1、线程池的优点:
1、线程在程序中是保宝贵的资源,创建和销毁线程会消耗大量的系统资源,而线程池中的线程创建完成之后可以重复利用,避免频繁创建和销毁
2、线程池可以通过参数调节线程的数量,可根据系统的资源进行调配/
2、线程池的创建

public static void main(String[] args) {
//缓冲线程池
ExecutorService cachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
//固定线程池
ExecutorService fixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
//为一个线程的线程池
ExecutorService singleThreadExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
//待定时任务的线程池
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutorService = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(20);
}根据代码我们可以获得4中常用的线程池,但是他们底层调用的都是同一个构造方法:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
//我们可以通过上面的构造函数直接进行创建,效果和java提供的是一样的
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
15,
100,
60L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());我们可以通过上面的构造函数直接进行创建,效果通过Executors 创建的是一样的,唯一的区别在于,Executors方法已经帮我们封装好了一些固定的参数
注意:一般我们推荐通过构造函数来创建线程池,使用默认的可能会导致一些问题,后面在讲参数说明的时候会详细的说
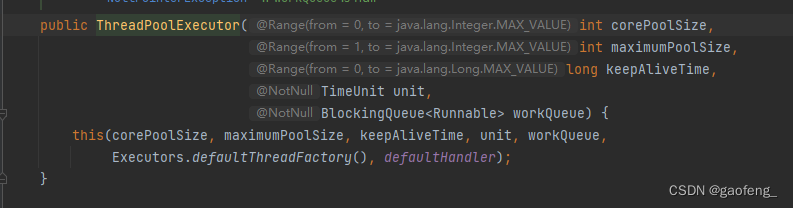
构造方法如下:
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
- corePoolSize : 核心线程数,创建完成后不会进行销毁,会一直存在的线程数量
- maximumPoolSize:最大线程数,当核心线程数用完之后,排队的队列也满了之后,才会创建临时的线程去处理当前的任务(非公平),创建临时线程+核心 <= 最大线程
- keepAliveTime:线程存活时间,创建的临时线程如果没有任务的情况下,超过存活时间就会被销毁
- unit:时间单位
- workQueue:任务队列,提交的任务会进入到队列中,等待被调度执行
- threadFactory:应来制定线程池的名称
- handler:拒绝策略,当任务队列满了之后,在提交的任务,回绝的策略,默认提供了5中拒绝策略,但也可以自己进行实现
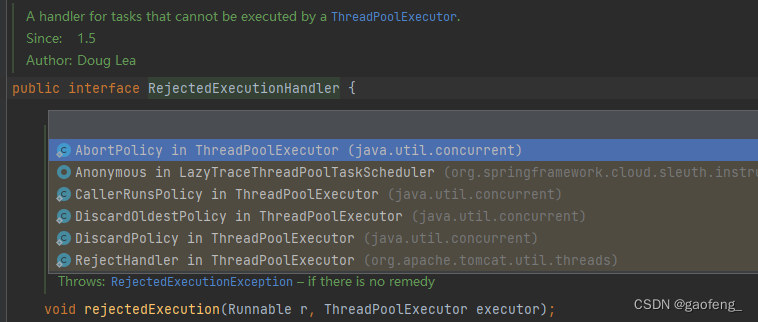
拒绝策略实现
3、工具类生成的线程池和自己定义的线程池对比
1、缓冲类的线程池
ExecutorService cachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
上代码:
//这是缓冲线程的构造方法
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}可以看到核心线程是0,最大的线程数是int的最大值,也就是说如果不停的提交任务,只要没有空闲的线程,线程池会不停的创建线程来执行任务,只到21亿个(int最大值),试想下那个服务器能成载这么大的线程数量。
另外,当60秒内没有任务的情况下,线程就会被全部销毁,不会在复用,所以这种方式在错误使用的情况下是会出现异常的。
虽然有缓冲 了,但是缓冲的有点过头了。
2、固定的线程池
ExecutorService fixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}这个看起来好像是没有什么问题,但是 任务队列( new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>())没有指定数量 ,同样在大量任务进来的时候,有可能将内存撑满,因为最大和核心的线程数一样的,所以没有弹性,可能一天中就某个时间段的任务比较多,按照正常的现实经验,可能就想,搞几个临时的用用,没活干临时工就可干掉了,但是固定线程池是做不到的。
虽然固定了但是没有缓冲
3、唯一的线程
ExecutorService singleThreadExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}跟固定的是一样的只不过是线程数量是1
3、拒绝策略
比较简单,直接上代码
1、AbortPolicy 被拒绝任务的处理程序,抛出RejectedExecutionException异常
public static class AbortPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* Creates an {@code AbortPolicy}.
*/
public AbortPolicy() { }
/**
* Always throws RejectedExecutionException.
*
* @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
* @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
* @throws RejectedExecutionException always
*/
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
throw new RejectedExecutionException("Task " + r.toString() +
" rejected from " +
e.toString());
}
}2、CallerRunsPolicy 被拒绝任务的处理程序,它直接在execute方法的调用线程中运行被拒绝的任务,除非执行程序已经关闭,在这种情况下任务将被丢弃
如果线程池没有关闭,该任务将自己创建线程进行执行
/**
* A handler for rejected tasks that runs the rejected task
* directly in the calling thread of the {@code execute} method,
* unless the executor has been shut down, in which case the task
* is discarded.
*/
public static class CallerRunsPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* Creates a {@code CallerRunsPolicy}.
*/
public CallerRunsPolicy() { }
/**
* Executes task r in the caller's thread, unless the executor
* has been shut down, in which case the task is discarded.
*
* @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
* @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
*/
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
if (!e.isShutdown()) {
r.run();
}
}
}3、DiscardOldestPolicy 被拒绝任务的处理程序,丢弃最早的未处理请求,然后重试执行,除非执行程序关闭,在这种情况下任务将被丢弃。
e.getQueue().poll();
e.execute(r);
从上面代码来看,丢弃最早的任务,执行当前的
/**
* A handler for rejected tasks that discards the oldest unhandled
* request and then retries {@code execute}, unless the executor
* is shut down, in which case the task is discarded.
*/
public static class DiscardOldestPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* Creates a {@code DiscardOldestPolicy} for the given executor.
*/
public DiscardOldestPolicy() { }
/**
* Obtains and ignores the next task that the executor
* would otherwise execute, if one is immediately available,
* and then retries execution of task r, unless the executor
* is shut down, in which case task r is instead discarded.
*
* @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
* @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
*/
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
if (!e.isShutdown()) {
e.getQueue().poll();
e.execute(r);
}
}
}4、DiscardPolicy 不做任何处理,悄无声息的丢掉
/**
* A handler for rejected tasks that silently discards the
* rejected task.
*/
public static class DiscardPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
/**
* Creates a {@code DiscardPolicy}.
*/
public DiscardPolicy() { }
/**
* Does nothing, which has the effect of discarding task r.
*
* @param r the runnable task requested to be executed
* @param e the executor attempting to execute this task
*/
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor e) {
}
}5、RejectHandler 抛出拒绝的异常
private static class RejectHandler implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
private RejectHandler() {
}
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
throw new RejectedExecutionException();
}
}
}4、总结
1、缓冲线程池虽然缓冲了,但是有点过头
2、固定线程池虽然节省了开销,但是没有一点缓冲的余地
3、自己定义的话,可以根据服务器的性能定义,固定的线程数、临时的线程数、存活时间、还有拒绝策略等,非常灵活,也能保护系统
5、线程池的实现原理
休息时间编写时间有限,下节在讲那个线程的工作原理。
提个问题:线程池的原理和开饭馆有啥关联那?






















 394
394











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








