- mybatis的链接mysql的配置环境与连接池
<environments default="mysql">
<environment id="mysql">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy_mybatis"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="0916"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/wk/dao/IUserDao.xml"></mapper>
</mappers>
- IUserDao.xml中查询与保存用户的语句

- 测试保存用户和查询用户的语句



狂神版本的mybatis
1.前言
maven仓库:
org.mybatis mybatis 3.5.22.搭建环境
1. 创造数据库
2. 新建项目
- 新建一个普通的maven项目
- 删除src目录
3. 导入maven依赖(mysql驱动,mybatis,junit)
以上是父项目(project)工程,然后我们创建子项目(module)的时候,就不用了再导包了
4. 在resources中建立mybatis-config.xml 配置文件;并在其中导入下方
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<!--configuration核心配置文件-->
<configuration>
<!--environments可以配置多个环境-->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<!--transactionManager事务管理-->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useSSL=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="0916"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
</configuration>
5. 编写工具类
public class MybatisUtils {
private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
static{
try {
//使用mybatis第一步:获取sqlSessionFactory对象
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 既然有了 SqlSessionFactory,顾名思义,我们可以从中获得 SqlSession 的实例。
// SqlSession 提供了在数据库执行 SQL 命令所需的所有方法。
// 你可以通过 SqlSession 实例来直接执行已映射的 SQL 语句。
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(){
return sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
}
}
6. 编写代码
- 实现类pojo
//实体类
public class User {
//名字与数据库中的一样
private int id;
private String name;
private String pwd;
public User() {
}
public User(int id, String name, String pwd) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.pwd = pwd;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPwd() {
return pwd;
}
public void setPwd(String pwd) {
this.pwd = pwd;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", pwd='" + pwd + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
- Dao接口
public interface UserDao {
List<User> getUserList();
}
- 接口实现类由原来的UserDaoImpl转变为一个Mapper配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--namespace 绑定一个对应的Dao或mapper接口-->
<mapper namespace="com.wk.dao.UserDao">
<!-- select查询语句-->
<select id="getUserList" resultType="com.wk.pojo.User">
select * from mybatis.user;
</select>
</mapper>
7. junit测试
- 注意:Type interface com.wk.dao.UserDao is not known to the MapperRegistry【配置文件需要注册】
在mybatis-config.xml中加上,否则会出现上面的错
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/wk/dao/UserMapper.xml"></mapper>
</mappers>
- 注意:要在pom.xml中加上下方的

- 注意:maven导出资源问题
<build>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
- 测试:
@Test
public void test(){
//第一步:获得sqlSession对象
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
//1. 执行sql,用getMapper来获取
UserDao userDao = sqlSession.getMapper(UserDao.class);
List<User> userList = userDao.getUserList();
for (User user : userList) {
System.out.println(user);
}
//关闭sqlSession
sqlSession.close();
}
- 整体步骤如下图

3. CRUD
1. namespace
namespace中的包名要和 Dao/mapper接口的包名一致
<!--namespace 绑定一个对应的Dao或mapper接口-->
<mapper namespace="com.wk.dao.UserMapper">
2. 千篇一律
- 编写接口
//查询全部用户
List<User> getUserList();
//根据ID查询用户
User getUserById(int id);
//insert 一个用户
int addUser(User user);
//修改用户
int updateUser(User user);
//删除用户
int deleteUser(int id);
- 编写对应的mapper中的SQL语句
<!-- select查询语句-->
<select id="getUserList" resultType="com.wk.pojo.User">
select * from mybatis.user
</select>
<select id="getUserById" parameterType="int" resultType="com.wk.pojo.User">
select * from mybatis.user where id = #{id}
</select>
<insert id="addUser" parameterType="com.wk.pojo.User">
insert into mybatis.user(id, name , pwd) values (#{id},#{name},#{pwd})
</insert>
<update id="updateUser" parameterType="com.wk.pojo.User">
update mybatis.user set name = #{name}, pwd=#{pwd} where id = #{id};
</update>
<delete id="deleteUser" parameterType="int">
delete from mybatis.user where id = #{id}
</delete>
- 测试,特别注意:增删改 需要提交事务
@Test
public void getUserById(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user = mapper.getUserById(4);
System.out.println(user);
sqlSession.close();
}
//增删改需要提交事务
@Test
public void addUser(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
int haha = mapper.addUser(new User(4, "haha", "123465"));
if (haha>0){
System.out.println("插入成功");
}
//提交事务
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void updateUser(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
mapper.updateUser(new User (4,"hehe","123654"));
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
@Test
public void deleteUser(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
mapper.deleteUser(4);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
3. 万能的MAP
如果一个User中含有多个属性(名字,性别,爱好,,,,,)那么,此时用map比较好
int addUser2(Map<String ,Object> map);
<!-- 传递map的key,可以直接取出来,对象中的属性-->
<insert id="addUser2" parameterType="map">
-- values后面名字可以随意
insert into mybatis.user(id,name,pwd) values (#{Id},#{Name},#{Pwd})
</insert>
@Test
public void addUser2(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
Map<String ,Object> map = new HashMap<String,Object>();
map.put("Id",5);
map.put("Name","tiantian");
map.put("Pwd","596835");
mapper.addUser2(map);
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
4. properties只能放在最上面
- 我们可以通过创建db.properties来将之前的我们配置的driver,url等变得更简单


5.起别名(放在xml中的第三个位置)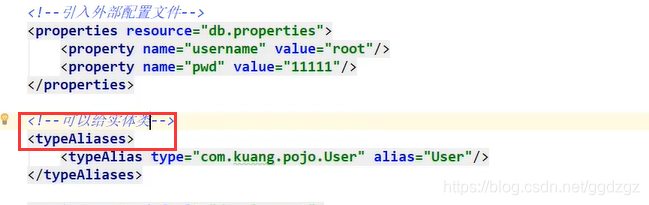
4.解决属性名与字段名不一致的问题

新建一个项目,拷贝之前的,测试实体类字段不一致的情况
测试出现问题

原因是找不到password,而应该是pwd
解决方法:
- 起别名(最笨重的一种做法)
- resultMap
结果集映射

将数据库中的一个字段,映射到一个字段
其中,只需要将不相同的字段映射,id与id相同,所以不需要映射
4. 日志
4.1 日志工厂
如果一个数据库操作出现异常,我们需要排错,日志是好的助手!!
曾经:sout,debug
现在:日至工厂
- STDOUT_LOGGING是标准的配置日志的工具,而且是在settings中配置,注意,配制的时候,不要多加空格
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/>
</settings>
注意:ClassNotFoundException可能是没有导包
- LOG4J 的实现; 【log4j.properties】
- 可以分等级输出日志,可以一条一条的输出
- 可以通过配置文件来配置
- 先导入log4j的包
- 配置log4j为日志的实现
<settings>
<setting name="logImpl" value="LOG4J"/>
</settings>
- 简单使用
static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(UserDaoTest.class);
@Test
public void testLog4()
{
logger.info("info:进入了testLog4j");
logger.debug("debug:进入了testLog4J");
logger.error("error:进入了testLog4j");
}
4.2 分页查询
- limit查询
SELECT * FROM USER LIMIT 0,2;分页查询前两个
select * from user limit 2; 从0到2
- 使用mybatis实现分页,核心就是SQL
- 接口
- Mapper.xml
- 测试

mybatis 分页插件 pageHelper
5.注解开发
5.1、面向接口编程
- 注解在接口上实现
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("select * from user")
List<User> getUsers();
}
- 使用核心配置文件绑定接口
<mappers>
<mapper class="com.wk.dao.UserMapper"/>
</mappers>
- 关于@Param()注解
- 基本数据类型或String类型,需要加上
- 引用类型不用加
- 在SQL中引用的就是我们在这里的@Param()中设定的属性名
-
#{} 与 ${} 的联系与区别
-
#{} 解析为一个 JDBC 预编译语句(prepared statement)的参数标记符,一个 #{ } 被解析为一个参数占位符;而${}仅仅为一个纯碎的 string 替换,在动态 SQL 解析阶段将会进行变量替换。
-
#{} 解析之后会将String类型的数据自动加上引号,其他数据类型不会;而${} 解析之后是什么就是什么,他不会当做字符串处理。
-
#{} 很大程度上可以防止SQL注入(SQL注入是发生在编译的过程中,因为恶意注入了某些特殊字符,最后被编译成了恶意的执行操作);而${} 主要用于SQL拼接的时候,有很大的SQL注入隐患。
-
在某些特殊场合下只能用${},不能用#{}。例如:在使用排序时ORDER BY ${id},如果使用#{id},则会被解析成ORDER BY “id”,这显然是一种错误的写法。
联系:他们都是在SQL中动态地传入参数
-
-
lombok《步骤:安装插件,导入jar包,在实体User类加上注解
- 可以将我们get set toString给简化,只需要加一个注解@Data
- @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor可以生成有参无参构造


按照结果嵌套查询的方法
<!-- 按结果嵌套查询-->
<select id="getTeacher" resultMap="TeacherStudent">
select s.id sid, s.name sname, t.name tname, t.id tid
from student s, teacher t
where s.tid = t.id and t.id = #{tid}
</select>
<!--复杂的属性我们需要单独处理, 对象:association 集合: collection -->
<!-- javaType: 时指定的属性类型
集合中的泛型信息,我们是用ofType获取-->
<resultMap id="TeacherStudent" type="com.wk.pojo.Teacher">
<result property="id" column="tid"/>
<result property="name" column="tname"/>
<collection property="students" ofType="com.wk.pojo.Student">
<result property="id" column="sid"/>
<result property="name" column="sname"/>
<result property="tid" column="tid"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
按照查询嵌套处理
<!-- 按照查询嵌套处理-->
<select id="getTeacher2" resultMap="TeacherStudent2">
select * from mybatis.teacher where id = #{tid}
</select>
<resultMap id="TeacherStudent2" type="com.wk.pojo.Teacher">
<collection property="students" javaType="ArrayList" ofType="com.wk.pojo.Student" select="getStudentByTeacherId" column="id"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="getStudentByTeacherId" resultType="com.wk.pojo.Student">
select * from mybatis.student where tid= #{tid}
</select>
小结:
1. 关联:association 【多对一】
2. 集合:Collection 【一对多】
3. javaType:用来指定实体类中属性的类型
4. ofType: 用来指定映射到List或者集合中的pojo类型,泛型中的约束类型!
注意点:
- 保证sql的可读性,尽量保真通俗易懂
- 注意一对多和多对一中,属性名和字段的问题
- 如果问题不好排查错误,可以使用日志,log4j
6.动态SQL
根据不同条件生成不同的sql语句
搭建工程
编写基础工程
-
导包
-
编写配置文件
-
编写实体类
-
编写实体类对应的mapper接口和mapper。xml文件
-
if 的使用
<select id="queryBlogIF" parameterType="map" resultType="com.wk.pojo.Blog">
select * from mybatis.blog where 1 = 1
<if test="title != null">
and title = #{title}
</if>
<if test="author != null">
and author = #{author}
</if>
</select>
select * from mybatis.blog
<where>
<if test="title != null">
title = #{title}
</if>
<if test="author != null">
and author = #{author}
</if>
</where>
</select>
动态sql还是sql语句,但是我们能够在sql层面去就行逻辑代码【if where set choose when】
ForEach
Sql片段
动态SQL就是在拼接SQL语句,我们只要保证SQL的正确性,按SQL的格式,去排列组合就可以了
- 现在Mysql中写出完整的sql,然后再去修改成为我们的动态SQL
缓存
1.缓存失效情况
User user = mapper.queryUserById(1);
System.out.println(user);
System.out.println("=============");
User user2 = mapper.queryUserById(1);
System.out.println(user2);
基本上就是这样。这个简单语句的效果如下:
- 映射语句文件中的所有 select 语句的结果将会被缓存。
- 映射语句文件中的所有 insert、update 和 delete 语句会刷新缓存:所以会重复输出同一个字段。
- 手动清理缓存的方法
- sqlSession.clearCache()
- 一级缓存默认是开启的,只在一次sqlSession中有效,也就是拿到连接到关闭连接这个区间段
- 相当于一个 map - 缓存会使用最近最少使用算法(LRU, Least Recently Used)算法来清除不需要的缓存。
- 缓存不会定时进行刷新(也就是说,没有刷新间隔)。
- 缓存会保存列表或对象(无论查询方法返回哪种)的 1024 个引用。
- 缓存会被视为读/写缓存,这意味着获取到的对象并不是共享的,可以安全地被调用者修改,而不干扰其他调用者或线程所做的潜在修改。
2.二级缓存
步骤:
1. 开启全局缓存(也称二级缓存)
2. 在要使用耳机缓存的Mapper中开启
<!-- 在当前的mapper。xml中使用二级缓存-->
<cache eviction="FIFO"
flushInterval="60000"
size = "512"
readOnly="true"/>
3. 不同的SQLSession如果第一个输出后,第二个可以直接输出,而不用再次查询之后再输出,前提是在同一个Mapper下面;
4. 二级缓存当一级缓存消失的时候开始生效
5. 我们需要将POJO实体类序列化
public class User implements Serializable {
缓存原理
























 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








