首先感谢一下雷神,提供了这么多优质的资源。今天正好有空,使用FFMpeg的API编写如何将H.264的源文件解压成YUV源的过程。
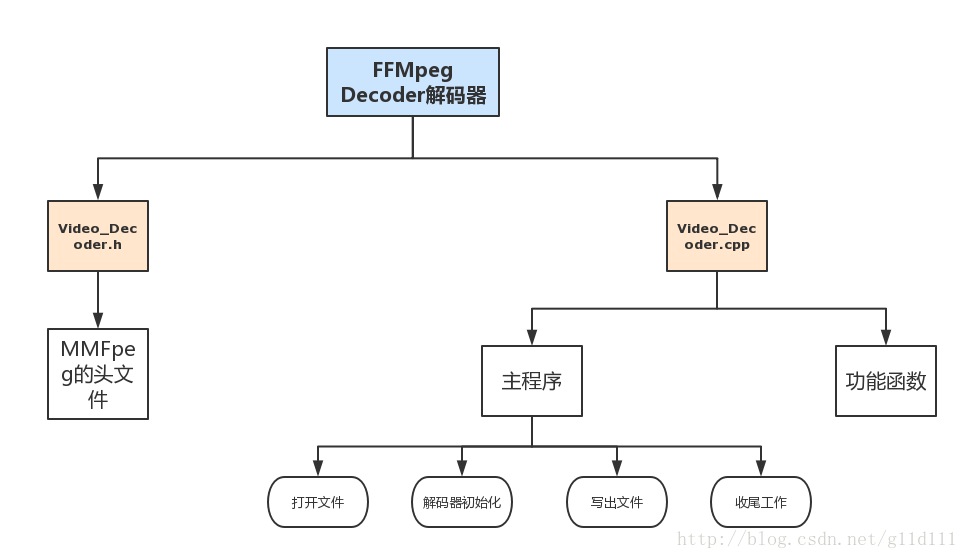
主要步骤
基本步骤分为如下几步,下面,开始讲述用到哪些API来实现这个程序。
代码组织
这里,就不再赘述如何构造一个可以使用的工程了,具体请参考雷神或其它牛人的博客。
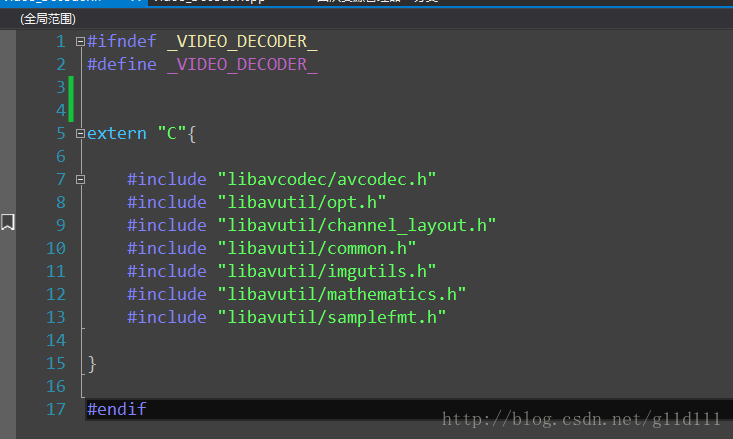
Video_Decoder.h
头文件主要就是包含了需要用到的MMFpeg的库。注意,由于MMFpeg主要用C开发,我们写C++程序的时候,务必要加上extern “C”。
Video_Decoder.cpp
#include "Video_Decoder.h"
#define INBUF_SIZE 4096
// 输入输出文件指针
FILE *pFin = NULL;
FILE *pFout = NULL;
// 解码中需要的结构
AVCodec *pCodec = NULL;
AVCodecContext *pCodecCtx = NULL;
AVCodecParserContext *pCodecParserCtx = NULL;
AVFrame *frame = NULL;
AVPacket pkt;
// 打开文件 功能函数1
static int open_io_file(char** argv) {
// 打开输入的码流文件
const char* inputFileName = argv[1];
const char* outputFileName = argv[2];
fopen_s(&pFin, inputFileName, "rb+");
if (!pFin) {
printf("Error: can not open input file. \n");
return -1;
}
fopen_s(&pFout, outputFileName, "wb+");
if (!pFout) {
printf("Error: can not open output file. \n");
return -1;
}
return 0;
};
// 解码器初始化 功能函数2
static int open_decoder()
{
// 注册与编解码相关的组件
avcodec_register_all();
// 初始化pkt,用于接收我们传入给它的码流
av_init_packet(&pkt);
// 查找解码器H.264
pCodec = avcodec_find_decoder(AV_CODEC_ID_H264);
if (!pCodec) {
printf("Error: can not find specified codec!");
return -1;
}
// 配置解码器的环境
pCodecCtx = avcodec_alloc_context3(pCodec);
if (!pCodecCtx) {
printf("Error: can not find specified codec context!");
return -1;
}
// 和编码器不同的地方: 保证输入NULL data的时候不会出错
if (pCodec->capabilities & AV_CODEC_CAP_TRUNCATED){
pCodecCtx->flags = AV_CODEC_CAP_TRUNCATED;
}
// 配置parser的环境
pCodecParserCtx = av_parser_init(AV_CODEC_ID_H264);
if (!pCodecParserCtx)
{
printf("Error: alloc parser failed. \n");
return -1;
}
// 看看pCodec能否打开,如果可以打开,则继续
if (avcodec_open2(pCodecCtx, pCodec, NULL) < 0)
{
printf("Error: Opening Codec failed! \n");
return -1;
}
// frame
frame = av_frame_alloc();
if (!frame)
{
printf("Error: alloc avframe failed. \n");
return -1;
}
return 0;
};
// 写出文件 功能函数3
static void write_out_yuv_frame(AVFrame *frame) {
uint8_t **pBuf = frame->data;
int *pStride = frame->linesize;
for (int color_idx = 0; color_idx < 3; color_idx++) {
int nWidth = color_idx == 0 ? frame->width : frame->width / 2;
int nHeight = color_idx == 0 ? frame->height : frame->height / 2;
for (int idx = 0; idx < nHeight; idx++) {
// 逐行写入
fwrite(pBuf[color_idx], 1, nWidth, pFout);
pBuf[color_idx] += pStride[color_idx];
}
// 刷新一下
fflush(pFout);
}
};
// 收尾工作:关闭输入输出文件以及环境回收。 功能函数4
static void close() {
fclose(pFin);
fclose(pFout);
avcodec_close(pCodecCtx);
av_free(pCodecCtx);
av_frame_free(&frame);
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
avcodec_register_all();
// 从输入的码流文件中保存数据的内存缓存大小 4096 + 32
uint8_t intbuf[INBUF_SIZE + AV_INPUT_BUFFER_PADDING_SIZE];
if (open_io_file(argv) < 0) {
return -1;
}
else {
printf("成功打开文件 \n");
}
if (open_decoder() < 0) {
return -1;
}
else {
printf("成功打开解码器 \n");
}
// 循环读取
// uDataSize 表示一次读取到缓存中的长度
// got_frame 表示是否完整的解码了一个像素的数据
int uDataSize = 0, len = 0; // uDataSize不能用uint8_t,要用int
int got_frame = 0;
uint8_t * pDataPtr = NULL;
while (true) {
// 把pFin的数据读到intbuf中
uDataSize = fread_s(intbuf, INBUF_SIZE, 1, INBUF_SIZE, pFin);
if (uDataSize == 0) {
break;
}
// 解析成Packet包,这块也是跟压缩不一样的地方。
// 首先要用pDataPtr指向缓存空间
pDataPtr = intbuf;
while (uDataSize > 0) {
// 数据在pkt里面
len = av_parser_parse2(pCodecParserCtx, pCodecCtx,
&pkt.data, &pkt.size,
pDataPtr, uDataSize,
AV_NOPTS_VALUE, AV_NOPTS_VALUE, AV_NOPTS_VALUE);
pDataPtr += len;
uDataSize -= len;
if (pkt.size == 0) {
continue;
}
// 成功解析出一个packet的码流
printf("Parse 1 packet. \n");
int ret = avcodec_decode_video2(pCodecCtx, frame, &got_frame, &pkt);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("解码出现错误!\n");
return -1;
}
// 如果got_frame不为0,那么表示解析出了图像。
if (got_frame) {
// 打印输出图像的宽和髙
printf("Decoded 1 frame OK! Width x Height: (%d x %d)\n", frame->width, frame->height);
write_out_yuv_frame(frame);
}
}
};
// 将剩余数据输出
pkt.data = NULL;
pkt.size = 0;
while (true) {
int ret = avcodec_decode_video2(pCodecCtx, frame, &got_frame, &pkt);
if (ret < 0) {
printf("解码出现错误!\n");
return -1;
}
// 如果got_frame为1,那么表示解析出了图像。
if (got_frame) {
// 打印输出图像的宽和髙
printf("Flush decoder; Decoded 1 frame OK! Width x Height: (%d x %d)\n", frame->width, frame->height);
write_out_yuv_frame(frame);
}
else {
break;
}
}
close();
return 0;
}输入和输出
这里,我们的输入是一个后缀为.264的文件:
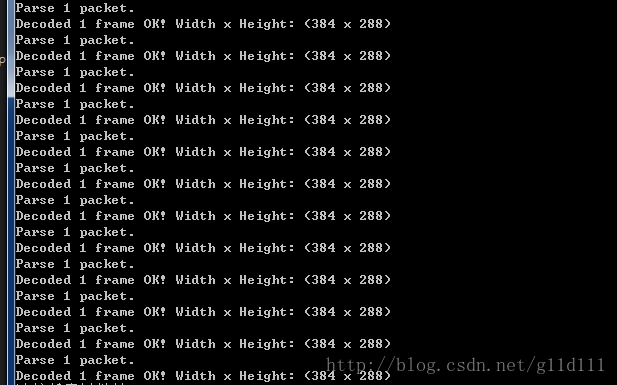
输出结果为:
可以看出,压缩比接近50%。对于视频服务提供商来说,视频压缩技术这块可以节省相当大的一笔带宽和服务器开支,是非常有价值的。同时,也降低了用户的观看成本。

























 7977
7977











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








