一、UDP数据报服务与TCP流式服务的示图分析
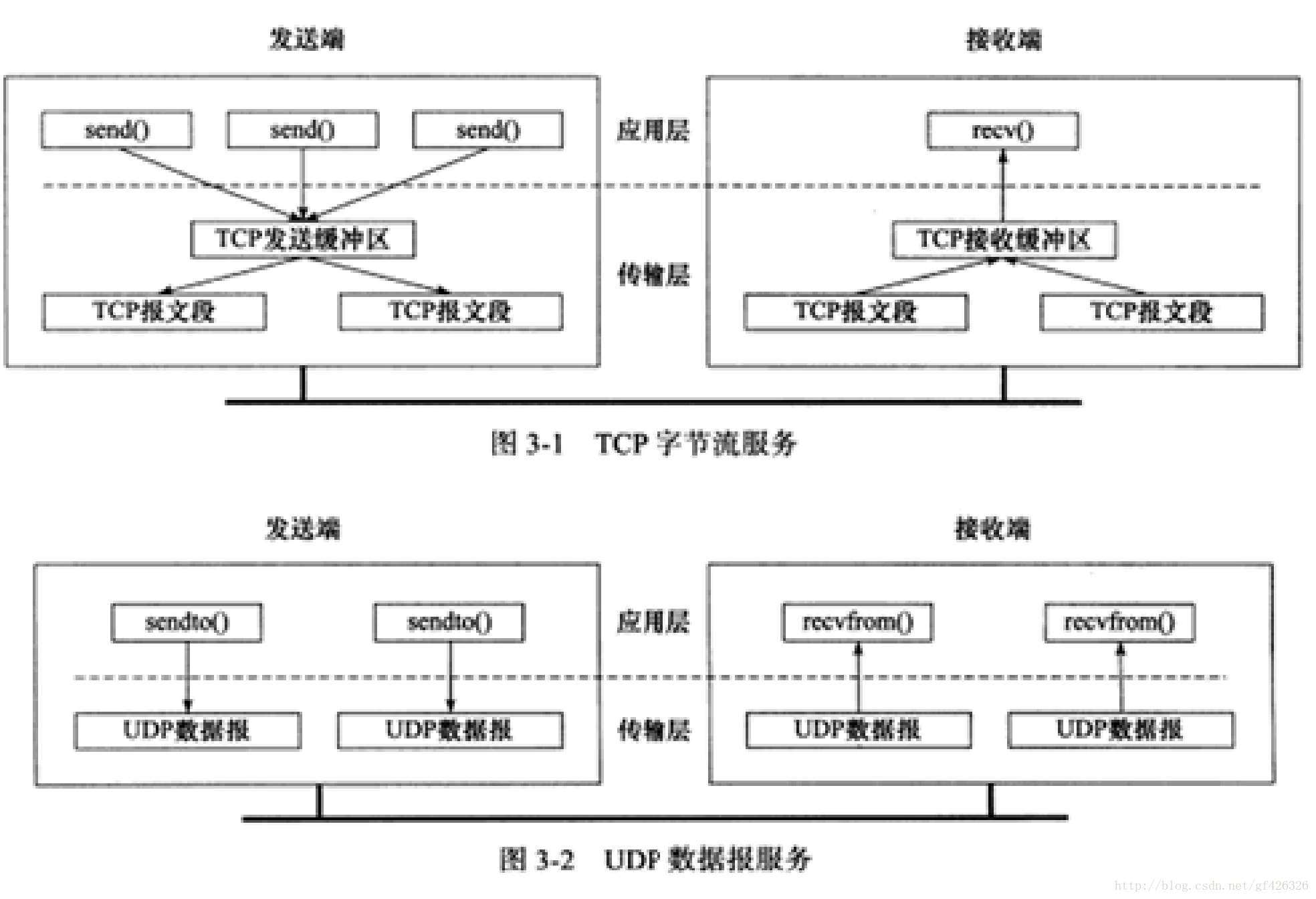
1、字节流服务:发送端send()只是将数据写到TCP发送缓冲区中,然后将发送缓冲区中的数据打包成报文段发送出去。接收端又将接收到的报文段写到缓冲区中,最后recv()直接取数据。
字节流服务特点:数据没有明确分割(由底层做分割),不分一定的报文段,什么时候想发便可将写入缓冲区的数据,进行打包再发送,即send()与recv()的次数没有必然联系。
2、数据报服务:发送端sendto()将数据直接打包成相对应的报文段发送。
数据报服务特点:数据有明确分割,拿数据按报文段拿。
3、代码示例:
TCP协议
TCP协议服务端:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
void main()
{
//创建socket
int sock=socket(PF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);//第一个参数告诉系统使用哪个底层协议族,对于tcp协议来说,一般设置为PF—INET表示IPv4,PF—INET6表示IPv6;第二个参数表示服务类型为流服务,第三个参数表示默认协议,一般为0;
assert(sock!=-1);
struct sockaddr_in ser,cli;//ser服务端,cli客-户端
memset(&ser,0,sizeof(&ser));
ser.sin_family= AF_INET;//地址族
ser.sin_port=htons(6500);//端口号(用户向网络,以short类型)
ser.sin_addr.s_addr=inet_addr("127.0.0.1");//IP地址
//绑定socket
int res=bind(sock,(struct sockaddr*)&ser,sizeof(ser));
assert(res!=-1);
//监听socket
listen(sock,5);
while(1)
{
int len=sizeof(cli);
//接受连接
int c=accept(sock,(struct sockaddr*)&cli,&len);
assert(c!=-1);
printf("one client link\n");
//接收数据
while(1)
{
char buff[128]={0};
int n=recv(c,buff,2,0);
if(n<=0)
{
printf("client link break\n");
break;
}
printf("buff:%s,n=%d\n",buff,n);
//发送数据
send(c,"OK",2,0);//第二个和第三个参数分别指写缓冲区位置和大小
}
close(c);
}
//关闭
close(sock);
}TCP协议客户端:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
void main()
{
//创建socket
int sock=socket(PF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);
assert(sock!=-1);
struct sockaddr_in ser,cli;//ser服务端,cli客户端
ser.sin_family = AF_INET;//地址族
ser.sin_port=htons(6500);//端口号(用户向网络,以short类型)
ser.sin_addr.s_addr=inet_addr("127.0.0.1");//IP地址
//发起socket
int res= connect(sock,(struct sockaddr*)&ser,sizeof(ser));//第二个参数指定链接的是服务器上哪个进程
assert(res!=-1);
while(1)
{
printf("please input: "),fflush(stdout);
char buff[128]={0};
fgets(buff,128,stdin);
buff[strlen(buff)-1]=0;
if(strncmp(buff,"end",3)==0)
{
break;
}
send(sock,buff,strlen(buff),0);
memset(buff,0,128);
recv(sock,buff,2,0);
printf("%s\n",buff);
}
close(sock);
}
UDP协议:
UDP协议服务端:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
void main()
{
int sock=socket(PF_INET,SOCK_DGRAM,0);
assert(sock!=-1);
struct sockaddr_in ser,cli;//ser服务端,cli客户端
memset(&ser,0,sizeof(&ser));
ser.sin_family= AF_INET;//地址族
ser.sin_port=htons(6500);//端口号(用户向网络,以short类型)
ser.sin_addr.s_addr=inet_addr("192.168.1.129");//IP地址
//绑定socket
int res=bind(sock,(struct sockaddr*)&ser,sizeof(ser));
assert(res!=-1);
while(1)
{
char buff[128]={0};
int len=sizeof(cli);
recvfrom(sock,buff,2,0,(struct sockaddr*)&cli,&len);
printf("srcaddr:%s,port:%d\n",inet_ntoa(cli.sin_addr),
ntohs(cli.sin_port));
printf("buff:%s\n",buff);
sendto(sock,"OK",2,0,(struct sockaddr*)&cli,len);
}
close(sock);
}
UDP协议客户端:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
void main()
{
int sock=socket(PF_INET,SOCK_DGRAM,0);
assert(sock!=-1);
struct sockaddr_in ser,cli;//ser服务端,cli客户端
memset(&ser,0,sizeof(&ser));
ser.sin_family= AF_INET;//地址族
ser.sin_port=htons(6500);//端口号(用户向网络,以short类型)
ser.sin_addr.s_addr=inet_addr("192.168.1.129");//IP地址
while(1)
{
printf("please input: "),fflush(stdout);
char buff[128]={0};
fgets(buff,128,stdin);
buff[strlen(buff)-1]=0;
int len=sizeof(cli);
sendto(sock,"OK",strlen(buff),0,(struct sockaddr*)&ser,sizeof(ser));
memset(buff,0,128);
recvfrom(sock,buff,2,0,NULL,NULL);
printf("%s\n",buff);
}
close(sock);
}
























 2328
2328

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








