In this tutorial, it will reuse the entire infrastructure of the previous “Hibernate one to one relationship example – XML mapping” tutorial, enhance it to support Hibernate / JPA annotation.
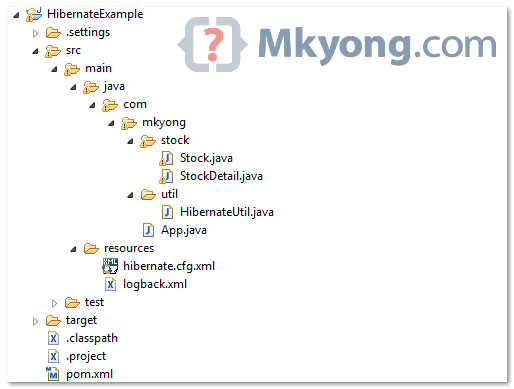
Project Structure
See the final project structure of this tutorial.
Note
Since Hibernate 3.6, annotation codes are merged into the Hibernate core module, so, the “previouspom.xmlfile can be reuse.
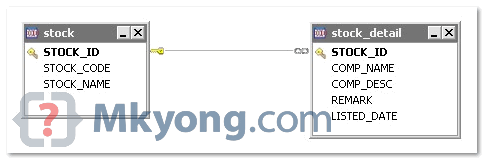
1. “One-to-one” table relationship
See the previous one to one table relationship again.
2. Hibernate Model Class
Create two model classes – Stock.java and StockDetail.java, and put the annotation code inside.
File : Stock.java
package com.mkyong.stock;
import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.FetchType;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import static javax.persistence.GenerationType.IDENTITY;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToOne;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import javax.persistence.UniqueConstraint;
@Entity
@Table(name = "stock", catalog = "mkyongdb", uniqueConstraints = {
@UniqueConstraint(columnNames = "STOCK_NAME"),
@UniqueConstraint(columnNames = "STOCK_CODE") })
public class Stock implements java.io.Serializable {
private Integer stockId;
private String stockCode;
private String stockName;
private StockDetail stockDetail;
public Stock() {
}
public Stock(String stockCode, String stockName) {
this.stockCode = stockCode;
this.stockName = stockName;
}
public Stock(String stockCode, String stockName, StockDetail stockDetail) {
this.stockCode = stockCode;
this.stockName = stockName;
this.stockDetail = stockDetail;
}
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "STOCK_ID", unique = true, nullable = false)
public Integer getStockId() {
return this.stockId;
}
public void setStockId(Integer stockId) {
this.stockId = stockId;
}
@Column(name = "STOCK_CODE", unique = true, nullable = false, length = 10)
public String getStockCode() {
return this.stockCode;
}
public void setStockCode(String stockCode) {
this.stockCode = stockCode;
}
@Column(name = "STOCK_NAME", unique = true, nullable = false, length = 20)
public String getStockName() {
return this.stockName;
}
public void setStockName(String stockName) {
this.stockName = stockName;
}
@OneToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY, mappedBy = "stock", cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
public StockDetail getStockDetail() {
return this.stockDetail;
}
public void setStockDetail(StockDetail stockDetail) {
this.stockDetail = stockDetail;
}
}File : StockDetail.java
package com.mkyong.stock;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.FetchType;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToOne;
import javax.persistence.PrimaryKeyJoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import javax.persistence.Temporal;
import javax.persistence.TemporalType;
import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator;
import org.hibernate.annotations.Parameter;
@Entity
@Table(name = "stock_detail", catalog = "mkyongdb")
public class StockDetail implements java.io.Serializable {
private Integer stockId;
private Stock stock;
private String compName;
private String compDesc;
private String remark;
private Date listedDate;
public StockDetail() {
}
public StockDetail(Stock stock, String compName, String compDesc,
String remark, Date listedDate) {
this.stock = stock;
this.compName = compName;
this.compDesc = compDesc;
this.remark = remark;
this.listedDate = listedDate;
}
@GenericGenerator(name = "generator", strategy = "foreign",
parameters = @Parameter(name = "property", value = "stock"))
@Id
@GeneratedValue(generator = "generator")
@Column(name = "STOCK_ID", unique = true, nullable = false)
public Integer getStockId() {
return this.stockId;
}
public void setStockId(Integer stockId) {
this.stockId = stockId;
}
@OneToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
@PrimaryKeyJoinColumn
public Stock getStock() {
return this.stock;
}
public void setStock(Stock stock) {
this.stock = stock;
}
@Column(name = "COMP_NAME", nullable = false, length = 100)
public String getCompName() {
return this.compName;
}
public void setCompName(String compName) {
this.compName = compName;
}
@Column(name = "COMP_DESC", nullable = false)
public String getCompDesc() {
return this.compDesc;
}
public void setCompDesc(String compDesc) {
this.compDesc = compDesc;
}
@Column(name = "REMARK", nullable = false)
public String getRemark() {
return this.remark;
}
public void setRemark(String remark) {
this.remark = remark;
}
@Temporal(TemporalType.DATE)
@Column(name = "LISTED_DATE", nullable = false, length = 10)
public Date getListedDate() {
return this.listedDate;
}
public void setListedDate(Date listedDate) {
this.listedDate = listedDate;
}
}3. Hibernate Configuration File
Puts annotated classes Stock.java and StockDetail.java in your Hibernate configuration file, and also MySQL connection details.
File : hibernate.cfg.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD 3.0//EN"
"http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
<hibernate-configuration>
<session-factory>
<property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mkyongdb</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.username">root</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.password">password</property>
<property name="hibernate.dialect">org.hibernate.dialect.MySQLDialect</property>
<property name="show_sql">true</property>
<mapping class="com.mkyong.stock.Stock" />
<mapping class="com.mkyong.stock.StockDetail" />
</session-factory>
</hibernate-configuration>4. Run It
Run it, Hibernate will insert a row into the STOCK table and a row into the STOCK_DETAIL table.
File : App.java
package com.mkyong;
import java.util.Date;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import com.mkyong.stock.Stock;
import com.mkyong.stock.StockDetail;
import com.mkyong.util.HibernateUtil;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hibernate one to one (Annotation)");
Session session = HibernateUtil.getSessionFactory().openSession();
session.beginTransaction();
Stock stock = new Stock();
stock.setStockCode("7052");
stock.setStockName("PADINI");
StockDetail stockDetail = new StockDetail();
stockDetail.setCompName("PADINI Holding Malaysia");
stockDetail.setCompDesc("one stop shopping");
stockDetail.setRemark("vinci vinci");
stockDetail.setListedDate(new Date());
stock.setStockDetail(stockDetail);
stockDetail.setStock(stock);
session.save(stock);
session.getTransaction().commit();
System.out.println("Done");
}
}Output
Hibernate one to one (Annotation)
Hibernate: insert into mkyongdb.stock (STOCK_CODE, STOCK_NAME) values (?, ?)
Hibernate: insert into mkyongdb.stock_detail
(COMP_DESC, COMP_NAME, LISTED_DATE, REMARK, STOCK_ID) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)Done






















 1023
1023

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








