哈夫曼树概念
哈夫曼(Huffman)树又称最优二叉树。它是n个带权叶子结点构成的二叉树中,带权路径长度WPL最小的二叉树。因为构造这种树的算法是最早由哈夫曼于1952年提出的,所以被称之为哈夫曼树。
二叉树的性质
二叉树中有五点性质非常重要,需要记住。
性质1:在二叉树的第 i 层上至多有2^(i-1)个结点
性质2:深度为k的二叉树至多有2^k-1个结点
性质3:对任何一颗二叉树T,如果其终端结点数为n0,度为2的结点数为n2,则n0=n2+1
性质4:具有n个结点的完全二叉树的深度为[log(n)]+1([x]表示不大于x的最大整数)
性质5:如果对一棵有n个结点的完全二叉树(其深度为[log(n)]+1)的结点按层序编号(从第1层到第[log(n)]+1层,每层从左到右),对任一结点i(1<=i<=n)有:
(1).如果i=1,则结点i是二叉树的根,无双亲;如果i>1,则其双亲是结点[i/2]
(2).如果2i>n,则结点i无左孩子(结点i为叶子结点);否则其左孩子是结点2i
(3).如果2i+1>n,则结点i无右孩子;否则其右孩子是结点2i+1
基本术语
结点的权
“权”就相当于“重要度”,我们形象的用一个具体的数字来表示,然后通过数字的大小来决定谁重要,谁不重要。
路径
树中从“一个结点”到“另一个结点”之间的分支。
路径长度
一个路径上的分支数量。
树的路径长度
从树的根节点到每个节点的路径长度之和。
节点的带权路径路径长度
其实也就是该节点到根结点的路径长度乘以该节点的权。
树的带权路径长度
树中各个叶节点的路径长度*该叶节点的权的和,常用WPL(Weight Path Length)表示。
其中二叉树性质3证明如下:
T = n0 + n1 +n2
(1) 按照边求和得: T = n1 + 2 * n2 + 1
(2) 所以 (2) - (1)可得 n2 + 1 - n0 = 0
所以n0 = n2 + 1
哈弗曼树有一个性质:
哈夫曼树的总结点数是2n-1(n是叶子节点数)
证明如下:
因为二叉树中n0=n2+1;
所以节点总数T=n0+n1+n2=n2+1+n1+n2;
又n1=0,
所以T=2n2+1=2(n0-1)+1=2n0-1,得证
哈夫曼数构建和编码
详见《入门经典》P235
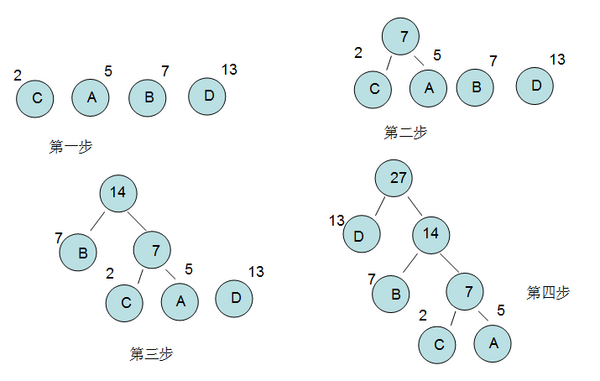
1.首先将字符按权值大小排序成向量P;
2.每次合并后的点push_back到向量Q,因为后合并的点一定小于先合并的点,所以Q内也是有序的;
3.这样每次比较P,Q的首元素就可以提取出两个最小的点,进行合并
2、3步骤相当于时间复杂度为O(n),加上1排序O(nlgn),总时间复杂度为O(nlgn)
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
struct node{
int w;
node* lchild;
node* rchild;
node():w(0),lchild(NULL),rchild(NULL){}
};
node* huffman(int weights[],int len){
sort(weights,weights+len);
vector<node*> P;
for (int m = 0; m < len;m++){
node* n = new node();
n->w = weights[m];
P.push_back(n);
}
vector<node*> Q;
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i<len || Q.size()<len-1){//因为度为2的节点数为len-1个
if (i==0){
node* p = new node();
p->lchild = P[0];
p->rchild = P[1];
p->w = P[0]->w + P[1]->w;
Q.push_back(p);
i += 2;
}
else{
node* p = new node();
vector<node*> tmp(2);
for (int cnt = 0; cnt < 2;cnt++){
if (i < len){
if (j<Q.size() && P[i]->w > Q[j]->w){
tmp[cnt] = Q[j];
j++;
}
else{
tmp[cnt] = P[i];
i++;
}
}
else{//处理P向量用完的情况
tmp[cnt] = Q[j];
j++;
}
}
p->lchild = tmp[0];
p->rchild = tmp[1];
p->w = tmp[0]->w + tmp[1]->w;
Q.push_back(p);
}
}
return Q[len - 2];
}
void print(node* root){
if (root != NULL){
cout << root->w<<" ";
}
if (root->lchild != NULL){
print(root->lchild);
}
if (root->rchild!=NULL){
print(root->rchild);
}
}
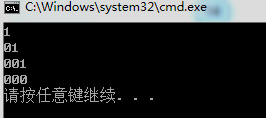
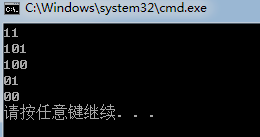
void huffman_code(node* root,int code[],int cur){
if (root->lchild == NULL&&root->rchild == NULL){
for (int i = 0; i < cur;i++){
cout << code[i];
}
cout << endl;
}
if (root->lchild!=NULL){
code[cur] = 1;
huffman_code(root->lchild, code, cur + 1);
code[cur] = 0;//修改了全局变量一定要改回来
}
if (root->rchild!=NULL){
code[cur] = 0;
huffman_code(root->rchild, code, cur + 1);
code[cur] = 1;
}
}
int main(){
int weights[] = {2,5,7,13};
int len = 4;
node* root = huffman(weights, len);
//print(root);
int *code=new int[len];
huffman_code(root, code, 0);
return 0;
}






















 8379
8379

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








