
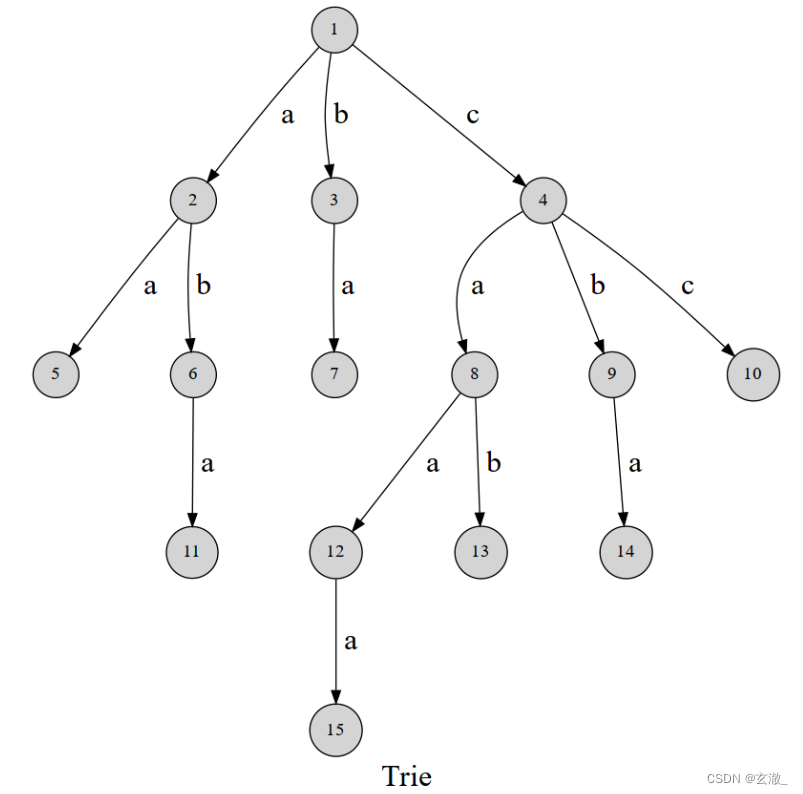
Trie
Trie(字典树)是一种用于实现字符串快速检索的多叉树结构。Trie树的每个结点都拥有若干个字符指针,若在插入或者检索字符串时扫描到一个字符 c,就沿着当前结点的 c 字符指针,走向该节点指向的节点。
AcWing 835. Trie字符串统计
输入样例:
5 I abc Q abc Q ab I ab Q ab输出样例:
1 0 1
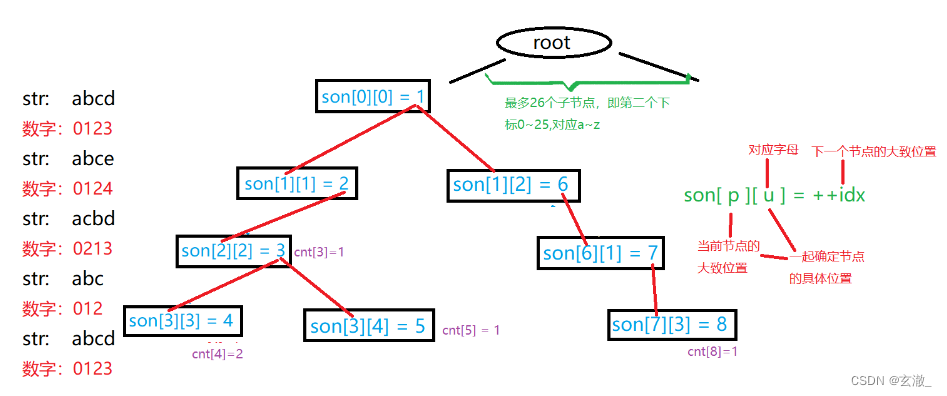
插入操作
void insert(char str[])
{
int p = 0;
for(int i = 0; str[i]; i ++ )
{
int u = str[i] - 'a';
// 不存在节点就创建一个结点
if(!son[p][u]) son[p][u] = ++ idx;
p = son[p][u];
}
// 结尾标记
cnt[p] ++ ;
}查询操作
int query(char str[])
{
int p = 0;
for(int i = 0; str[i]; i ++ )
{
int u = str[i] - 'a';
if(!son[p][u]) return 0;
p = son[p][u];
}
return 1;
} https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/14695/
https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/14695/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
// 下标是0的点既是根节点,又是空节点
int son[N][26], cnt[N], idx;
char str[N];
void insert(char str[])
{
int p = 0;
for(int i = 0; str[i]; i ++ )
{
int u = str[i] - 'a';
// 不存在节点就创建一个结点
if(!son[p][u]) son[p][u] = ++ idx;
p = son[p][u];
}
// 结尾标记
cnt[p] ++ ;
}
int query(char str[])
{
int p = 0;
for(int i = 0; str[i]; i ++ )
{
int u = str[i] - 'a';
if(!son[p][u]) return 0;
p = son[p][u];
}
return cnt[p];
}
int main()
{
int n; cin >> n;
while(n -- )
{
char op[2];
scanf("%s%s", op, str);
if(op[0] == 'I') insert(str);
else printf("%d\n", query(str));
}
return 0;
}
AcWing 143. 最大异或对
输入样例:
3 1 2 3输出样例:
3
暴力做法
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
for(int j = 0; j < i; j ++ )
res = max(res, a[j] ^ a[i]);
}
优化
第二层循环等价于在 a0 ~ ai 找一个异或对最大的数,这里可以采用Trie树的结构来优化
其实来说,一个整数,是可以转化成为一个32位的二进制数,而也就可以变成长度为32位的二进制字符串.
既然如此话,那么我们可以这么做,每一次检索的时候,我们都走与当前AiAi这一位相反的位置走,也就是让Xor值最大,如果说没有路可以走的话,那么就走相同的路.
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010,M = 31 * N;
int n;
int a[N];
int son[M][2],idx;
void insert(int x)
{
int p = 0;
for(int i = 30;i >= 0;i --)
{
int u = x >> i & 1;
if(!son[p][u]) son[p][u] = ++ idx;
p = son[p][u];
}
}
int query(int x)
{
int p = 0,res = 0;
for(int i = 30;i >= 0;i --)
{
int u = x >> i & 1;
if(son[p][!u]) {
p = son[p][!u];
res = res * 2 + !u;
}else {
p = son[p][u];
res = res * 2 + u;
}
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i ++) scanf("%d",&a[i]);
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i ++)
{
//减少一次特判
insert(a[i]);
int t = query(a[i]);
res = max(res,a[i] ^ t);
}
cout << res;
return 0;
}并查集
并查集(Disjoint-Set)是一种可以动态维护若干个不重叠的集合,并支持合并与查询的数据结构,主要可以实现以下两个操作:
- 将两个集合合并
- 询问两个元素是否在一个集合中
并查集用一个树形结构来存储每个集合,树上的每个节点都是一个元素,树根是集合的代表元素。整个并查集就是一个森林(若干棵树)。
每个集合用一棵树来表述。树根的编号就是整个集合的编号。每个节点存储它的父节点,p[x]表示x的父节点
问题1:如何判断树根:p[x] == x问题2:如何求 x 的集合编号 :while(p[x] != x) x = p[x]
问题3:如何合并两个集合:pa是x的集合编号,pb是y的集合编号,p[pa] =pb
AcWing 836. 合并集合
输入样例:
4 5 M 1 2 M 3 4 Q 1 2 Q 1 3 Q 3 4输出样例:
Yes No Yes
https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/33345/
初始化
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) p[i] = i;
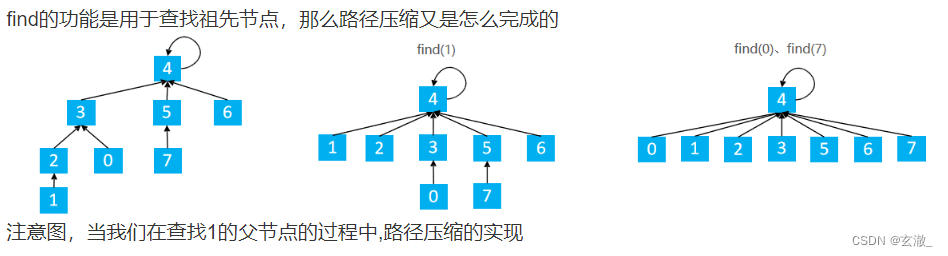
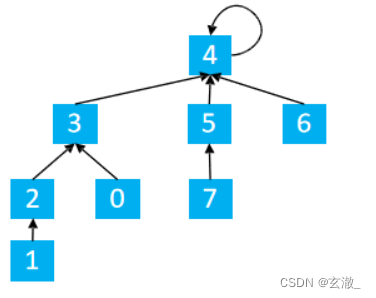
查找 + 路径压缩
int find(int x){ //返回x的祖先节点 + 路径压缩
//祖先节点的父节点是自己本身
if(p[x] != x){
//将x的父亲置为x父亲的祖先节点,实现路径的压缩
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
} 合并操作
合并操作
p[find(a)] = find(b)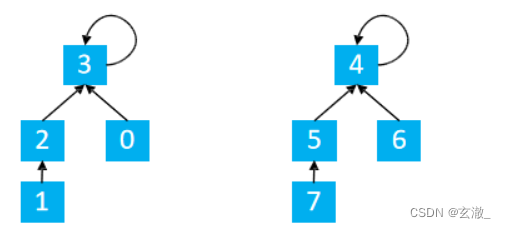
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int n, m;
int p[N];
int find(int x)
{
if(x != p[x]) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) p[i] = i;
while(m -- )
{
char op[2];
int a, b;
scanf("%s%d%d", op, &a, &b);
if(op[0] == 'M') p[find(a)] = find(b);
else
{
if(find(a) == find(b)) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
}
return 0;
}AcWing 837. 连通块中点的数量
输入样例:
5 5 C 1 2 Q1 1 2 Q2 1 C 2 5 Q2 5输出样例:
Yes 2 3
注意事项:当两个点已经是连通的状态时,再在这两个点直接连边的时候,不能增加连通块点的数量
#include <iostream> using namespace std; const int N = 100010; int n, m; int p[N], cnt[N]; int find(int x) { if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]); return p[x]; } int main() { cin >> n >> m; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) { p[i] = i; cnt[i] = 1; } while (m -- ) { string op; int a, b; cin >> op; if (op == "C") { cin >> a >> b; a = find(a), b = find(b); if (a != b) { p[a] = b; cnt[b] += cnt[a]; } } else if (op == "Q1") { cin >> a >> b; if (find(a) == find(b)) puts("Yes"); else puts("No"); } else { cin >> a; cout << cnt[find(a)] << endl; } } return 0; }
AcWing 240. 食物链
输入样例:
100 7 1 101 1 2 1 2 2 2 3 2 3 3 1 1 3 2 3 1 1 5 5输出样例:
3
TIPS:记录每个点和根节点之间的关系
余1:可以吃根节点
余2:可以被根节点吃
余0:与根节点是-同类
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 50010;
int n, m;
int p[N], d[N];
int find(int x)
{
if (p[x] != x)
{
int t = find(p[x]);
d[x] += d[p[x]];
p[x] = t;
}
return p[x];
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) p[i] = i;
int res = 0;
while (m -- )
{
int t, x, y;
scanf("%d%d%d", &t, &x, &y);
if (x > n || y > n) res ++ ;
else
{
int px = find(x), py = find(y);
if (t == 1)
{
if (px == py && (d[x] - d[y]) % 3) res ++ ;
else if (px != py)
{
p[px] = py;
d[px] = d[y] - d[x];
}
}
else
{
if (px == py && (d[x] - d[y] - 1) % 3) res ++ ;
else if (px != py)
{
p[px] = py;
d[px] = d[y] + 1 - d[x];
}
}
}
}
printf("%d\n", res);
return 0;
}
堆
从二叉堆的结构说起,它是一棵二叉树,并且是完全二叉树,每个结点中存有一个元素(或者说,有个权值)。
堆性质:父亲的权值不小于儿子的权值(大根堆)。同样的,我们可以定义小根堆。本文以大根堆为例。
由堆性质,树根存的是最大值
考虑使用一个序列
来表示堆。
的两个儿子分别是
和
, 1 是根结点
如何手写一个堆:
1.插入一个数:
2.求集合当中的最小数:
3.删除最小数:
4.删除任意一个元素:
5.修改任意一个
AcWing 838. 堆排序
输入样例:
5 3 4 5 1 3 2输出样例:
1 2 3
AcWing 838. 堆排序 分析i=n/2 - AcWing

#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010;
int n, m;
int h[N], size;
void down(int u)
{
int t = u;
if(u * 2 <= size && h[u * 2] < h[t] ) t = u * 2;
if(u * 2 + 1<= size && h[u * 2 + 1] < h[t] ) t = u * 2 + 1;
if(u != t)
{
swap(h[u], h[t]);
down(t);
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n ; i ++ ) scanf("%d", h[i]);
for(int i = n / 2; i; i -- ) down(i);
while(m -- )
{
printf("%d ", h[1]);
h[1] = h[size --];
down(1);
}
}AcWing 839. 模拟堆
输入样例:
8 I -10 PM I -10 D 1 C 2 8 I 6 PM DM输出样例:
-10 6
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <string.h> using namespace std; const int N = 100010; int h[N], ph[N], hp[N], cnt; void heap_swap(int a, int b) { swap(ph[hp[a]],ph[hp[b]]); swap(hp[a], hp[b]); swap(h[a], h[b]); } void down(int u) { int t = u; if (u * 2 <= cnt && h[u * 2] < h[t]) t = u * 2; if (u * 2 + 1 <= cnt && h[u * 2 + 1] < h[t]) t = u * 2 + 1; if (u != t) { heap_swap(u, t); down(t); } } void up(int u) { while (u / 2 && h[u] < h[u / 2]) { heap_swap(u, u / 2); u >>= 1; } } int main() { int n, m = 0; scanf("%d", &n); while (n -- ) { char op[5]; int k, x; scanf("%s", op); if (!strcmp(op, "I")) { scanf("%d", &x); cnt ++ ; m ++ ; ph[m] = cnt, hp[cnt] = m; h[cnt] = x; up(cnt); } else if (!strcmp(op, "PM")) printf("%d\n", h[1]); else if (!strcmp(op, "DM")) { heap_swap(1, cnt); cnt -- ; down(1); } else if (!strcmp(op, "D")) { scanf("%d", &k); k = ph[k]; heap_swap(k, cnt); cnt -- ; up(k); down(k); } else { scanf("%d%d", &k, &x); k = ph[k]; h[k] = x; up(k); down(k); } } return 0; }
































 385
385











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










