[1] + 1.0);
return vec3(1.0 - t, 1.0 - t, 1.0 - t) + vec3(t*0.5, t*0.7, t*1.0);
}
main中
//add
list<Hitable*> list;
list.push_back(new Sphere(vec3(-1, -1, -1), 1));
list.push_back(new Sphere(vec3(0, 0, -1), 0.5));
Hitable_list object_list(list);
//change
vec3 rgb = color(r, object_list);

6. 反走样
- 添加相机
// camera
class Camera
{
public:
Camera()
{
left_lower_corner = vec3(-2, -1, -1);
up = vec3(0, 2, 0);
right = vec3(4, 0, 0);
origin = vec3(0, 0, 0);
}
Camera(vec3& left_lower_corner, vec3& up, vec3& right, vec3& origin):
left_lower_corner(left_lower_corner), up(up), right(right), origin(origin)
{}
Ray get_ray(float u, float v){return Ray(origin, left_lower_corner + u * right + v * up - origin);}
private:
vec3 left_lower_corner, up, right, origin;
};
- 每个像素点内采样,取normal平均值作为颜色
#define random_float_0_1() rand()/double(RAND_MAX)
//change in main -- in for
vec3 rgb(0);
for (int s = 0; s < ns; s++)
{
float u = (float(i) + random_float_0_1()) / float(nx),
v = (float(j) + random_float_0_1()) / float(ny);
rgb += color(cam.get_ray(u, v), object_list);
}
rgb /= ns;


7. 漫反射
漫反射不发光,吸收周围的光,吸收的越多表面越暗;而漫反射的反射方向是任意的。

- 出射光线 PS:ray和object的交点P,normal为N,以(P+N)为圆心做单位元,在此单位圆内随机采样漫反射方向
- 递归求交,不断漫反射,直至不再与物体相交
vec3 random_in_unit_sphere()
{
vec3 p;
do {
p = vec3(2*random_float_0_1(), 2*random_float_0_1(), 2*random_float_0_1()) - vec3(1);
} while (length(p) >= 1.0);
return p;
}
vec3 color(const Ray& r, Hitable_list& object_list)
{
// the color for hit
hit_record rec;
if (object_list.hit(r, 0, INT_MAX, rec))
{
//return vec3(0.5)*(rec.normal + vec3(1));
vec3 s = rec.p + rec.normal + random_in_unit_sphere();
return color(Ray(rec.p, s-rec.p), object_list)*vec3(0.5);
}
// background
vec3 unit_direction = normalize(r.direction());
float t = 0.5*(unit_direction[1] + 1.0);
return vec3(1.0 - t, 1.0 - t, 1.0 - t) + vec3(t*0.5, t*0.7, t*1.0);
}

颜色变浅,表明吸收的光线变少,结果边界处阴影明显
rgb = sqrt(rgb);

因为精度问题,需要修改t_min为0.001
//if (object_list.hit(r, 0, INT_MAX, rec)) =>
if (object_list.hit(r, 0.001, INT_MAX, rec))
8. 镜面反射
统一描述物质的材质:
- 产生散射(反射、透射)的出射光线
- 散射后的光强衰弱程度
class Material
{
public:
virtual bool scatter(const Ray& r_in, const hit_record& rec,
vec3& attenuation, Ray& scattered) const = 0; // attenuation:less scattered:direction
};
Lambertian
class Lambertian :public Material
{
public:
Lambertian(const vec3& a):albedo(a){}
virtual bool Lambertian::scatter(const Ray& r_in, const hit_record& rec, vec3& attenuation, Ray& scattered) const
{
vec3 s = rec.p + rec.normal + random_in_unit_sphere();
attenuation = albedo;
scattered = Ray(rec.p, s - rec.p);
return true;
}
private:
vec3 albedo;
};
镜面反射
- 反射方向 = V+2B, B = -N.dot(V)
- 发生反射的条件为出射方向和normal之间的夹角小于90°

vec3 reflect(const vec3& v, const vec3& n)
{
return v - 2 * dot(v, n)*n;
}
class Metal :public Material
{
public:
Metal(const vec3& a) :albedo(a) {}
virtual bool scatter(const Ray& r_in, const hit_record& rec, vec3& attenuation, Ray& scattered) const;
private:
vec3 albedo;
};
bool Metal::scatter(const Ray& r_in, const hit_record& rec, vec3& attenuation, Ray& scattered) const
{
vec3 ref = reflect(normalize(r_in.direction()), rec.normal);
attenuation = albedo;
scattered = Ray(rec.p, ref);
return (dot(scattered.direction(), rec.normal) >0);
}
结构修改
hit_record中多了Material的指针,记录交点的材质以便计算颜色 rec.material_ptr->scatter(r, rec, attenuation, scattered)
class Material;
struct hit_record
{
float t;
vec3 p, normal;
Material* material_ptr;
};
in Sphere::hit
rec.material_ptr = material;
color()函数修改:
vec3 color(const Ray& r, Hitable_list& object_list, const int depth)
{
// the color for hit
hit_record rec;
if (object_list.hit(r, 0.001, INT_MAX, rec))
{
Ray scattered;
vec3 attenuation;
if (depth < 50 && rec.material_ptr->scatter(r, rec, attenuation, scattered))
{
return attenuation * color(scattered, object_list, depth+1);
}
else
return vec3(0);
}
// background
vec3 unit_direction = normalize(r.direction());
float t = 0.5*(unit_direction[1] + 1.0);
return vec3(1.0 - t, 1.0 - t, 1.0 - t) + vec3(t*0.5, t*0.7, t*1.0);
}
main
// change 1
list<Hitable*> list;
list.push_back(new Sphere(vec3(-1, -1, -1), 1, new Lambertian(vec3(0.8,0.3,0.3))));
list.push_back(new Sphere(vec3(0, 0, -1), 0.5, new Metal(vec3(0.0, 0.0, 0.8))));
Hitable_list object_list(list);
// change 2
rgb += color(cam.get_ray(u, v), object_list, 0);

模糊
scattered = Ray(rec.p, ref + fuzzier * random_in_unit_sphere());
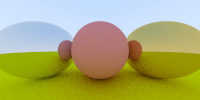

9. 折射
透明材料如水、玻璃和钻石都是介质。当一束光线击中它们时,就会分裂成反射光线和折射(透射)光线。我们将通过在反射和折射之间随机选择来处理这个问题,并且每个交互作用只产生一个散射光线。
c
o
s
θ
1
=
−
N
⋅
L
cosθ_1=-N·L
cosθ1=−N⋅L
n
1
⋅
s
i
n
θ
1
=
n
2
⋅
s
i
n
θ
2
n_1·sinθ_1 = n_2·sinθ_2
n1⋅sinθ1=n2⋅sinθ2
η
=
n
1
/
n
1
=
s
i
n
θ
2
/
s
i
n
θ
1
η=n_1/n_1=sinθ_2/sinθ_1
η=n1/n1=sinθ2/sinθ1
c
o
s
θ
2
=
s
q
r
t
(
1
−
s
i
n
2
θ
2
)
=
s
q
r
t
(
1
−
(
1
/
η
⋅
s
i
n
θ
1
)
2
)
=
s
q
r
t
(
1
−
(
1
/
η
2
)
(
1
−
c
o
s
2
θ
1
)
)
cosθ_2=sqrt(1-sin^2θ_2) = sqrt(1-(1/η·sinθ_1)^2)=sqrt(1-(1/η^2)(1-cos^2θ_1))
cosθ2=sqrt(1−sin2θ2)=sqrt(1−(1/η⋅sinθ1)2)=sqrt(1−(1/η2)(1−cos2θ1))
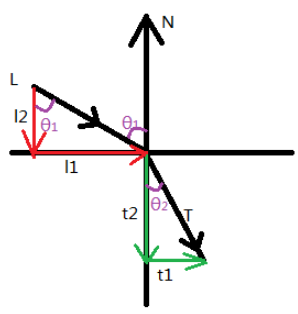
将L和T分解为两个向量, l 1 l_1 l1和 t 1 t_1 t1的方向是相同的, ∣ l 1 ∣ = ∣ L ∣ s i n θ 1 = s i n θ 1 |l_1|=|L|sinθ_1=sinθ_1 ∣l1∣=∣L∣sinθ1=sinθ1, ∣ t 1 ∣ = ∣ T ∣ s i n θ 2 = s i n θ 2 |t_1|=|T|sinθ_2=sinθ_2 ∣t1∣=∣T∣sinθ2=sinθ2,则 t 1 = ( s i n θ 2 / s i n θ 1 ) ∗ l 1 = ( 1 / η ) ∗ l 1 t_1=(sinθ_2/sinθ_1)*l_1=(1/η)*l_1 t1=(sinθ2/sinθ1)∗l1=(1/η)∗l1
∵
∣
l
2
∣
=
∣
L
∣
c
o
s
θ
1
=
c
o
s
θ
1
∵|l_2|=|L|cosθ_1=cosθ_1
∵∣l2∣=∣L∣cosθ1=cosθ1
=>
l
2
=
−
N
c
o
s
θ
1
l_2=-Ncosθ_1
l2=−Ncosθ1
=>
l
1
=
L
−
l
1
=
L
+
N
c
o
s
θ
1
l_1=L-l_1=L+Ncosθ_1
l1=L−l1=L+Ncosθ1
∴ t 1 = ( 1 / η ) ∗ ( L + N c o s θ 1 ) ∴t_1=(1/η)*(L+Ncosθ_1) ∴t1=(1/η)∗(L+Ncosθ1)
∵
∣
t
1
∣
2
+
∣
t
2
∣
2
=
∣
T
∣
2
=
1
|t_1|^2+|t_2|^2=|T|^2=1
∣t1∣2+∣t2∣2=∣T∣2=1
又∵同理
t
2
=
−
N
∗
t
2
=
−
s
q
r
t
(
1
−
∣
t
1
∣
2
)
∗
N
t_2=-N*t_2=-sqrt(1-|t_1|^2)*N
t2=−N∗t2=−sqrt(1−∣t1∣2)∗N
∴
t
2
=
−
c
o
s
θ
2
∗
N
∴t_2 = -cosθ_2*N
∴t2=−cosθ2∗N
∴ T = t 1 + t 2 = ( 1 / η ) ( L + N ⋅ c o s θ 1 ) − N ⋅ c o s θ 2 ∴T=t_1+t_2=(1/η)(L+N·cosθ_1)-N·cosθ_2 ∴T=t1+t2=(1/η)(L+N⋅cosθ1)−N⋅cosθ2
[注] θ 2 < 90 ° θ_2<90° θ2<90°时才有折射角
bool refract(const vec3& v, const vec3& n, float ni_over_nt, vec3& refracted)
{
//n sin(theta) = n’ sin(theta’)
vec3 L = normalize(v);
float cos1 = dot(-L, n);
float discriminant = 1.0 - ni_over_nt * ni_over_nt*(1 - cos1 * cos1);
if (discriminant > 0) {
refracted = ni_over_nt * (L + n * cos1) - n * sqrt(discriminant);
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
//发生折射的概率,schlick:近似地计算出不同入射角旳菲涅耳反射比
float schlick(float cosine, float ref_idx)
{
float r0 = (1 - ref_idx) / (1 + ref_idx);
r0 = r0 * r0;
return r0 + (1 - r0)*pow((1 - cosine), 5);
}
bool Dielectric::scatter(const Ray& r_in, const hit_record& rec, vec3& attenuation, Ray& scattered) const {
// reflection
vec3 reflected = reflect(r_in.direction(), rec.normal);
// refraction
vec3 outward_normal;
float ni_over_nt;
attenuation = vec3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
vec3 refracted;
float reflect_prob;
float cosine;
if (dot(r_in.direction(), rec.normal) > 0) {
outward_normal = -rec.normal;
ni_over_nt = ref_idx;
//cosine = ref_idx * dot(r_in.direction(), rec.normal) / r_in.direction().length();
cosine = dot(r_in.direction(), rec.normal) / r_in.direction().length();
cosine = sqrt(1 - ref_idx * ref_idx*(1 - cosine * cosine));
}
else {
outward_normal = rec.normal;
ni_over_nt = 1.0 / ref_idx;
cosine = -dot(r_in.direction(), rec.normal) / r_in.direction().length();
}
//
if (refract(r_in.direction(), outward_normal, ni_over_nt, refracted))
reflect_prob = schlick(cosine, ref_idx);
else
reflect_prob = 1.0;
// choose
if (random_float_0_1() < reflect_prob)
scattered = Ray(rec.p, reflected);
else
scattered = Ray(rec.p, refracted);
return true;
}
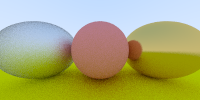
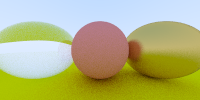
半径为负,则可以是normal指向球内,有泡泡的感觉:
list.push_back(new Sphere(vec3(-1, 0, -1), -0.45, new Dielectric(1.5)));
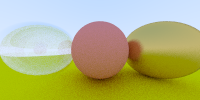
10. 相机位置
z=-1为成像平面,fov以y方向为准。

Camera::Camera(vec3& lookfrom, vec3& lookat, vec3& vup, float vfov, float aspect_ratio)
:origin(lookfrom)
{
float half_height = tan(vfov * PI / 360),
half_width = aspect_ratio * half_height;
vec3 w(normalize(lookfrom - lookat)),
u(normalize(cross(vup, w))),
v(cross(w, u));
left_lower_corner = lookfrom - half_width * u - half_height * v - w;
up = 2 * half_height*v;
right = 2 * half_width*u;
}

11. 虚化
Defocus Blur 散焦模糊,即虚化。利用光圈和焦距实现。
引入aperture(光圈),focus_dist(焦距) 2个参数,来实现画面的虚化效果。以下为原书代码:
class camera
{
vec3 origin;
vec3 u,v,w;
vec3 horizontal;
vec3 vertical;
vec3 lower_left_corner;
float len_radius;
public :
camera(vec3 lookfrom, vec3 lookat, vec3 vup, float vfov, float aspect, float aperture, float focus_dist)
{
len_radius = aperture/2;
float theta = vfov*M_PI/180;
float half_height = tan(theta/2);
float half_width = aspect * half_height;
origin = lookfrom;
w = unit_vector(lookfrom - lookat);
u = unit_vector(cross(vup, w));
v = cross(w,u);
lower_left_corner = origin - half_width*focus_dist*u - half_height*focus_dist*v - focus_dist*w;
horizontal = 2*half_width*focus_dist*u;
vertical = 2*half_height*focus_dist*v;
}
ray get_ray(float s,float t)
{
vec3 rd = len_radius * random_in_unit_disk();
vec3 offset = u * rd.x() +v*rd.y();
return ray(origin + offset,lower_left_corner+s*horizontal + t*vertical - origin - offset);
}
vec3 random_in_unit_disk()
{
vec3 p;
do{
p = 2.0*vec3(drand48(),drand48(),0)-vec3(1,1,0);
}while (dot(p,p)>=1.0);
return p;
}
};
最终效果
vec3 color(const Ray& r, Hitable_list& object_list, const int depth)
{
// the color for hit
hit_record rec;
if (object_list.hit(r, 0.001, INT_MAX, rec))
{
Ray scattered;
vec3 attenuation;
if (depth < 50 && rec.material_ptr->scatter(r, rec, attenuation, scattered))
{
return attenuation * color(scattered, object_list, depth+1);
}
else
return vec3(0);
}
// background
vec3 unit_direction = normalize(r.direction());
float t = 0.5*(unit_direction[1] + 1.0);
return vec3(1.0 - t, 1.0 - t, 1.0 - t) + vec3(t*0.5, t*0.7, t*1.0);
}























 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








