1 创建模式
1.1 单例模式(singleton)
1.1.1 描述
l 正规描述
单例模式确保某一个类只有一个实例,而且自行实例化并向整个系统提供这个实例单例模式。单例模式只应在有真正的“单一实例”的需求时才可使用。
l 形象描述
对于一个拥有多个孩子的父亲,不管哪一个孩子喊“爸爸”,指的都是同一个人。
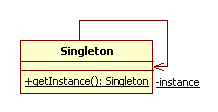
1.1.2 类图&示意代码
一般性类图
形式1:饿汉模式
| public class EagerSingleton(){ private static final EagerSingleton instance = new EagerSingleton ();//初始化就生成新对象
private EagerSingleton (){}
public static EagerSingleton getInstance(){ return instance; }
public void Operation1(){//示意方法 System.out.println(“This is eager singleton”); } }
public class Client(){ public void main(String args[]){ EagerSingleton.getInstance().Operation11(); } } |
注:
1、 构造子必须是私有的
2、 提供类方法向外提供类实例
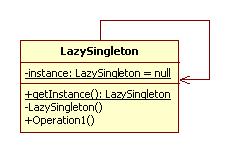
形式2:懒汉模式
| public class LazySingleton(){ private static LazySingleton instance = null;//初始化为null对象
private LazySingleton (){}
public synchronized static LazySingleton getInstance(){//这个synchronized关键字很重要 if(instance == null){ instance = new LazySingleton (); } return instance; }
public void Operation1(){//示意方法 System.out.println(“This is lazy singleton”); } }
public class Client(){//客户类 public void main(String args[]){ LazySingleton.getInstance().Operation1(); } } |
注:
1、 必须要有synchronized关键字,保证实例的唯一性
2、 相对来说,形式2不如形式1安全
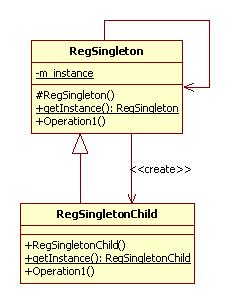
形式3:登记模式
| public class RegSingleton(){ private static HashMap m_instance = new HashMap();
protected RegSingleton (){}//构造子是保护的
static{ RegSingleton instance = new RegSingleton (); m_instance.put(instance.getClass().getName(),instance); }
public static RegSingleton getInstance(String name){ if(name == null){ name = “RegSingleton”; }
if(m_instance.get(name) == null){ try{ m_instance.put(name,Class.forName(name).newInstance()); }catch(Exception e){ System.out.println(“Error happened”); } }
return (RegSingleton)(m_instance.get(name)); }
public void Operation1(){//示意方法 System.out.println(“This is regist singleton”); } }
public class RegSingletonChild extends RegSingleton(){ public RegSingletonChild (){}
public static RegSingletonChild getInstance(){//调用父类的getInstance方法获取子类对象 return (RegSingletonChild) RegSingleton.getInstance(“RegSingletonChild”); }
public void Operation1(){//示意方法 System.out.println(“This is regist singleton child”); } }
public class Client(){//客户类 public void main(String args[]){ RegSingletonChild.getInstance().Operation1(); } } |
注:
1、 父类构造子是保护的
2、 子类调用父类的getInstance方法获取自己的对象
3、 登记模式是单例模式么,感觉是多例模式?























 316
316

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








