原文见http://www.cs.washington.edu/research/projects/uns/F9/src/boost_1_37_0/libs/statechart/doc/tutorial.html
原文以Camera为例,讲解了Boost状态机模型的使用方法;而本文的主要:
- 对原文中的Camera模型略加修改与完善;
- 写出了完整代码;可编译运行;
- 演示各个对象(事件对象和状态对象)的生命周期;
- 更清晰的模块化各个组件(事件、状态); 故可以当作一个简单的代码框架;
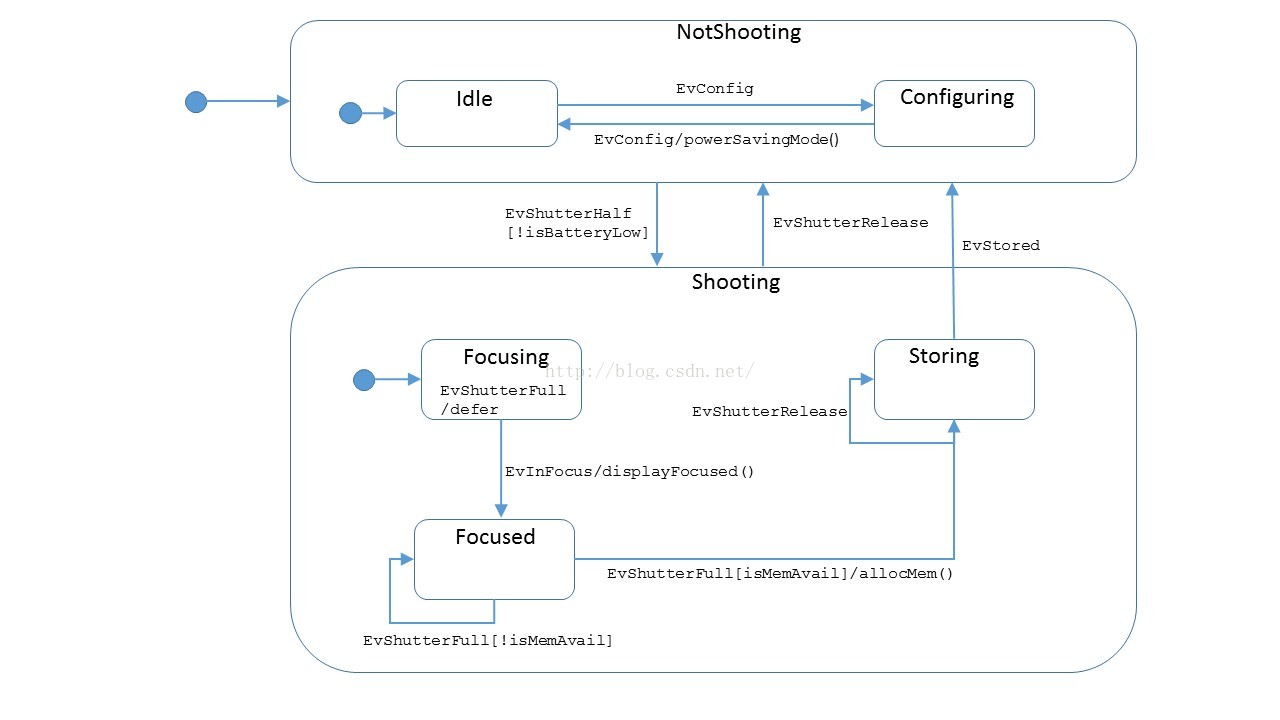
- 配置键(Config Button): 按此键会产生一个EvConfig事件,EvConfig事件用于在空闲状态(Idle)和配置状态(Configuring)之间切换;
- 快门键(Shutter Button): 可以半按(半按时产生一个EvShutterHalf事件)、全按(全按时产生一个EvShutterFull事件)以及释放(释放时产生一个EvShutterRelease事件);
- 非拍摄状态(NotShooting): 包含两个子状态,空闲状态(Idle)和配置状态(Configuring);EvConfig事件用于二者之间的切换;
- 拍摄状态(Shooting): 包含对焦状态(Focusing)、聚焦状态(Focused)和照片存储状态(Storing);
- Camera初始状态是NotShooting,NotShooting的初始状态是Idle,所以Camera启动时会自动进入Idle状态;
- 处于Idle状态时,若User按下Config Button(产生一个EvConfig事件),Camera进入配置状态(Configuring);反之,处于Configuring状态时,若User按下Config Button,Camera进入Idle状态并启用省电模式(powerSavingMode);
- 处于NotShooting(Idle或Configuring)状态时,若用户半按快门键(产生一个EvShutterHalf事件)并且电量充足(isBatteryLow为非)Camera进入对焦状态(Focusing),镜头前后移动以自动对焦;
- 处于Focusing状态时,若自动对焦成功,Camera显示聚焦的物体(displayFocused),并在自己内部产生一个EvInFocus事件,然后Camera进入聚焦状态(Focused);
- 处于Focused状态时,User全按快门(产生一个EvShutterFull事件),若内存充足则分配内存(allocMem)并进入照片存储状态(Storing);若内存不足则停在Foused状态;
- 当Camera处于Focusing状态User全按快门时,产生一个EvShutterFull事件,拷贝此事件(拷贝构造函数);
- 把事件的拷贝放入一个单独的queue中;
- 销毁原EvShutterFull事件(析构函数);
- 当Camera离开Focusing状态进入Focused状态时,从queue中取出事件(EvShutterFull的拷贝)并处理;
- 销毁EvShutterFull事件的拷贝(析构函数);
代码:
[root@localhost camera]# tree
.
├── bin
├── Makefile
└── src
├── camera
│ ├── camera.cpp
│ └── camera.hpp
├── event
│ ├── events.cpp
│ └── events.hpp
└── state
├── istate.hpp
├── notshoot
│ ├── configuring.cpp
│ ├── configuring.hpp
│ ├── idle.cpp
│ ├── idle.hpp
│ ├── notshooting.cpp
│ └── notshooting.hpp
└── shoot
├── focused.cpp
├── focused.hpp
├── focusing.cpp
├── focusing.hpp
├── shooting.cpp
├── shooting.hpp
├── storing.cpp
└── storing.hpp
Makefile
INCLUDES=
LIBLINKS=
SOURCES= \
src/camera/camera.cpp \
src/event/*.cpp \
src/state/notshoot/idle.cpp \
src/state/notshoot/notshooting.cpp \
src/state/notshoot/configuring.cpp \
src/state/shoot/shooting.cpp \
src/state/shoot/focusing.cpp \
src/state/shoot/focused.cpp \
src/state/shoot/storing.cpp \
EXE=bin/run
all: clean build
build:
mkdir -p bin
g++ -g -o $(EXE) $(INCLUDES) $(SOURCES) $(LIBLINKS)
clean:
rm -f $(EXE)
test:
./$(EXE)
src/event/events.hpp
#ifndef __EVENTS_HPP__
#define __EVENTS_HPP__
#include <boost/statechart/event.hpp>
using namespace boost::statechart;
class EvConfig : public event< EvConfig >
{
public:
EvConfig();
~EvConfig();
};
class EvShutterHalf : public event< EvShutterHalf >
{
public:
EvShutterHalf();
~EvShutterHalf();
};
class EvShutterFull : public event< EvShutterFull >
{
public:
EvShutterFull();
EvShutterFull(const EvShutterFull & other);
~EvShutterFull();
};
class EvShutterRelease : public event< EvShutterRelease >
{
public:
EvShutterRelease();
~EvShutterRelease();
};
class EvInFocus : public event< EvInFocus >
{
public:
EvInFocus();
~EvInFocus();
};
class EvStored : public event< EvStored >
{
public:
EvStored();
~EvStored();
};
#endif
src/event/events.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "events.hpp"
using namespace std;
//============EvConfig============//
EvConfig::EvConfig()
{
cout<<"Construct EvConfig"<<endl;
}
EvConfig::~EvConfig()
{
cout<<"Destruct EvConfig"<<endl;
}
//============EvShutterHalf============//
EvShutterHalf::EvShutterHalf()
{
cout<<"Construct EvShutterHalf"<<endl;
}
EvShutterHalf::~EvShutterHalf()
{
cout<<"Destruct EvShutterHalf"<<endl;
}
//============EvShutterFull============//
EvShutterFull::EvShutterFull()
{
cout<<"Construct EvShutterFull"<<endl;
}
EvShutterFull::EvShutterFull(const EvShutterFull & other)
{
cout<<"Copy Construct EvShutterFull"<<endl;
}
EvShutterFull::~EvShutterFull()
{
cout<<"Destruct EvShutterFull"<<endl;
}
//============EvShutterRelease============//
EvShutterRelease::EvShutterRelease()
{
cout<<"Construct EvShutterRelease"<<endl;
}
EvShutterRelease::~EvShutterRelease()
{
cout<<"Destruct EvShutterRelease"<<endl;
}
//============EvInFocus============//
EvInFocus::EvInFocus()
{
cout<<"Construct EvInFocus"<<endl;
}
EvInFocus::~EvInFocus()
{
cout<<"Destruct EvInFocus"<<endl;
}
//============EvStored============//
EvStored::EvStored()
{
cout<<"Construct EvStored"<<endl;
}
EvStored::~EvStored()
{
cout<<"Destruct EvStored"<<endl;
}
src/camera/camera.hpp
#ifndef __CAMERA_HPP__
#define __CAMERA_HPP__
#include <boost/statechart/state_machine.hpp>
#include "../event/events.hpp"
using namespace boost::statechart;
using namespace std;
//Yuanguo: forward declaration
class NotShooting;
class Camera : public state_machine< Camera, NotShooting >
{
public:
Camera();
~Camera();
bool isMemAvail() const;
bool isBatteryLow() const;
string getCurState() const;
//transition actions
void displayFocused(const EvInFocus & evInFocus);
void allocMem(const EvShutterFull & evShutterFull);
void powerSavingMode(const EvConfig & evConfig);
};
#endif
src/camera/camera.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "camera.hpp"
#include "../state/istate.hpp"
//Yuanguo: although the full definition of the initial state "NotShooting" is not needed when
//declare Camera (thus only forward declaration is needed), the full definition of the states
//are necessary for
// camera.initiate();
//thus, include NotShooting and its inner states definition here;
#include "../state/notshoot/notshooting.hpp"
#include "../state/notshoot/idle.hpp"
#include "../state/shoot/shooting.hpp"
using namespace std;
Camera::Camera()
{
cout<<"Construct Camera"<<endl;
}
Camera::~Camera()
{
cout<<"Destruct Camera"<<endl;
}
bool Camera::isMemAvail() const
{
return true;
}
bool Camera::isBatteryLow() const
{
return false;
}
string Camera::getCurState() const
{
return string("CurrentState ------> ") + state_cast< const IState & >().getStateName();
}
void Camera::displayFocused(const EvInFocus & evInFocus)
{
cout<<"[Transition Action]: Camera focused on objects"<<endl;
}
void Camera::allocMem(const EvShutterFull & evShutterFull)
{
cout<<"[Transition Action]: Memory allocated for storing the picture"<<endl;
}
void Camera::powerSavingMode(const EvConfig & evConfig)
{
cout<<"[Transition Action]: Camera goes into Power Saving Mode"<<endl;
}
int main()
{
Camera camera;
camera.initiate();
cout<<camera.getCurState()<<endl;
camera.process_event(EvConfig()); //模拟按Config键
cout<<camera.getCurState()<<endl;
camera.process_event(EvConfig()); //<span style="font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;">模拟按Config键</span>
cout<<camera.getCurState()<<endl;
camera.process_event(EvShutterHalf()); //模拟半按快门
cout<<camera.getCurState()<<endl;
cout<<"Press Shutter Full before focused"<<endl;
camera.process_event(EvShutterFull()); //在对焦完成之前,模拟全按快门
cout<<camera.getCurState()<<endl;
camera.process_event(EvInFocus()); //模拟对焦完成事件
cout<<camera.getCurState()<<endl;
camera.process_event(EvShutterRelease()); //模拟释放快门
cout<<camera.getCurState()<<endl;
camera.process_event(EvStored()); //模拟存储完成
cout<<camera.getCurState()<<endl;
return 0;
}
src/state/istate.hpp
#ifndef __ISTATE_HPP__
#define __ISTATE_HPP__
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class IState {
public:
virtual string getStateName() const = 0;
};
#endifsrc/state/notshoot/notshooting.hpp
#ifndef __NOTSHOOTING_HPP__
#define __NOTSHOOTING_HPP__
#include <boost/statechart/simple_state.hpp>
#include <boost/statechart/custom_reaction.hpp>
#include "../istate.hpp"
#include "../../event/events.hpp"
//Yuanguo: NotShooting is the initial state of Camera, and Camera is the context of NotShooting, so
// 1. forward declaration of NotShooting is needed when defining Camera, see camera.hpp;
// 2. full definition of Camera is needed when defining NotShooting, thus include camera.hpp here;
#include "../../camera/camera.hpp"
using namespace boost::statechart;
//Yuanguo: forward declaration;
class Idle;
class NotShooting : public simple_state< NotShooting, Camera, Idle >, public IState
{
public:
typedef custom_reaction< EvShutterHalf > reactions;
NotShooting();
~NotShooting();
string getStateName() const;
result react(const EvShutterHalf & evShutterHalf);
};
#endif
src/state/notshoot/notshooting.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "notshooting.hpp"
//Yuanguo:
//We need a full definition of Shooting in line
// return transit<Shooting>();
//Focusing is the initial state of Shooting, thus we have to include focusing.hpp
//here, otherwise, compiler will complain about error like
// incomplete type 'boost::statechart::simple_state ...
// ... MostDerived = NotShooting, Context = Camera ....'
//inclusion of non-initial states of Shooting is not necessary;
#include "../shoot/shooting.hpp"
#include "../shoot/focusing.hpp"
using namespace std;
NotShooting::NotShooting()
{
cout<<"Enter NotShooting"<<endl;
}
NotShooting::~NotShooting()
{
cout<<"Exit NotShooting"<<endl;
}
string NotShooting::getStateName() const
{
return string("NotShooting");
}
result NotShooting::react(const EvShutterHalf & evShutterHalf)
{
cout<<"NotShooting::react(const EvShutterHalf & evShutterHalf), ";
if( context< Camera >().isBatteryLow() )
{
cout<<"Guard: isBatteryLow() is true"<<endl;
//Yuanguo: We cannot react to the event ourselves, so we forward it
//to our outer state (this is also the default if a state
//defines no reaction for a given event).
return forward_event();
}
else
{
cout<<"Guard: isBatteryLow() is false"<<endl;
return transit<Shooting>(); //no transition action
}
}
src/state/notshoot/idle.hpp
#ifndef __IDLE_HPP__
#define __IDLE_HPP__
#include <boost/statechart/simple_state.hpp>
#include <boost/statechart/custom_reaction.hpp>
#include "../istate.hpp"
#include "../../event/events.hpp"
//Yuanguo: Idle is the initial state of NotShooting, and NotShooting is the context of Idle, so
// 1. forward declaration of Idle is needed when defining NotShooting, see notshooting.hpp;
// 2. full definition of NotShooting is needed when defining Idle, thus include notshooting.hpp here;
#include "notshooting.hpp"
using namespace boost::statechart;
class Idle : public simple_state< Idle, NotShooting >, public IState
{
public:
typedef custom_reaction< EvConfig > reactions;
Idle();
~Idle();
string getStateName() const;
result react(const EvConfig & evConfig);
};
#endif
src/state/notshoot/idle.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "configuring.hpp"
#include "idle.hpp"
using namespace std;
Idle::Idle()
{
cout<<"Enter Idle"<<endl;
}
Idle::~Idle()
{
cout<<"Exit Idle"<<endl;
}
string Idle::getStateName() const
{
return string("Idle");
}
result Idle::react(const EvConfig & evConfig)
{
cout<<"Idle::react(const EvConfig & evConfig)"<<endl;
return transit<Configuring>(); //no transition action
}
src/state/notshoot/configuring.hpp
#ifndef __CONFIGURING_HPP__
#define __CONFIGURING_HPP__
#include <boost/statechart/simple_state.hpp>
#include <boost/statechart/transition.hpp>
#include "../../event/events.hpp"
#include "../istate.hpp"
//Yuanguo: NotShooting is the context of Configuring, so
// full definition of NotShooting is needed when defining Configuring, thus include notshooting.hpp here;
#include "notshooting.hpp"
//Yuanguo: full definition of Idle is needed in line
// typedef transition< EvConfig, Idle >
#include "idle.hpp"
using namespace boost::statechart;
class Configuring : public simple_state< Configuring, NotShooting >, public IState
{
public:
//Yuanguo: a short way for:
// typedef custom_reaction< EvConfig > reactions;
// result react( const EvConfig & evConfig)
// {
// return transit< Idle >(&Camera::powerSavingMode, evConfig); //transition action is Camera::powerSavingMode()
// }
typedef transition< EvConfig, Idle, Camera, &Camera::powerSavingMode > reactions; //transition action is Camera::powerSavingMode()
Configuring();
~Configuring();
string getStateName() const;
};
#endif
src/state/notshoot/configuring.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "configuring.hpp"
using namespace std;
Configuring::Configuring()
{
cout<<"Enter Configuring"<<endl;
}
Configuring::~Configuring()
{
cout<<"Exit Configuring"<<endl;
}
string Configuring::getStateName() const
{
return string("Configuring");
}
src/state/shoot/shooting.hpp
#ifndef __SHOOTING_HPP__
#define __SHOOTING_HPP__
#include <boost/statechart/simple_state.hpp>
#include <boost/statechart/custom_reaction.hpp>
#include <boost/statechart/transition.hpp>
#include "../istate.hpp"
#include "../../event/events.hpp"
//Yuanguo: Camera is the context of Shooting, so
// full definition of Camera is needed when defining Shooting, thus include camera.hpp here;
#include "../../camera/camera.hpp"
using namespace boost::statechart;
//Yuanguo: forward declaration
class Focusing;
class Shooting : public simple_state< Shooting, Camera, Focusing >, public IState
{
public:
typedef custom_reaction< EvShutterRelease > reactions;
Shooting();
~Shooting();
string getStateName() const;
result react(const EvShutterRelease & evShutterRelease);
};
#endif
src/state/shoot/shooting.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "shooting.hpp"
//Yuanguo:
//We need a full definition of NotShooting in line
// return transit< NotShooting >();
//Idle is the initial state of NotShooting, thus we have to include idle.hpp
//here, otherwise, compiler will complain about error like
// incomplete type 'boost::statechart::simple_state ...
// ... MostDerived = NotShooting, Context = Camera ....'
//inclusion of non-initial states of NotShooting is not necessary;
#include "../notshoot/notshooting.hpp"
#include "../notshoot/idle.hpp"
using namespace std;
Shooting::Shooting()
{
cout<<"Enter Shooting"<<endl;
}
Shooting::~Shooting()
{
cout<<"Exit Shooting"<<endl;
}
string Shooting::getStateName() const
{
return string("Shooting");
}
result Shooting::react(const EvShutterRelease & evShutterRelease)
{
cout<<"Shooting::react(const EvShutterRelease & evShutterRelease)"<<endl;
return transit< NotShooting >();
}
src/state/shoot/focusing.hpp
#ifndef __FOCUSING_HPP__
#define __FOCUSING_HPP__
#include <boost/statechart/simple_state.hpp>
#include <boost/statechart/custom_reaction.hpp>
#include <boost/mpl/list.hpp>
#include <boost/statechart/deferral.hpp>
#include "../../event/events.hpp"
#include "../istate.hpp"
//Yuanguo: Shooting is the context of Focusing, so
// full definition of Shooting is needed when defining Focusing, thus include
// shooting.hpp here;
#include "shooting.hpp"
using namespace boost::statechart;
class Focusing : public simple_state< Focusing, Shooting >, public IState
{
public:
//Yuanguo:
//if the user fully press shutter when the camera is still in focusing (has
//not focused yet), we defer the event until focused.
//that means:
//when an event of EvShutterFull comes:
// copy the EvShutterFull event by copy-constructor;
// put the copy in a separated queue;
// destruct the EvShutterFull event;
//when camera exits Focusing state (e.g. gets into Focused state):
// let Focused state process the events in the queue;
// empty the queue and destruct the copied events;
typedef boost::mpl::list<
custom_reaction< EvInFocus >,
deferral< EvShutterFull > > reactions;
Focusing();
~Focusing();
string getStateName() const;
result react(const EvInFocus & evInFocus);
};
#endif
src/state/shoot/focusing.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "focusing.hpp"
#include "focused.hpp"
#include "../../camera/camera.hpp"
using namespace std;
Focusing::Focusing()
{
cout<<"Enter Focusing"<<endl;
}
Focusing::~Focusing()
{
cout<<"Exit Focusing"<<endl;
}
string Focusing::getStateName() const
{
return string("Focusing");
}
result Focusing::react(const EvInFocus & evInFocus)
{
cout<<"Focusing::react(const EvInFocus & evInFocus)"<<endl;
return transit< Focused >(&Camera::displayFocused, evInFocus); //transition action is Camera::displayFocused()
}
src/state/shoot/focused.hpp
#ifndef __FOCUSED_HPP__
#define __FOCUSED_HPP__
#include <boost/statechart/simple_state.hpp>
#include <boost/statechart/custom_reaction.hpp>
#include "../../event/events.hpp"
#include "../istate.hpp"
//Yuanguo: Shooting is the context of Focused, so
// full definition of Shooting is needed when defining Focused, thus include shooting.hpp here;
#include "shooting.hpp"
class Focused : public simple_state< Focused, Shooting >, public IState
{
public:
typedef custom_reaction < EvShutterFull > reactions;
Focused();
~Focused();
string getStateName() const;
result react(const EvShutterFull & evShutterFull );
};
#endif
src/state/shoot/focused.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "focused.hpp"
#include "storing.hpp"
#include "../../camera/camera.hpp"
using namespace std;
Focused::Focused()
{
cout<<"Enter Focused"<<endl;
}
Focused::~Focused()
{
cout<<"Exit Focused"<<endl;
}
string Focused::getStateName() const
{
return string("Focused");
}
result Focused::react(const EvShutterFull & evShutterFull )
{
cout<<"Focused::react(const EvShutterFull & evShutterFull ), ";
if( context< Camera >().isMemAvail() )
{
cout<<"Guard: isMemAvail() is true"<<endl;
return transit<Storing>(&Camera::allocMem, evShutterFull); //transition action is Camera::allocMem()
}
else
{
cout<<"Guard: isMemAvail() is false"<<endl;
//Yuanguo: Indicate that the event can be discarded. So, the
// dispatch algorithm will stop looking for a reaction
// and the machine remains in the Focused state.
return discard_event();
}
}
src/state/shoot/storing.hpp
#ifndef __STORING_HPP__
#define __STORING_HPP__
#include <boost/statechart/simple_state.hpp>
#include <boost/statechart/custom_reaction.hpp>
#include <boost/statechart/deferral.hpp>
#include <boost/mpl/list.hpp>
#include "../../event/events.hpp"
#include "../istate.hpp"
//Yuanguo: Shooting is the context of Storing, so
// full definition of Shooting is needed when defining Storing, thus include shooting.hpp here;
#include "shooting.hpp"
using namespace boost::statechart;
class Storing : public simple_state< Storing, Shooting >, public IState
{
public:
//Yuanguo: we have multiple reactions for different events;
typedef boost::mpl::list<
custom_reaction < EvStored >,
custom_reaction < EvShutterRelease > > reactions;
Storing();
~Storing();
string getStateName() const;
result react(const EvStored & evStored);
result react(const EvShutterRelease & evShutterRelease);
};
#endif
src/state/shoot/storing.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "storing.hpp"
//Yuanguo:
//We need a full definition of NotShooting in line
// return transit< NotShooting >();
//Idle is the initial state of NotShooting, thus we have to include idle.hpp
//here, otherwise, compiler will complain about error like
// incomplete type 'boost::statechart::simple_state ...
// ... MostDerived = NotShooting, Context = Camera ....'
//inclusion of non-initial states of NotShooting is not necessary;
#include "../notshoot/notshooting.hpp"
#include "../notshoot/idle.hpp"
using namespace std;
Storing::Storing()
{
cout<<"Enter Storing"<<endl;
}
Storing::~Storing()
{
cout<<"Exit Storing"<<endl;
}
string Storing::getStateName() const
{
return string("Storing");
}
result Storing::react(const EvStored & evStored)
{
cout<<"Storing::react(const EvStored & evStored)"<<endl;
//Yuanguo: goto NotShooting when storing is finished;
return transit< NotShooting >();
}
result Storing::react(const EvShutterRelease & evShutterRelease)
{
cout<<"Storing::react(const EvShutterRelease & evShutterRelease)"<<endl;
cout<<"Discard EvShutterRelease"<<endl;
//Yuanguo: Don't go to NotShooting until storing is finished, even if the user
//releases the shutter
return discard_event();
}
测试(注意事件和状态对象的生命周期):
[root@localhost camera]# make; make test
rm -f bin/run
mkdir -p bin
g++ -g -o bin/run src/camera/camera.cpp src/event/*.cpp src/state/notshoot/idle.cpp src/state/notshoot/notshooting.cpp src/state/notshoot/configuring.cpp src/state/shoot/shooting.cpp src/state/shoot/focusing.cpp src/state/shoot/focused.cpp src/state/shoot/storing.cpp
./bin/run
Construct Camera
Enter NotShooting
Enter Idle
CurrentState ------> Idle //初始时进入Idle状态
Construct EvConfig //模拟按Config键,用于Idle到Configuring的切换
Idle::react(const EvConfig & evConfig) //处理EvConfig事件
Exit Idle
Enter Configuring
Destruct EvConfig //在进入“下一个状态”后,销毁事件
CurrentState ------> Configuring
Construct EvConfig //再此模拟按Config键,用于Configuring到Idle的切换
Exit Configuring
[Transition Action]: Camera goes into Power Saving Mode //transition action在退出“前一个状态”之后,进入“后一个状态”之前执行
Enter Idle
Destruct EvConfig
CurrentState ------> Idle
Construct EvShutterHalf //模拟半按快门
NotShooting::react(const EvShutterHalf & evShutterHalf), Guard: isBatteryLow() is false //处理EvShutterHalf事件
Exit Idle
Exit NotShooting
Enter Shooting
Enter Focusing
Destruct EvShutterHalf
CurrentState ------> Focusing //进入对焦状态
Press Shutter Full before focused //模拟提前全按快门
Construct EvShutterFull //<span style="font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;">在对焦完成之前按快门,构造EvShutterFull事件</span>
Copy Construct EvShutterFull //拷贝EvShutterFull事件并放入queue
Destruct EvShutterFull //销毁原EvShutterFull对象
CurrentState ------> Focusing
Construct EvInFocus //模拟对焦完成
Focusing::react(const EvInFocus & evInFocus)
Exit Focusing
[Transition Action]: Camera focused on objects //transition action在退出“前一个状态”之后,进入“后一个状态”之前执行
</span>Enter Focused
Focused::react(const EvShutterFull & evShutterFull ), Guard: isMemAvail() is true //进入“后一个状态”时,立即处理被延迟的事件
Exit Focused //处理被延迟的EvShutterFull事件,导致Camera退出Focused状态
[Transition Action]: Memory allocated for storing the picture
Enter Storing
Destruct EvShutterFull //销毁EvShutterFull的拷贝
Destruct EvInFocus
CurrentState ------> Storing
Construct EvShutterRelease //模拟释放快门
Storing::react(const EvShutterRelease & evShutterRelease)
Discard EvShutterRelease //EvShutterRelease被丢弃,因为storing还未完成
Destruct EvShutterRelease
CurrentState ------> Storing //仍然处于Storing状态
Construct EvStored //模拟storing完成事件
Storing::react(const EvStored & evStored)
Exit Storing //storing完成,退出Storing状态
Exit Shooting //层层退出外围状态(这里只有一层),直到“前一个状态”和“后一个状态”的“最小公共外围状态”
Enter NotShooting
Enter Idle //层层进入“后一个状态”(这里只有一层)
Destruct EvStored
CurrentState ------> Idle
Destruct Camera //销毁状态机时,层层退出所有状态;
Exit Idle
Exit NotShooting
[root@localhost camera]#
[总结1] reaction的实现方式有以下几种:
a. transition
typedef boost::statechart::transition< Event1, NextState1, optional Transition-Action > reactions;特点:1. 不需要自定义react函数,系统自动生成(自动生成的react函数做的事情可能就是:调用Transistion-Action然后转向NextState1);2. 因为react函数是自动生成的,Event1发生时,只能转向NextState1,而不能根据guard,转向不同的state;
b. 自定义reaction
typedef boost::statechart::custom_reaction< Event1 > reactions;
boost::statechart::result react( const Event1 & evt)
{
if(guard1)
{
// transiting to next state will destruct current state object (similar to delete this!),
// so transit() should be only called in return statement.
return transit< NextState1 >(optional Transition-Action, args);
}
else if(guard2)
{
return transit< NextState2 >(optional Transition-Action, args);
}
else //guard3
{
return transit< NextState3 >(optional Transition-Action, args);
}
}
特点:可以根据guard,转向不同的state;
注意:转向下一个state, transit<NextState>(...),意味着当前state被析构,所以这个语句应该是最后执行,即return语句;
c. defered events
typedef boost::statechart::deferral< Event1 > reactions;
特点:不需要定义react函数,系统也不会生成,因为当前state根本不会处理这个Event1。在当前state,若有Event1发生,则Event1被存起来,等到当前state退出的时候,把保存的Event1添加到main queue中(相当于Event1这时候才发生),由next state处理(当然,next state应该也可以defer它)。
d. 多个reactions
typdef mpl::list<
boost::statechart::transition< Event1, NextState1, Optional-Transition-Action >,
boost::statechart::custom_reaction< Event2 >,
boost::statechart::deferral< Event3 >
> reactions;
boost::statechart::result react( const Event2 & evt)
{
....
}
//Event1和Event3不需要定义react;
特点:这不算是一种新的reaction类型,只是上面几种的组合。通过它,一个state就可以响应多个event。
[总结2] forward_event
a. 如果state为某个event定义了reaction: 如果在某种情况下,本state不能处理这个event(例如,isBatteryLow=true的时候,无法处理EvShutterHalf事件),它可以通过forward_event抛给外围状态。
b. 如果state没有为某个event定义reaction:如果状态机处于这个state,并且这个event发生了,那么这个event被自动forward到它的外围state。例如:Camera处于Idle状态,EvShutterHalf事件发生了,但Idle状态没有定义这个事件的reaction,所以,被forward到Idle的外围状态NotShooting。
[总结3] discard_event
当状态机处于某个state,事件event发生了,但在某种情况下,不应该转移到别的state而应该保持在当前状态(例如,Camera处于Focused状态,EvShutterFull发生了,但是isMemAvail=false,即没有足够的存储来存照片,所以还应该保持在Focused状态)。这时,有两种选择:1. transit<CurrentState>(),即:退出CurrentState,然后重入——要求enter和exit(即CurrentState的构造和析构)是空的;2. discard_event。显然,2更高效。
[总结4] transition action的执行环境

class State_D: public simple_state< State_D, State_C >, public IState
{
public:
typedef custom_reaction< Ev > reactions;
State_D() {}
~State_D() {}
result react(const Ev & evt)
{
return transit<State_X>(t, evt);
}
};
从State_D转向State_X的过程是:
- ~State_D()
- ~State_C()
- ~State_B()
- ~State_A()
- t()
- State_X(),进而 State_Y(), State_Z();






















 1264
1264











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








