以下内容参考自博客:http://blog.csdn.net/derrantcm/article/details/46761093
题目:两个链表的第一个公共节点
输入两个链表,找出他们的第一个公共节点。
算法分析:
算法1.直接法
在链表上顺序遍历每个节点,每遍历一个节点的时候,在第二个链表上顺序遍历每个节点。如果在第二个链表上有一个节点和第一个链表上的节点相同,说明两个链表在这个节点上重合,于是就找到了他们的公共节点。如果第一个链表的长度为m,第二个链表的长度为n,显然该方法的时间复杂度为O(mn).
算法2.使用栈
由于两个链表是单向链表,因此从某一节点开始,他们的pNext都指向了下一节点,但由于是单向链表,每个节点只有一个pNext,因此从第一个公共节点开始后,他们的所有节点都是重合的,不可能再出现分叉。所以两个有公共节点的链表,拓扑形状看起来像Y,而不是X。
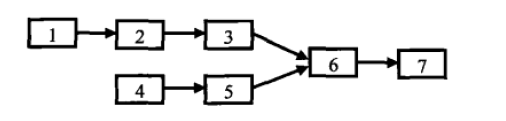
如果存在共同节点的话,那么从该节点起,两个链表之后的元素都是相同的。也就是说两个链表从尾部往前到某个点,节点都是一样的。我们可以用两个栈分别来装这两条链表。这样两个链表的尾节点有位于两个栈的栈顶,接下来比较两个栈顶节点是否相同。如果相同,则把栈顶弹出,接着比较下一个栈顶,直到找到最后一个相同的节点。
在上述思想中,我们需要用到两个辅助栈,如果两个链表的长度分别为m和n的话,那个空间复杂度为O(m+n)。这种思想的时间复杂度也是O(m+n)。和最开始的直接法相比,时间效率得到了提高,相当于用时间效率换取了空间效率。
算法3.先行法
首先遍历两个链表得到他们的长度,就能知道那个链表比较长,以及长的链表比短的链表多几个节点。在第二次遍历的时候,在较长的链表上先走若干步,接着再同时在两个链表上遍历,找到的第一个相同的节点就是他们的第一个公共节点。
这种思想的时间复杂度也是O(m+n),但我们不再需要辅助栈,因此提高了空间的效率。
算法4.使用哈希表
利用hash表的特点,想将链表1放入hashMap中,并设置每个键对应的值为空(因为这里不需要用到hashMap的值),然后循环第二个链表,判断第二个链表的每一个节点在hashMap中是否都存在相同的键,如果是,则表明找到 了第一个相同的节点,返回该节点,即返回了第一个相同的公共节点。
遇到的问题:
1.一个警告:The static method test3() from the type Solution should be accessed in a static way
* 原因:静态方法在对象创建前就存在了,它的使用不依赖对象是否被创建,所以可以用"类.方法"的方式调用,而不需要使用“对象.方法”的方式进行调用。
2.Java中单向链表的建立:
private static class ListNode{int val;ListNode next;/*public ListNode(){ //无参构造函数,可以不写,下文没有用到}*/public ListNode(int val){this.val = val;}@Overridepublic String toString(){return val + "";}}增加链表中成员的方法:1-2-3\6-74-5/ListNode n1 = new ListNode(1);ListNode n2 = new ListNode(2);ListNode n3 = new ListNode(3);ListNode n4 = new ListNode(4);ListNode n5 = new ListNode(5);ListNode n6 = new ListNode(6);ListNode n7 = new ListNode(7);n1.next = n2;n2.next = n3;n3.next = n6;n6.next = n7;n4.next = n5;n5.next = n6;
算法参考:http://blog.csdn.net/derrantcm/article/details/467610933、得到链表长度:private static int getListLength(ListNode head){int result = 0;while(head != null){result++;head = head.next;}return result;}
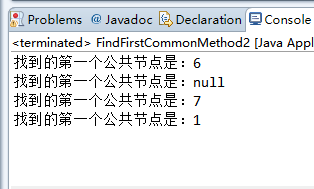
算法2源程序:/************************************************************** * Copyright (c) 2016, * All rights reserved. * 版 本 号:v1.0 * 题目描述:两个链表的第一个公共节点 * 输入两个链表,找出他们的第一个公共节点。 * 1-2-3\ 6-7 4-5/ * 例如,该链表的第一个公共节点为6。 * 输入描述:无 * 程序输出:找到的第一个公共节点是:6 * 找到的第一个公共节点是:null * 找到的第一个公共节点是:7 * 找到的第一个公共节点是:1 * * 问题分析: 1.一个警告:The static method test3() from the type Solution should be accessed in a static way * 原因:静态方法在对象创建前就存在了,它的使用不依赖对象是否被创建,所以可以用"类.方法"的方式调用 * 2.单向链表的生成方法:详见程序 * 3.得到链表长度:详见程序 * 算法描述:首先遍历两个链表得到他们的长度,就能知道那个链表比较长,以及长的链表比短的链表多几个节点。 * 在第二次遍历的时候,在较长的链表上先走若干步,接着再同时在两个链表上遍历,找到的第一个相同的节点就是他们的第一个公共节点。 * 这种思想的时间复杂度也是O(m+n),但我们不再需要辅助栈,因此提高了空间的效率。 * 完成日期:2016-09-24 ***************************************************************/ package org.marsguo.offerproject37; class Solution{ /* 链表节点类 */ private static class ListNode{ //ListNode被声明为了内部类 int val; ListNode next; /*public ListNode(){ //无参构造函数,可以不写,下文没有用到 }*/ public ListNode(int val){ this.val = val; } @Override public String toString(){ return val + ""; } } /** * 找两个结点的第一个公共结点,如果没有找到返回null,方法比较好,考虑了两个链表中有null的情况 * * @param head1 第一个链表 * @param head2 第二个链表 * @return 找到的公共结点,没有返回null */ public static ListNode findFirstCommonNode(ListNode head1,ListNode head2){ int length1 = getListLength(head1); //得到两个链表的长度 int length2 = getListLength(head2); int diff = length1 - length2; ListNode longListHead = head1; //现在还不能确定head1就是长链表,head2就是短链表,但可通过下一步确定。 ListNode shortListHead = head2; if(diff < 0){ //如果head1短head2长则调换两个头指针的指向,非常好 longListHead = head2; shortListHead = head1; diff = length2 - length1; } for(int i = 0; i < diff; i++){ //让长的链表先走diff步,之后两个链表指针在同时移动, longListHead = longListHead.next; } /* while循环用于找到第一个相同的公共节点,如果没有则不断找向下一个节点,直到找到后退出循环 */ while(longListHead != null && shortListHead != null && longListHead != shortListHead){ longListHead = longListHead.next; shortListHead = shortListHead.next; } return longListHead; //返回第一个相同的公共节点,如果没有返回null; } /* 得到单向链表长度 */ private static int getListLength(ListNode head){ int result = 0; while(head != null){ result++; head = head.next; } return result; } public static void test1(){ /* 第一个公共节点在链表的中间 1-2-3\ 6-7 4-5/ */ ListNode n1 = new ListNode(1); ListNode n2 = new ListNode(2); ListNode n3 = new ListNode(3); ListNode n4 = new ListNode(4); ListNode n5 = new ListNode(5); ListNode n6 = new ListNode(6); ListNode n7 = new ListNode(7); n1.next = n2; n2.next = n3; n3.next = n6; n6.next = n7; n4.next = n5; n5.next = n6; System.out.print("找到的第一个公共节点是:"); System.out.println(findFirstCommonNode(n1, n4)); //返回6 } public static void test2(){ /* 没有公共节点 1-2-3-4 5-6-7 */ ListNode n1 = new ListNode(1); ListNode n2 = new ListNode(2); ListNode n3 = new ListNode(3); ListNode n4 = new ListNode(4); ListNode n5 = new ListNode(5); ListNode n6 = new ListNode(6); ListNode n7 = new ListNode(7); n1.next = n2; n2.next = n3; n3.next = n4; n5.next = n6; n6.next = n7; System.out.print("找到的第一个公共节点是:"); System.out.println(findFirstCommonNode(n1, n5)); //返回null } public static void test3(){ /* 公共节点是最后一个节点 1-2-3-4\ 7 5-6/ */ ListNode n1 = new ListNode(1); ListNode n2 = new ListNode(2); ListNode n3 = new ListNode(3); ListNode n4 = new ListNode(4); ListNode n5 = new ListNode(5); ListNode n6 = new ListNode(6); ListNode n7 = new ListNode(7); n1.next = n2; n2.next = n3; n3.next = n4; n4.next = n7; n5.next = n6; n6.next = n7; System.out.print("找到的第一个公共节点是:"); System.out.println(findFirstCommonNode(n1, n5)); //返回7 } public static void test4(){ /* 公共节点是第一个节点 1-2-3-4-5 两个链表完全重合 */ ListNode n1 = new ListNode(1); ListNode n2 = new ListNode(2); ListNode n3 = new ListNode(3); ListNode n4 = new ListNode(4); ListNode n5 = new ListNode(5); ListNode n6 = new ListNode(6); ListNode n7 = new ListNode(7); n1.next = n2; n2.next = n3; n3.next = n4; n4.next = n5; n5.next = n6; n6.next = n7; System.out.print("找到的第一个公共节点是:"); System.out.println(findFirstCommonNode(n1, n1)); //返回7 } } public class FirstCommonNode { public static void main(String[] args){ //Solution solution = new Solution(); Solution.test1(); Solution.test2(); Solution.test3(); //solution.test3(); //The static method test3() from the type Solution should be accessed in a static way Solution.test4(); } }
算法3源程序:/************************************************************** * Copyright (c) 2016, * All rights reserved. * 版 本 号:v1.0 * 题目描述:两个链表的第一个公共节点 * 输入两个链表,找出他们的第一个公共节点。 * 1-2-3\ 6-7 4-5/ * 例如,该链表的第一个公共节点为6。 * 输入描述:无 * 程序输出:找到的第一个公共节点是:6 * 找到的第一个公共节点是:null * 找到的第一个公共节点是:7 * 找到的第一个公共节点是:1 * * 问题分析: 1.一个警告:The static method test3() from the type Solution should be accessed in a static way * 原因:静态方法在对象创建前就存在了,它的使用不依赖对象是否被创建,所以可以用"类.方法"的方式调用 * 2.单向链表的生成方法:详见程序 * 3.得到链表长度:详见程序 * 4.在Method1方法中,ListNode类被声明为了private,所以这里不能通过导入包的方式调用 * 算法描述:如果存在共同节点的话,那么从该节点起,两个链表之后的元素都是相同的。也就是说两个链表从尾部往前到某个点, * 节点都是一样的。我们可以用两个栈分别来装这两条链表。这样两个链表的尾节点有位于两个栈的栈顶, * 接下来比较两个栈顶节点是否相同。如果相同,则把栈顶弹出,接着比较下一个栈顶,直到找到最后一个相同的节点。 * 完成日期:2016-09-24 ***************************************************************/ package org.marsguo.offerproject37; import java.util.Stack; //import org.marsguo.offerproject37.Solution.ListNode; //import org.marsguo.offerproject37.Solution.ListNode; //在Method1方法中,ListNode类被声明为了private,所以这里不能通过导入包的方式调用 class Solution_Method2{ public static class ListNode{ int val; ListNode next; public ListNode(){ //无参构造函数,可以不写,下文没有用到 } public ListNode(int val){ this.val = val; } @Override public String toString(){ return val + ""; } } public static ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode head1,ListNode head2){ if(head1 == null || head2 == null){ return null; } /* 用栈存储ListNode */ Stack<ListNode> stack1 = new Stack<>(); Stack<ListNode> stack2 = new Stack<>(); while(head1 != null){ stack1.push(head1); //将链表1的内容压入栈 head1 = head1.next; } while(head2 != null){ stack2.push(head2); //将链表2的内容压入栈 head2 =head2.next; } ListNode commonListNode = null; //共同节点标志位,初始值设为空 /* 用stack1的栈顶元素和stack2每次出栈元素相比较,如果相同,则stack1出栈,并把 出栈元素赋给commonListNode */ while(!stack1.isEmpty() && !stack2.isEmpty() && stack1.peek() == stack2.pop()){ commonListNode = stack1.pop(); } return commonListNode; } public static void test1(){ /* 第一个公共节点在链表的中间 1-2-3\ 6-7 4-5/ */ ListNode n1 = new ListNode(1); ListNode n2 = new ListNode(2); ListNode n3 = new ListNode(3); ListNode n4 = new ListNode(4); ListNode n5 = new ListNode(5); ListNode n6 = new ListNode(6); ListNode n7 = new ListNode(7); n1.next = n2; n2.next = n3; n3.next = n6; n6.next = n7; n4.next = n5; n5.next = n6; System.out.print("找到的第一个公共节点是:"); System.out.println(FindFirstCommonNode(n1, n4)); //返回6 } public static void test2(){ /* 没有公共节点 1-2-3-4 5-6-7 */ ListNode n1 = new ListNode(1); ListNode n2 = new ListNode(2); ListNode n3 = new ListNode(3); ListNode n4 = new ListNode(4); ListNode n5 = new ListNode(5); ListNode n6 = new ListNode(6); ListNode n7 = new ListNode(7); n1.next = n2; n2.next = n3; n3.next = n4; n5.next = n6; n6.next = n7; System.out.print("找到的第一个公共节点是:"); System.out.println(FindFirstCommonNode(n1, n5)); //返回null } public static void test3(){ /* 公共节点是最后一个节点 1-2-3-4\ 7 5-6/ */ ListNode n1 = new ListNode(1); ListNode n2 = new ListNode(2); ListNode n3 = new ListNode(3); ListNode n4 = new ListNode(4); ListNode n5 = new ListNode(5); ListNode n6 = new ListNode(6); ListNode n7 = new ListNode(7); n1.next = n2; n2.next = n3; n3.next = n4; n4.next = n7; n5.next = n6; n6.next = n7; System.out.print("找到的第一个公共节点是:"); System.out.println(FindFirstCommonNode(n1, n5)); //返回7 } public static void test4(){ /* 公共节点是第一个节点 1-2-3-4-5 两个链表完全重合 */ ListNode n1 = new ListNode(1); ListNode n2 = new ListNode(2); ListNode n3 = new ListNode(3); ListNode n4 = new ListNode(4); ListNode n5 = new ListNode(5); ListNode n6 = new ListNode(6); ListNode n7 = new ListNode(7); n1.next = n2; n2.next = n3; n3.next = n4; n4.next = n5; n5.next = n6; n6.next = n7; System.out.print("找到的第一个公共节点是:"); System.out.println(FindFirstCommonNode(n1, n1)); //返回7 } } public class FindFirstCommonMethod2 { public static void main(String[] args){ Solution.test1(); Solution.test2(); Solution.test3(); Solution.test4(); } }
算法4源程序:/************************************************************** * Copyright (c) 2016, * All rights reserved. * 版 本 号:v1.0 * 题目描述:两个链表的第一个公共节点 * 输入两个链表,找出他们的第一个公共节点。 * 1-2-3\ 6-7 4-5/ * 例如,该链表的第一个公共节点为6。 * 输入描述:无 * 程序输出:找到的第一个公共节点是:6 * 找到的第一个公共节点是:null * 找到的第一个公共节点是:7 * 找到的第一个公共节点是:1 * * 问题分析: 1.一个警告:The static method test3() from the type Solution should be accessed in a static way * 原因:静态方法在对象创建前就存在了,它的使用不依赖对象是否被创建,所以可以用"类.方法"的方式调用 * 2.单向链表的生成方法:详见程序 * 3.得到链表长度:详见程序 * 4.在Method1方法中,ListNode类被声明为了private,所以这里不能通过导入包的方式调用 * 算法描述:使用哈希表 * 完成日期:2016-09-24 ***************************************************************/ package org.marsguo.offerproject37; import java.util.HashMap; import org.marsguo.offerproject37.Solution_Method2.ListNode; //调用该包下的ListNode节点。 class Solution_HashMap{ public static ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode head1,ListNode head2){ ListNode current1 = head1; ListNode current2 = head2; HashMap<ListNode,Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<ListNode,Integer>(); while(current1 != null){ hashMap.put(current1, null); //将链表值分别放入Hash表中,值都设为空 current1 = current1.next; } while(current2 != null){ /* 判断hash表中是否有和链表2相同的键,有则返回该键,该键即为第一个相同的节点 */ if(hashMap.containsKey(current2)) //hashMap.containsKey():判断一个Map中是否包含指定Key的key-value键值对存在。 return current2; current2 = current2.next; } return null; } public static void test1(){ /* 第一个公共节点在链表的中间 1-2-3\ 6-7 4-5/ */ ListNode n1 = new ListNode(1); ListNode n2 = new ListNode(2); ListNode n3 = new ListNode(3); ListNode n4 = new ListNode(4); ListNode n5 = new ListNode(5); ListNode n6 = new ListNode(6); ListNode n7 = new ListNode(7); n1.next = n2; n2.next = n3; n3.next = n6; n6.next = n7; n4.next = n5; n5.next = n6; System.out.print("找到的第一个公共节点是:"); System.out.println(FindFirstCommonNode(n1, n4)); //返回6 } public static void test2(){ /* 没有公共节点 1-2-3-4 5-6-7 */ ListNode n1 = new ListNode(1); ListNode n2 = new ListNode(2); ListNode n3 = new ListNode(3); ListNode n4 = new ListNode(4); ListNode n5 = new ListNode(5); ListNode n6 = new ListNode(6); ListNode n7 = new ListNode(7); n1.next = n2; n2.next = n3; n3.next = n4; n5.next = n6; n6.next = n7; System.out.print("找到的第一个公共节点是:"); System.out.println(FindFirstCommonNode(n1, n5)); //返回null } public static void test3(){ /* 公共节点是最后一个节点 1-2-3-4\ 7 5-6/ */ ListNode n1 = new ListNode(1); ListNode n2 = new ListNode(2); ListNode n3 = new ListNode(3); ListNode n4 = new ListNode(4); ListNode n5 = new ListNode(5); ListNode n6 = new ListNode(6); ListNode n7 = new ListNode(7); n1.next = n2; n2.next = n3; n3.next = n4; n4.next = n7; n5.next = n6; n6.next = n7; System.out.print("找到的第一个公共节点是:"); System.out.println(FindFirstCommonNode(n1, n5)); //返回7 } public static void test4(){ /* 公共节点是第一个节点 1-2-3-4-5 两个链表完全重合 */ ListNode n1 = new ListNode(1); ListNode n2 = new ListNode(2); ListNode n3 = new ListNode(3); ListNode n4 = new ListNode(4); ListNode n5 = new ListNode(5); ListNode n6 = new ListNode(6); ListNode n7 = new ListNode(7); n1.next = n2; n2.next = n3; n3.next = n4; n4.next = n5; n5.next = n6; n6.next = n7; System.out.print("找到的第一个公共节点是:"); System.out.println(FindFirstCommonNode(n1, n1)); //返回7 } } public class FindNodeHashMapMethod { public static void main(String[] args){ Solution_HashMap.test1(); Solution_HashMap.test2(); Solution_HashMap.test3(); Solution_HashMap.test4(); } }
程序运行结果:
























 503
503

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








