In this tutorial we show you how to develop a hello world web application using classic Struts 1.3 framework.
Tools and technologies used :
- Struts 1.3.10
- Maven 2.x
- Eclipse 3.6
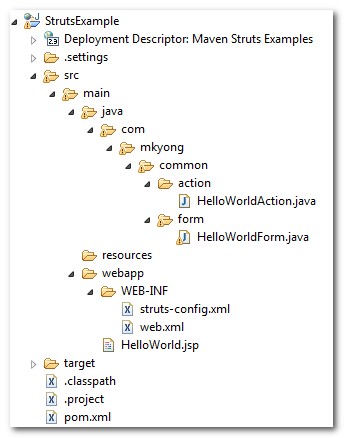
Final project structure
Let’s see the final folder structure first.
1. Maven Template
Generate a quick start Java project structure with Maven command “mvn archetype:generate“, select template 18 for a simple Java web project template.
Define value for groupId: : com.mkyong.common
Define value for artifactId: : StrutsExample
Define value for version: 1.0-SNAPSHOT: :
Define value for package: com.mkyong.common: : com.mkyong.common
...
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] BUILD SUCCESSFUL
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Total time: 1 minute 5 seconds
[INFO] Finished at: Thu Apr 08 11:29:30 SGT 2010
[INFO] Final Memory: 8M/14M
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------2. pom.xml file configuration
Add the Struts dependencies in pom.xml. In Struts 1.x, you need the struts-core.jarfor core module and struts-taglib.jar for tag library.
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.mkyong.common</groupId>
<artifactId>StrutsExample</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>StrutsExample Maven Webapp</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.struts</groupId>
<artifactId>struts-core</artifactId>
<version>1.3.10</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.struts</groupId>
<artifactId>struts-taglib</artifactId>
<version>1.3.10</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>StrutsExample</finalName>
</build>
</project>3. Eclipse IDE
Convert this project to Eclipse web project with Maven command “mvn eclipse:eclipse -Dwtpversion=1.5“. All the Struts dependent libraries will automatically download into your Maven local repository, link it in your project classpath, and convert it to Eclipse’s web project style.
E:\workspace\struts\StrutsExample>mvn eclipse:eclipse -Dwtpversion=1.5
[INFO] Scanning for projects...
[INFO] Searching repository for plugin with prefix: 'eclipse'.
[INFO] ------------------------------------------------------------------------
[INFO] Building StrutsExample Maven WebappJust import it into Eclipse IDE.
4. Action Form
Create a Struts Action Form to hold the “hello world” data later.
package com.mkyong.common.form;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForm;
public class HelloWorldForm extends ActionForm{
String message;
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
}5. Action (Controller)
Create a Struts Action (Action Controller) file to control how Struts will forward the request, just override the execute() method with your own logic here.
package com.mkyong.common.action;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.struts.action.Action;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForm;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionForward;
import org.apache.struts.action.ActionMapping;
import com.mkyong.common.form.HelloWorldForm;
public class HelloWorldAction extends Action{
public ActionForward execute(ActionMapping mapping,ActionForm form,
HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response)
throws Exception {
HelloWorldForm helloWorldForm = (HelloWorldForm) form;
helloWorldForm.setMessage("Hello World! Struts");
return mapping.findForward("success");
}
}6. JSP view page
Create a JSP page and access the Action Form object via Struts tag library and print it’s message property.
<%@taglib uri="http://struts.apache.org/tags-bean" prefix="bean"%>7. struts-config.xml
Create a struts-config.xml file for the Struts configuration details, and put it into the WEB-INF folder.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE struts-config PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 1.3//EN"
"http://jakarta.apache.org/struts/dtds/struts-config_1_3.dtd">
<struts-config>
<form-beans>
<form-bean name="helloWorldForm"
type="com.mkyong.common.form.HelloWorldForm"/>
</form-beans>
<action-mappings>
<action path="/helloWorld"
type="com.mkyong.common.action.HelloWorldAction"
name="helloWorldForm">
<forward name="success" path="/HelloWorld.jsp"/>
</action>
</action-mappings>
</struts-config>Define a form bean named “helloWorldForm” and action controller mapping “HelloWorldAction“, match the /helloWorld web path to HelloWorldAction. It’s means all the request from /helloWorld web path will redirect to HelloWorldAction. The “name” attribute is use to define which action form will pass to this HelloWorldAction.
8. The Web Application Deployment Descriptor
In web.xml file, configure the Struts ActionServlet instance and map it with url-pattern “*.do”, so that the container is aware of all the “*.do” pattern will redirect to Struts ActionServlet.
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC
"-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" >
<web-app>
<display-name>Maven Struts Examples</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>action</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.apache.struts.action.ActionServlet
</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>config</param-name>
<param-value>
/WEB-INF/struts-config.xml
</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>action</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>9. Java EE Module dependency (Optional)
If you want to do the debugging work in Eclipse IDE, you have to make sure the Java EE module dependencies is checked so that the Eclipse will deploy all the dependencies into correct folder. See details here.
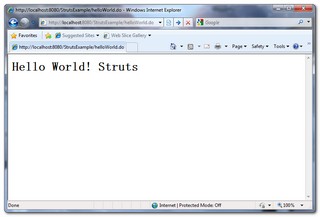
10. Run it
In Eclipse IDE, create a new server plugin and start it. You can access this example in the following URL.
http://localhost:8080/StrutsExample/helloWorld.do
HttpServletRequest class not found?
If you hit above error, make sure you include the javaee.jar (exists in your JDK/lib folder). Due to license issue, this javaee.jar is not able to use Maven to download it, you have to include it manually.
























 187
187

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








